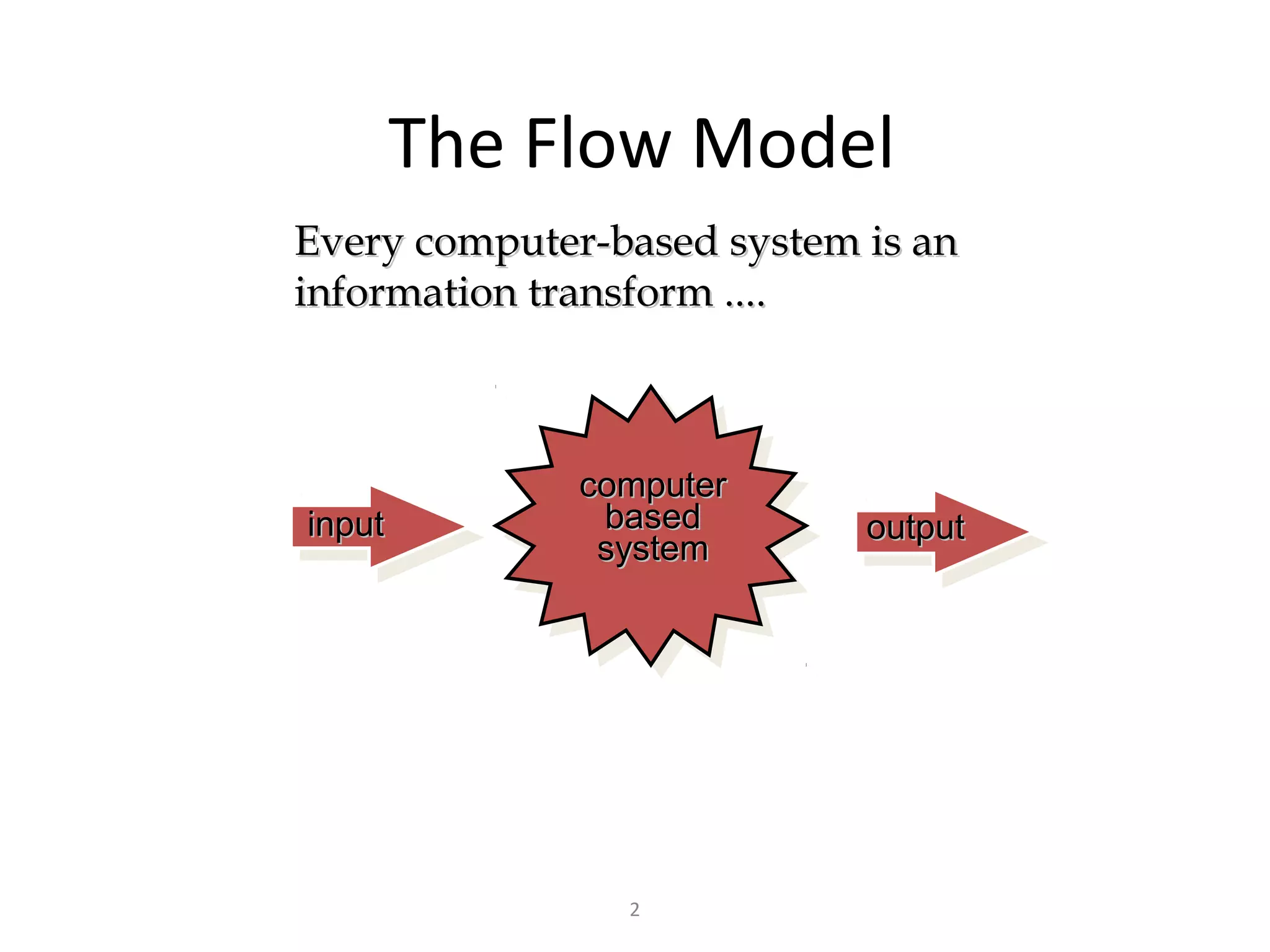
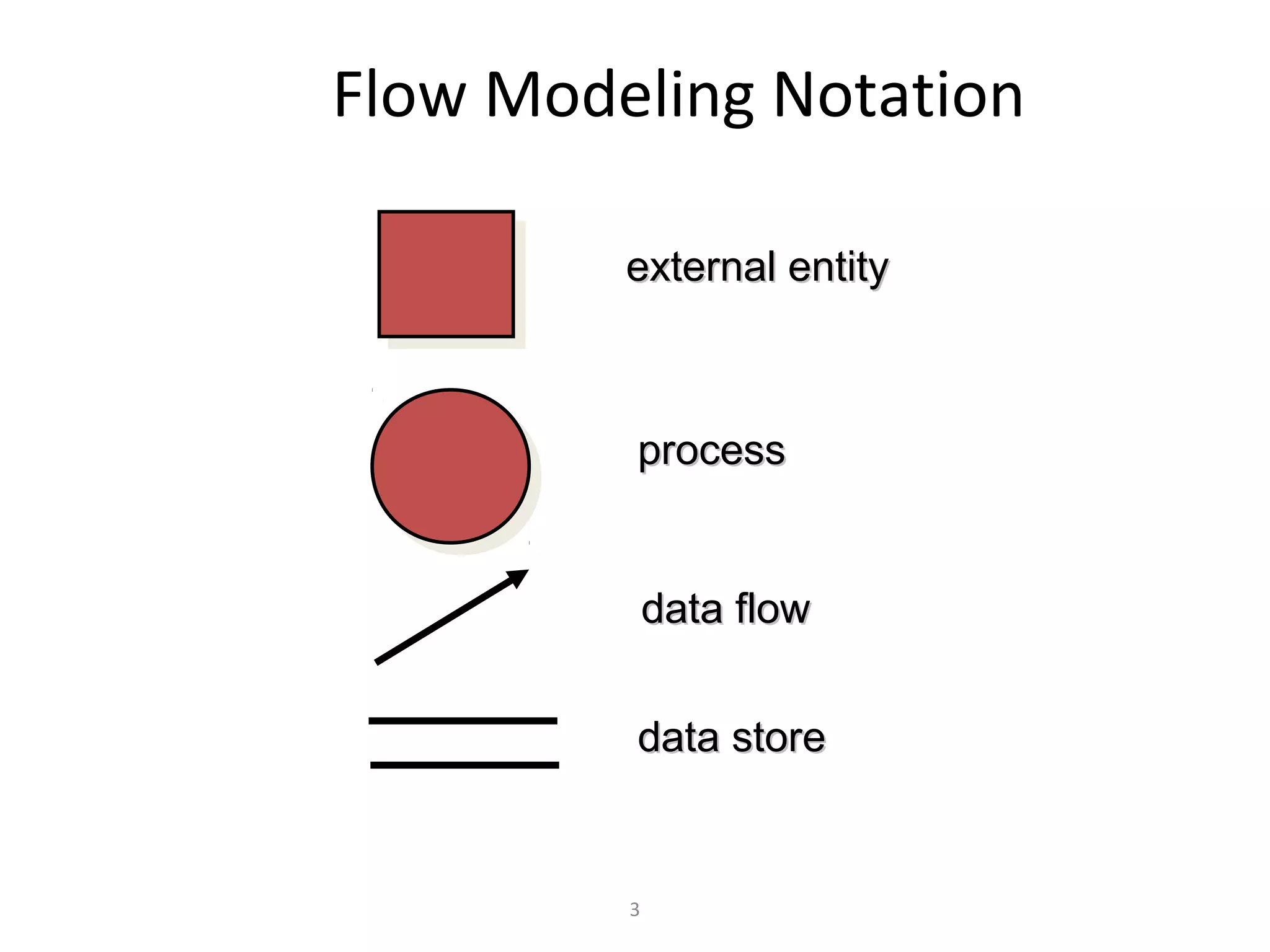
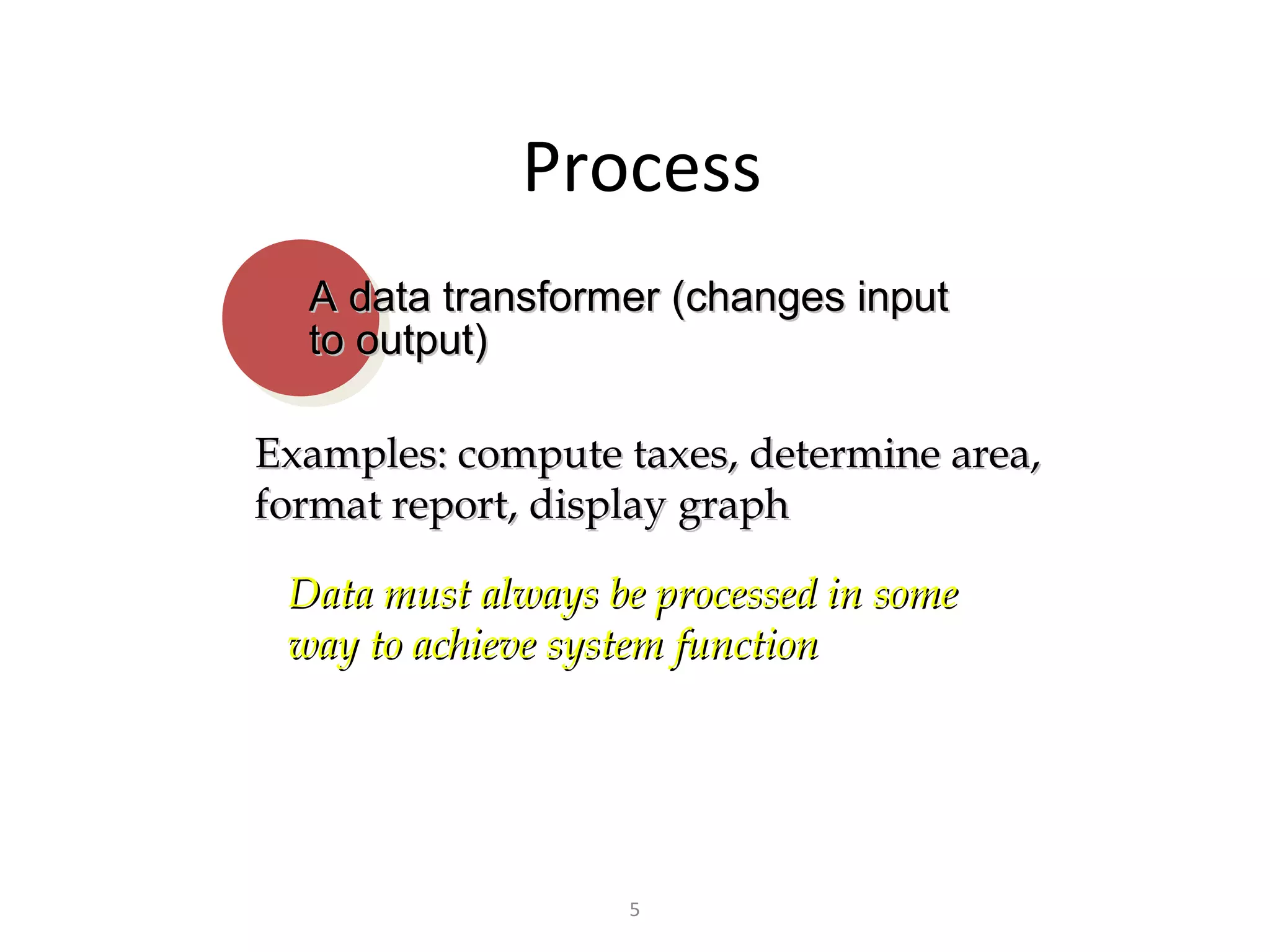
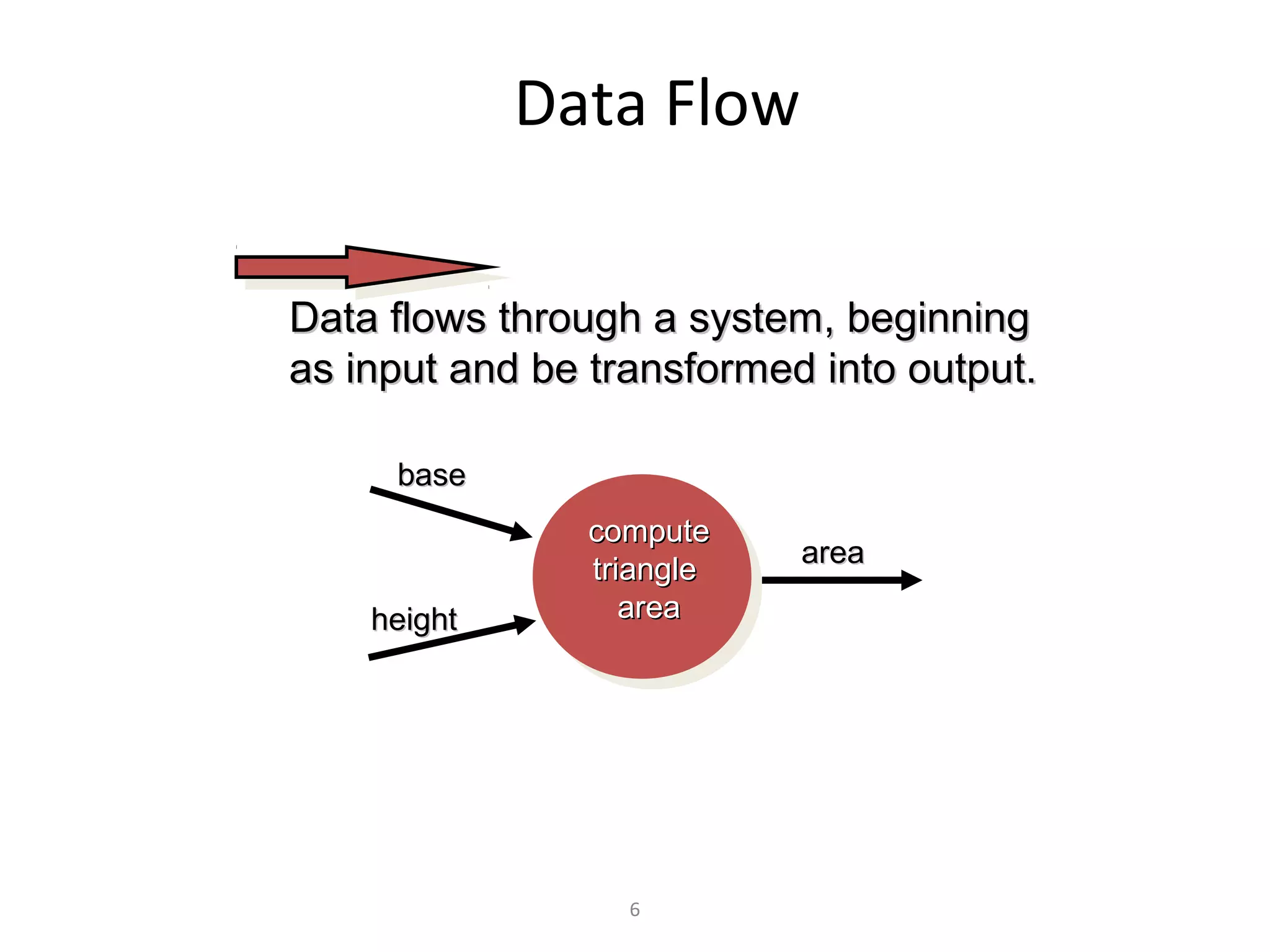
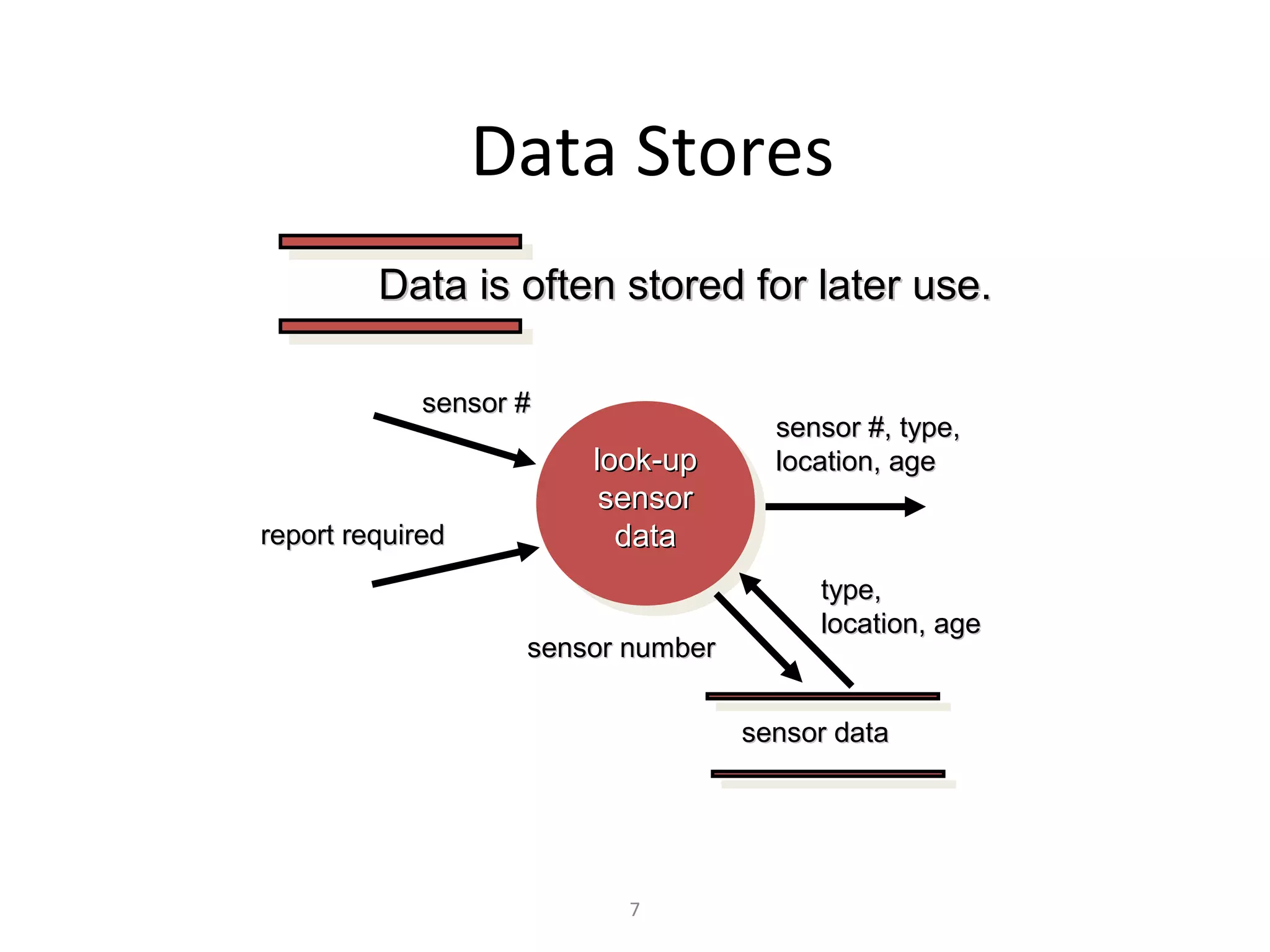
