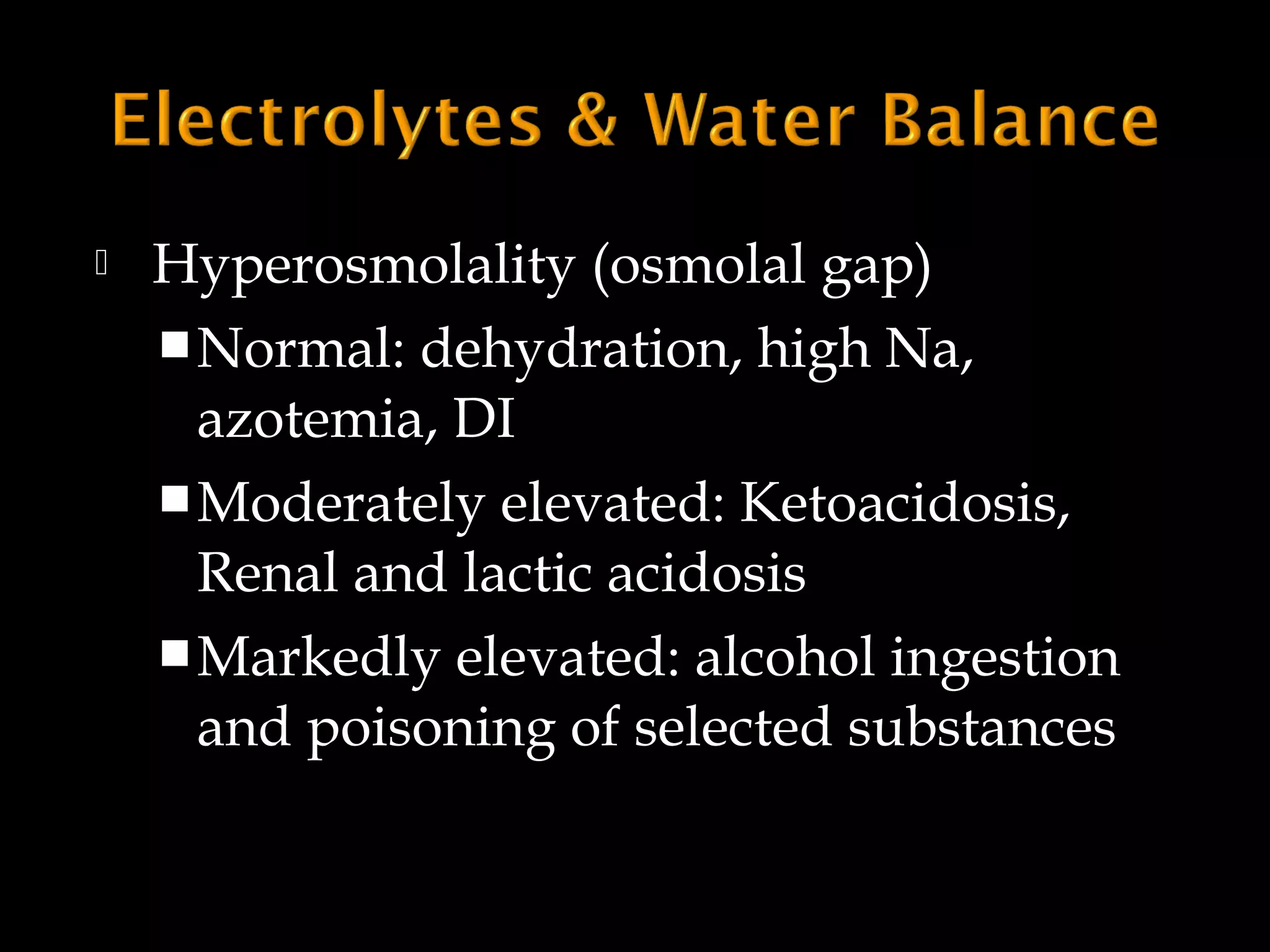
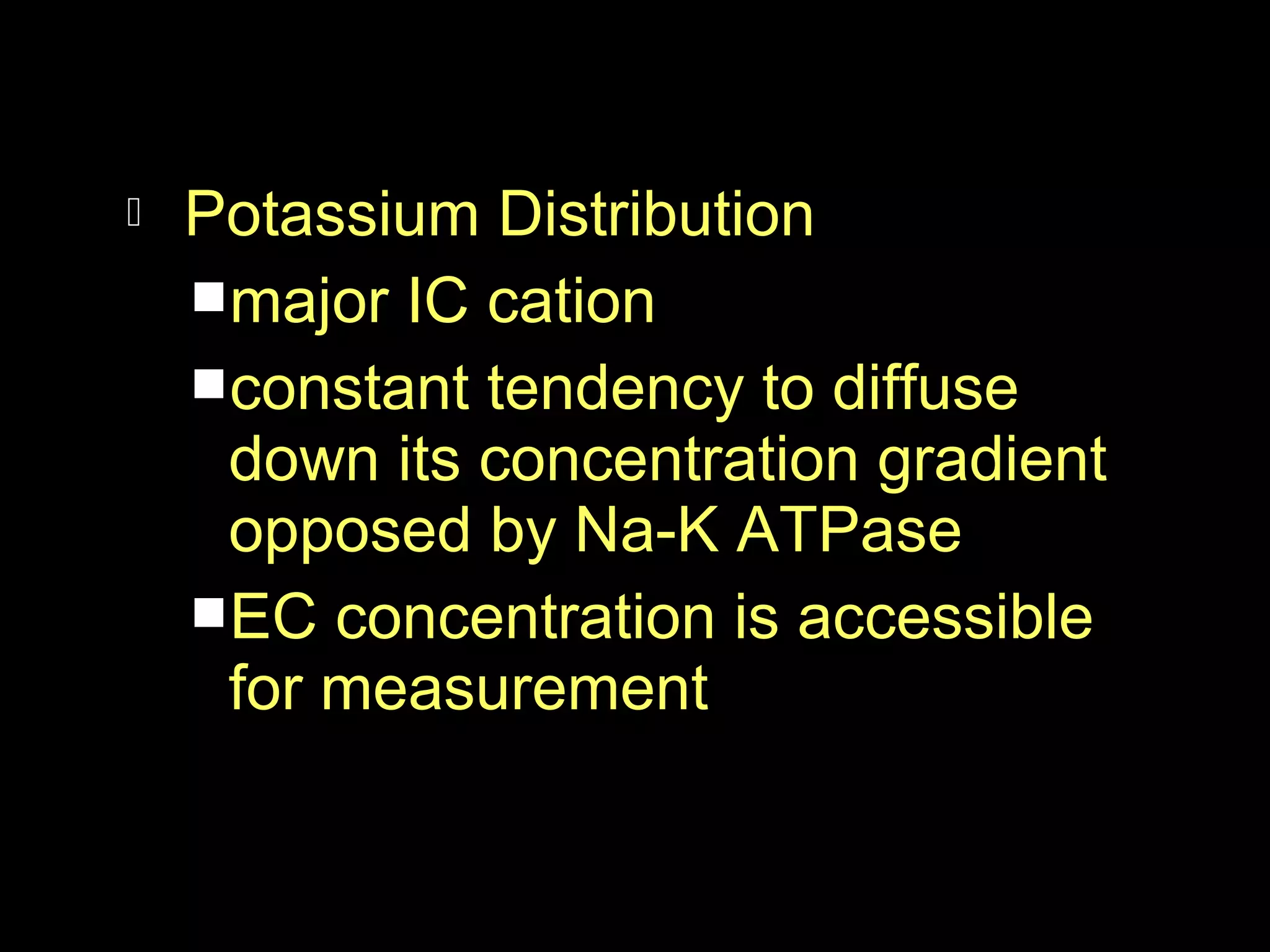
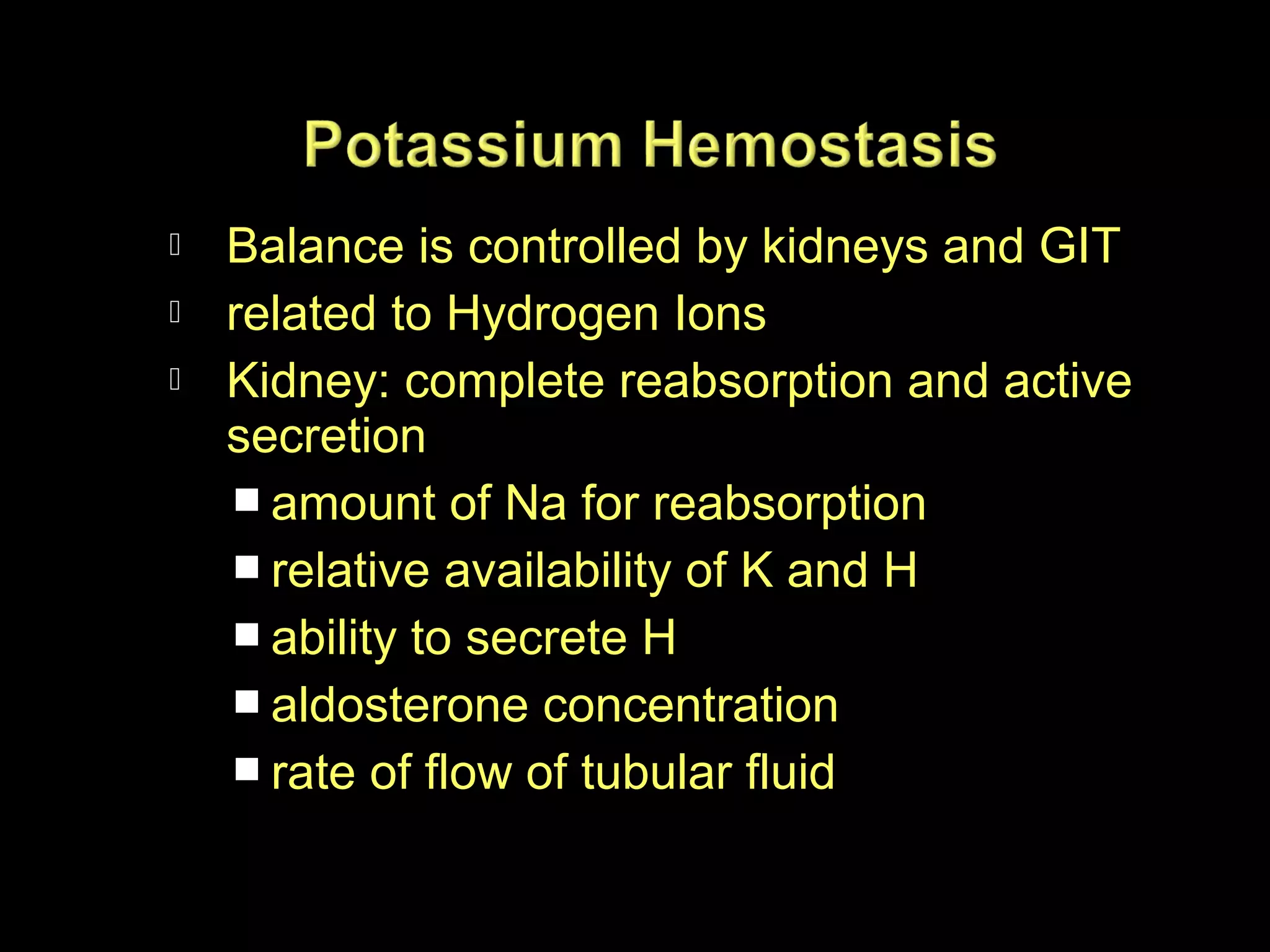
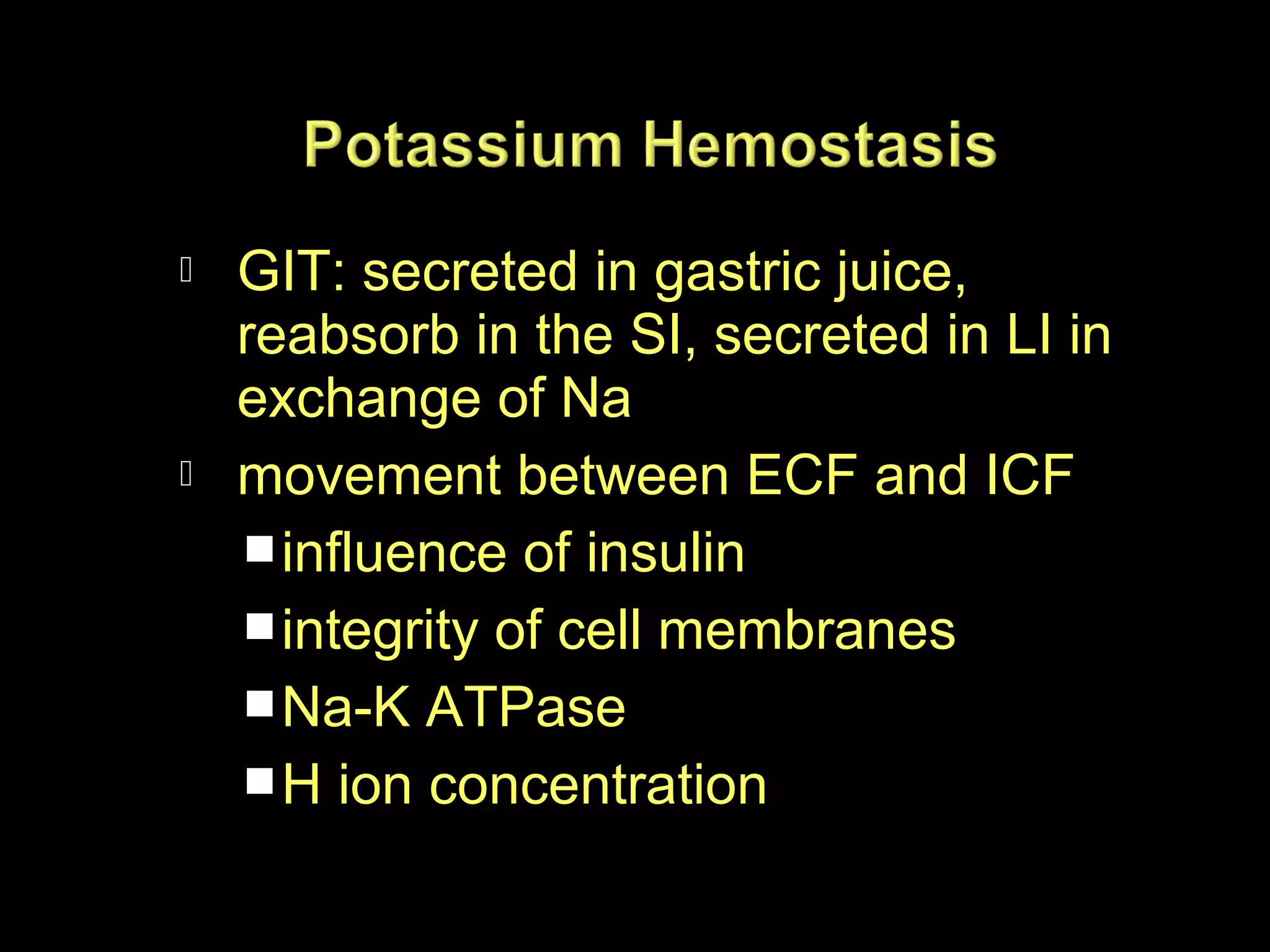
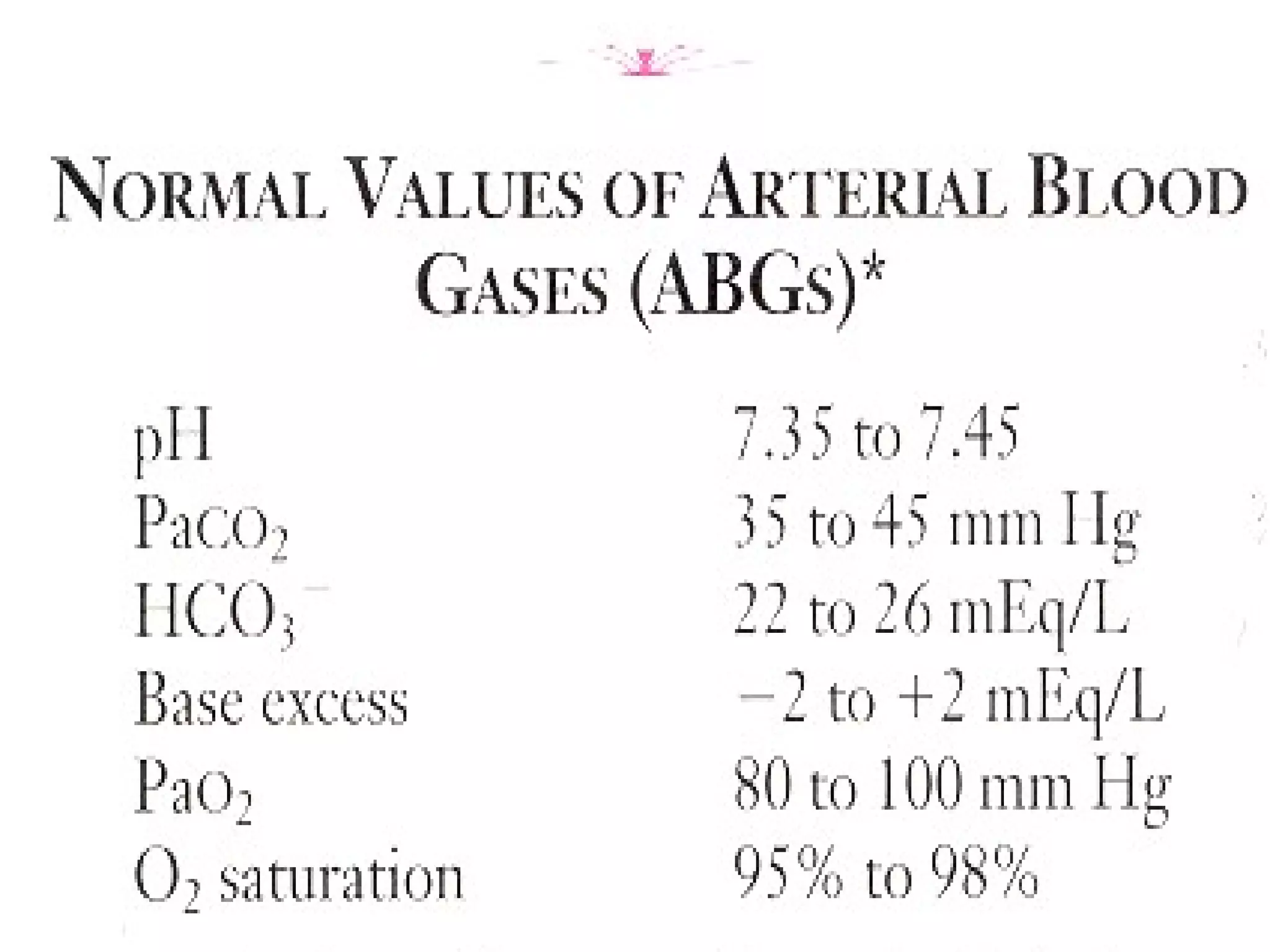
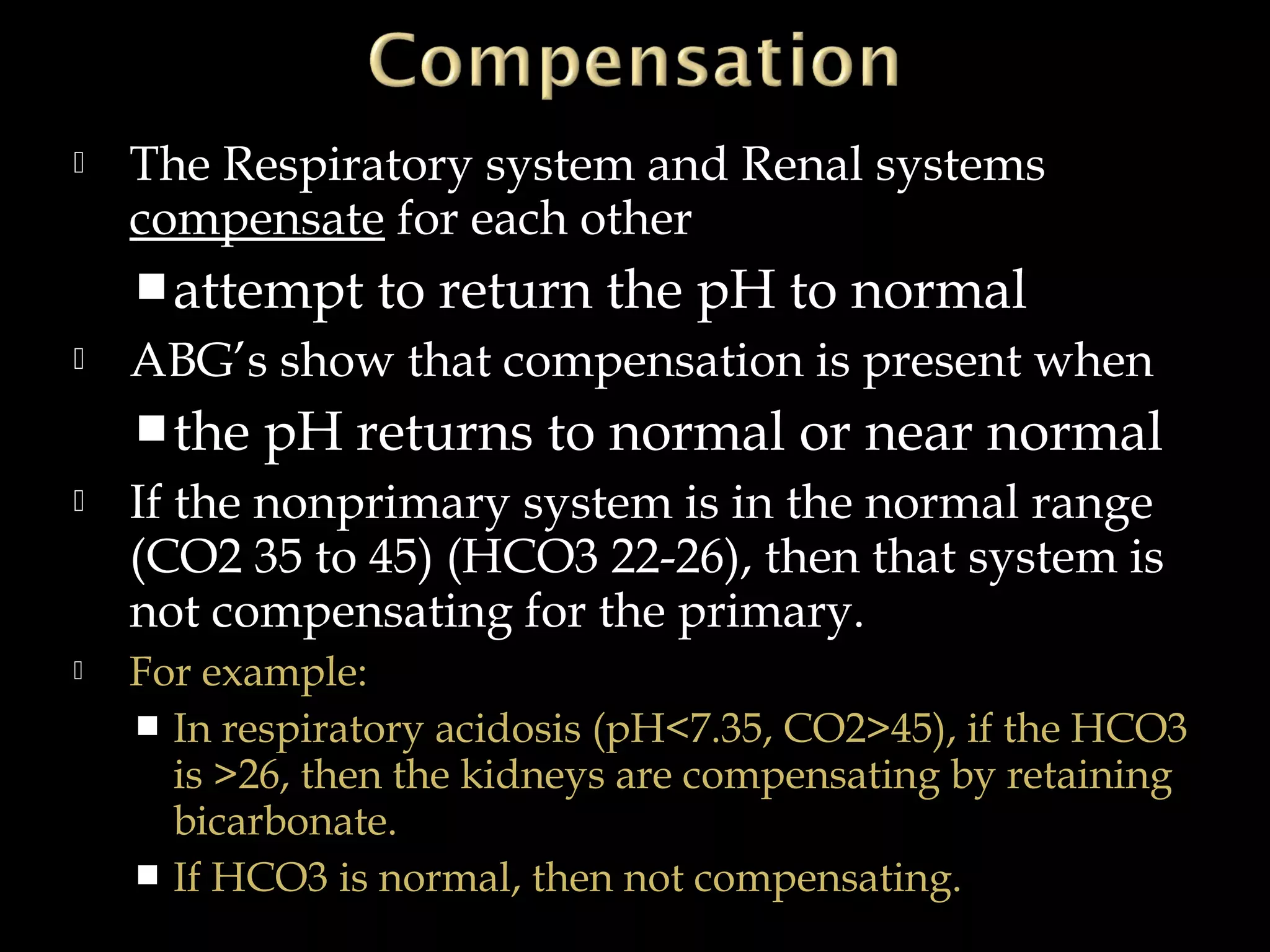
The document discusses fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance in the human body. It covers topics like intracellular and extracellular fluid composition and balance, electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and their regulation. It also discusses acid-base balance, the bicarbonate buffer system, and four major acid-base imbalances - respiratory acidosis, respiratory alkalosis, metabolic acidosis, and metabolic alkalosis. Key organs involved in regulation are the lungs and kidneys.