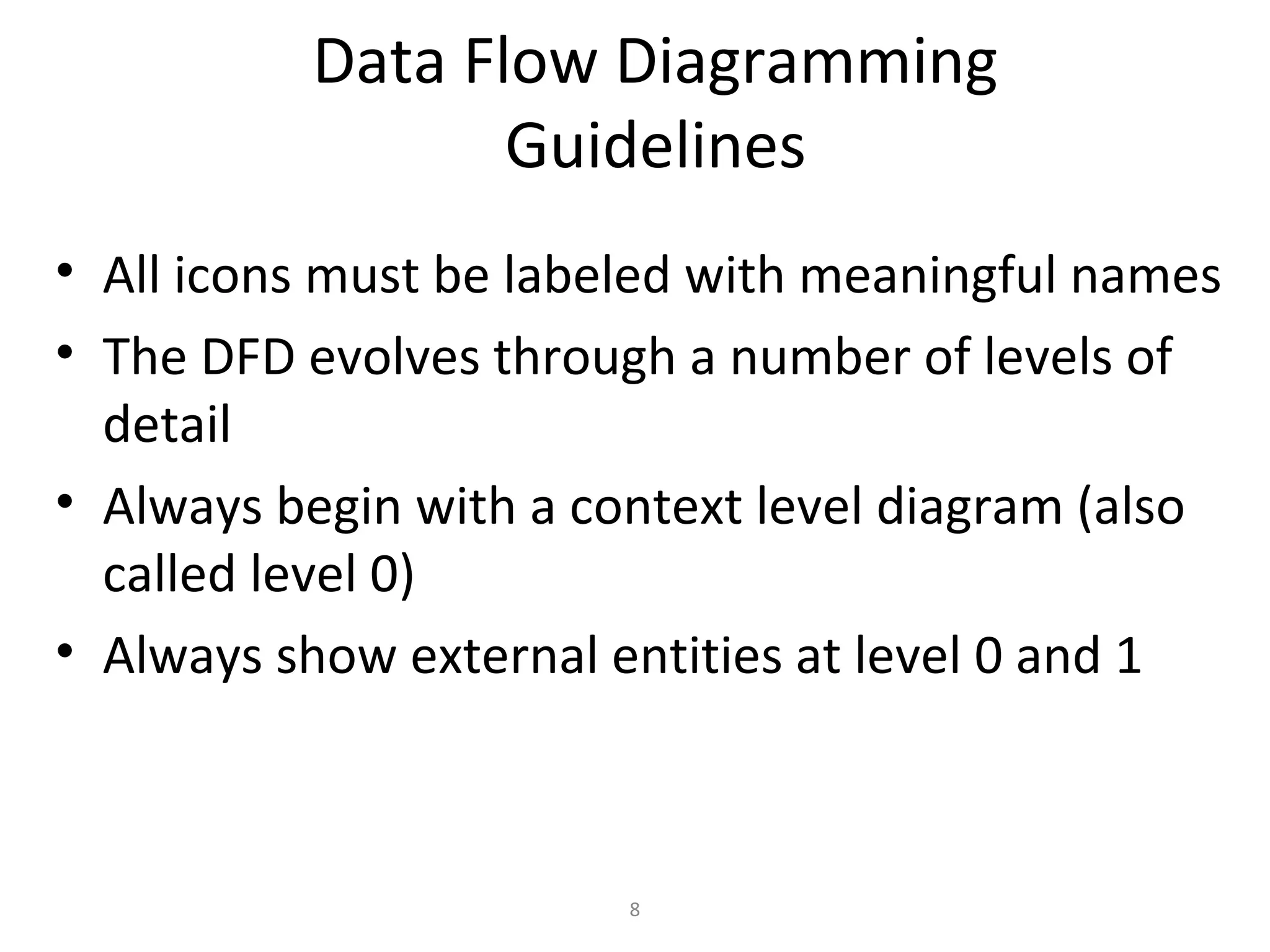
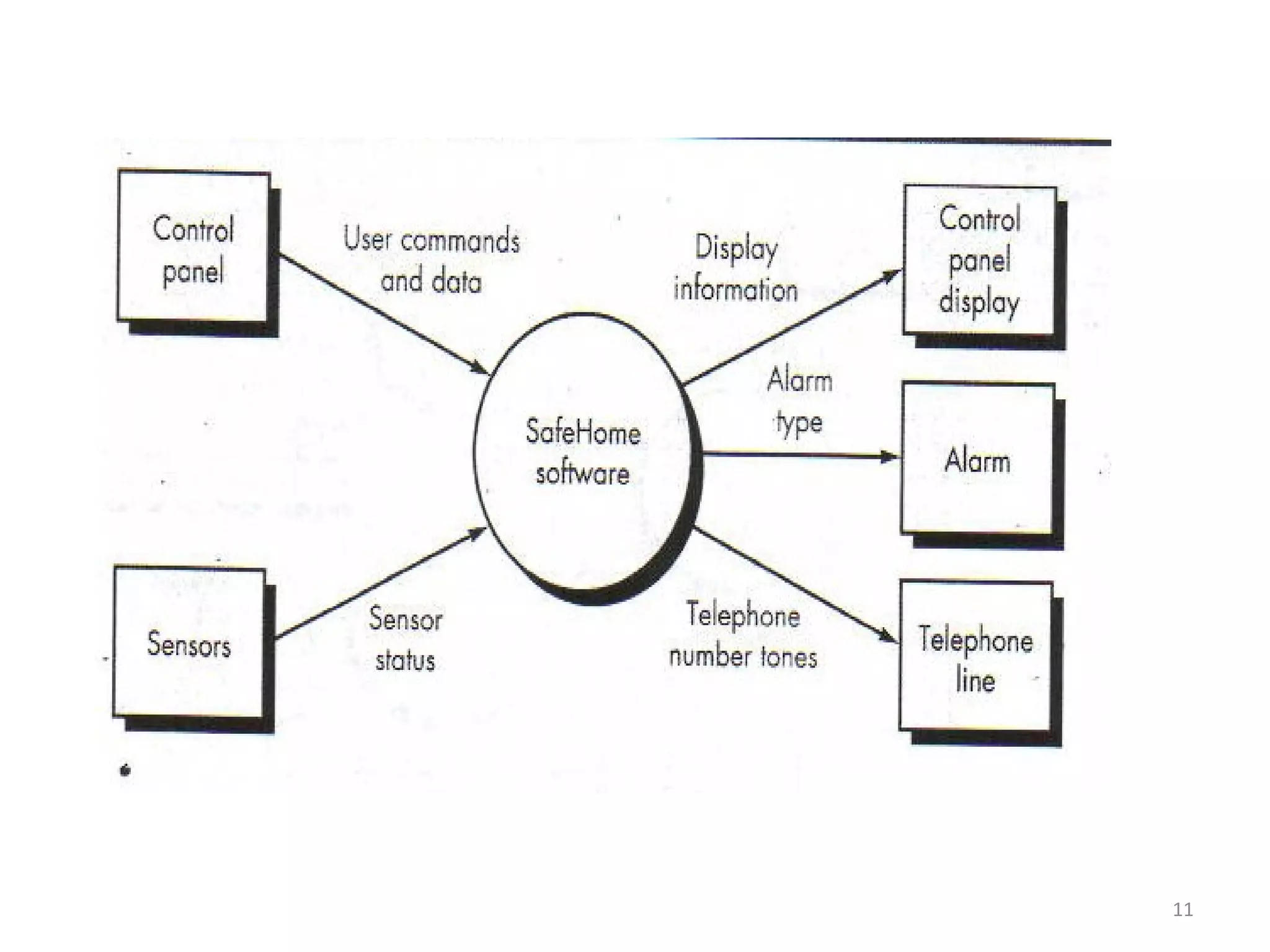
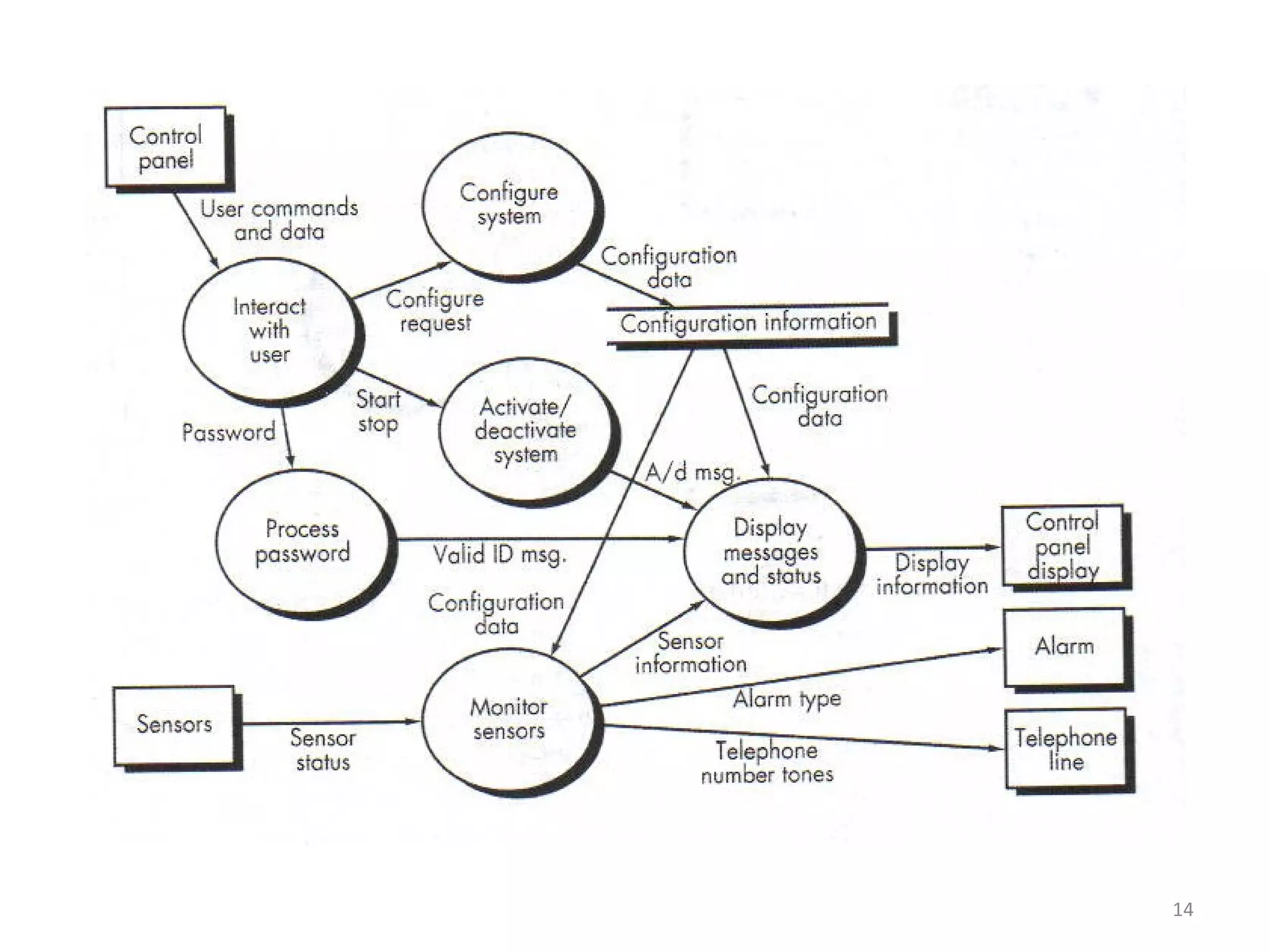
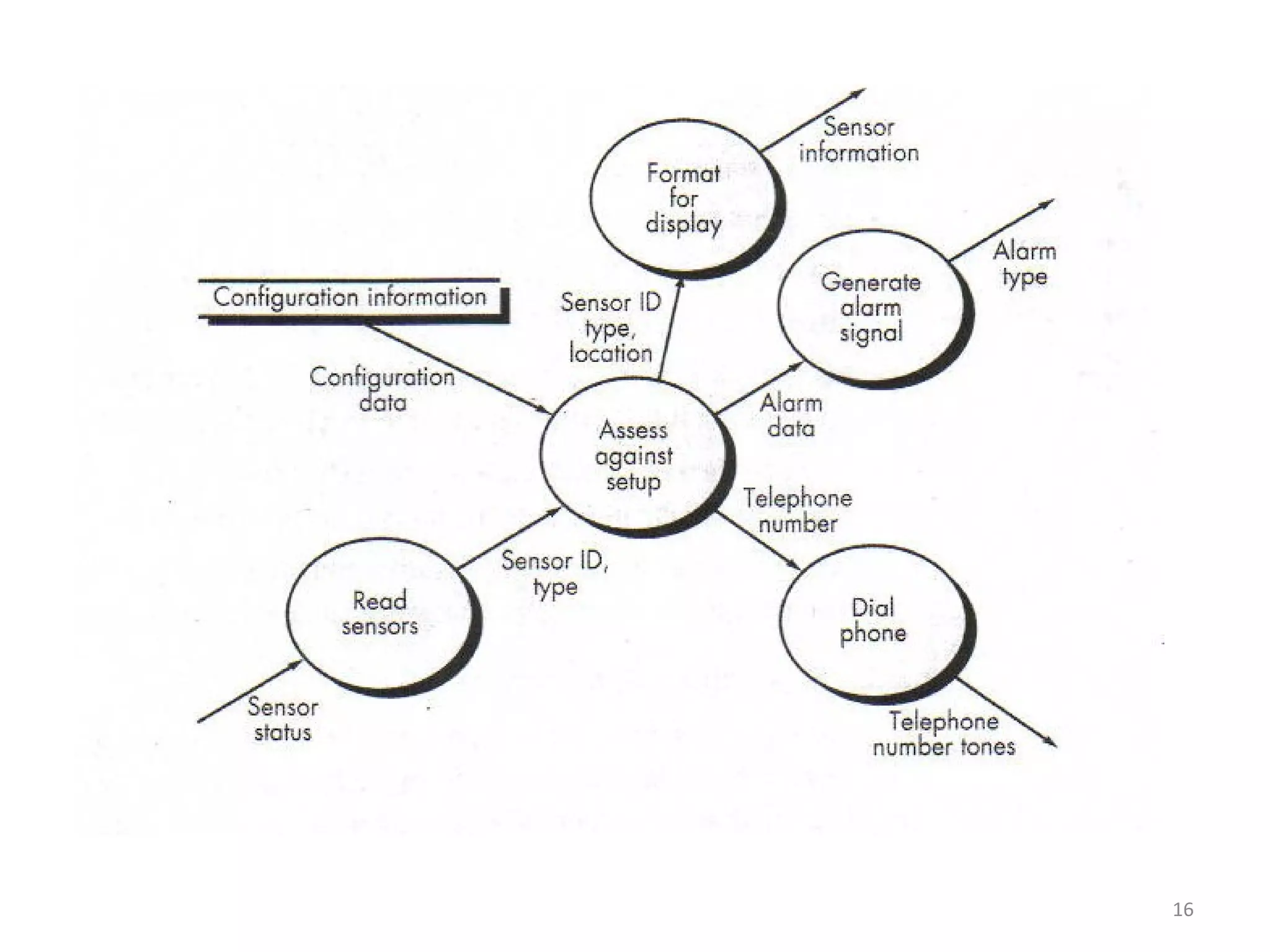
Flow-oriented modeling represents how data objects are transformed as they move through a system. A data flow diagram (DFD) is the diagrammatic form used to depict this approach. DFDs show the flow of data through processes and external entities of a system using symbols like circles and arrows. They provide a unique view of how a system works by modeling the input, output, storage and processing of data from level to level.





![PSPEC
• The process transform performs password validation at the control panel
for the SafeHome security function.
• Process password receives a four-digit password from the interact with
user function.
• The password is first compared to the master password stored within the
system.
• If the master password matches , [valid id message = true] is passed to the
message and status display function.
• If the master password does not match , the four digits are compared to a
table of secondary passwords (they may be assigned to house guests
and/or workers who require entry to the home when the owner is not
present).
• If the password matches an entry with the table, [valid id message = true]
is passed to the message and status display function.
• If there is no match, [valid id message = false] is passed to the message
and status display function.
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flow-orientedmodeling-130314061943-phpapp01/75/Flow-oriented-modeling-17-2048.jpg)