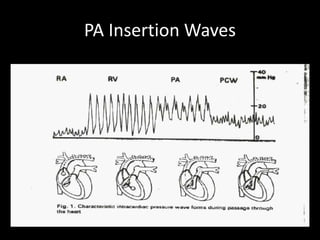
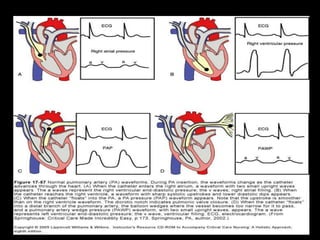
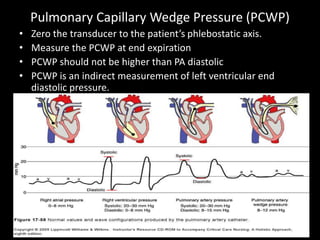
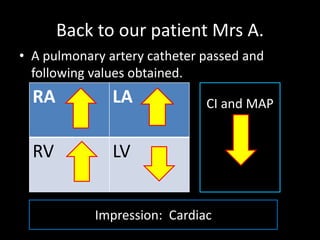
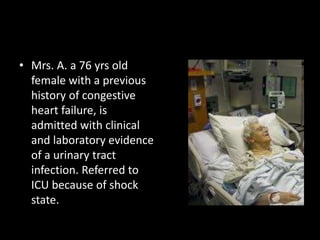
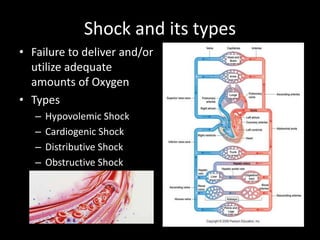
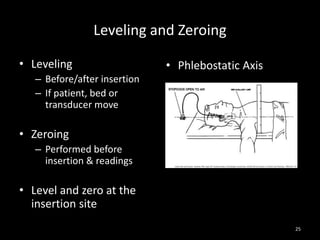
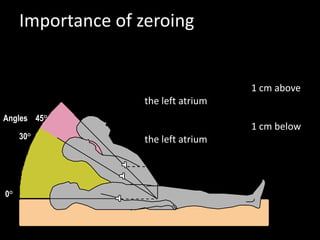
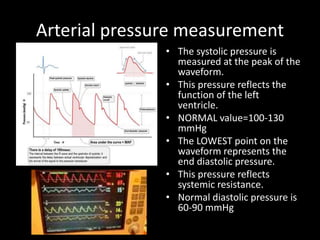
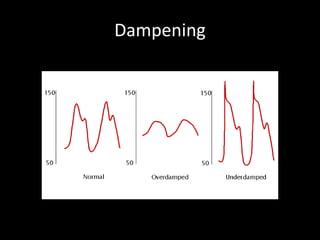
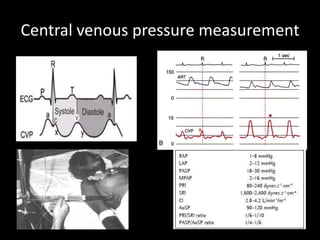
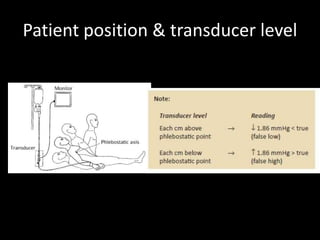
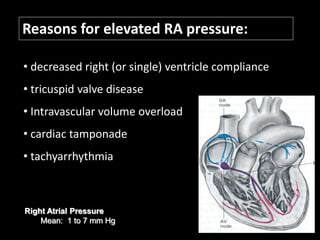
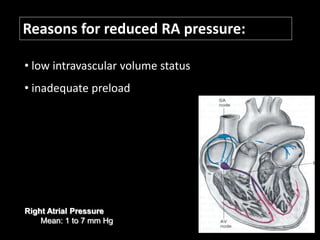
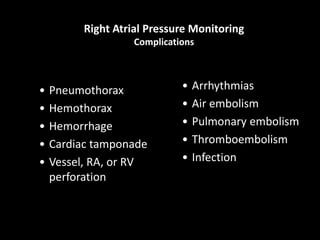
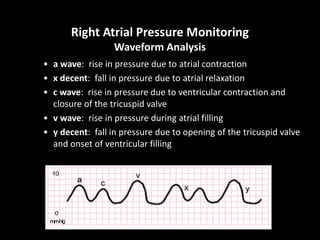
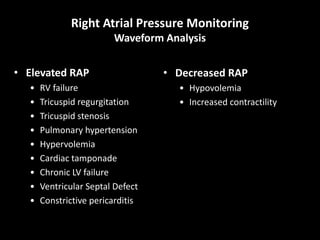
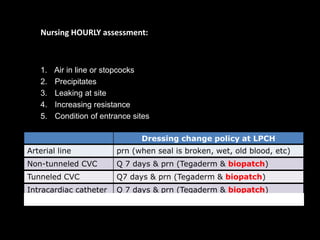
The document discusses basic hemodynamic monitoring, including its purposes, types, and significance in the management of critically ill patients. It emphasizes the use of various monitoring techniques, including invasive and non-invasive methods, to assess patients' cardiovascular status, particularly in cases of shock. Specific examples, such as a case study of a patient with urinary tract infection and shock, illustrate the application of monitoring techniques to guide treatment and improve patient outcomes.

























![Some common terminologies…
• Preload
• Afterload
• Cardiac Output
• Cardiac Index
• Systemic Vascular
Resistance [SVR]
• Pulmonary Vascular
Resistance [PVR]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basichemodynamicmonitoring-140618171505-phpapp02/85/Basic-hemodynamic-monitoring-for-nurses-51-320.jpg)
![Understanding basic terms
Preload
• Is the degree of muscle fiber
stretching present in the
ventricles right before systole
• Is the amount of blood in a
ventricle before it contracts;
also known as “filling
pressures”
• Left ventricular preload is
reflected by the PCWP
• Right ventricular preload is
reflected by the CVP [RAP]
Afterload
• Any resistance against
which the ventricles must
pump in order to eject its
volume
• How hard the heart [either
side left or right] has to
push to get the blood out
• Also thought of as the “
resistance to flow” or how
“clamped” the blood vessels
are](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basichemodynamicmonitoring-140618171505-phpapp02/85/Basic-hemodynamic-monitoring-for-nurses-52-320.jpg)
![Understanding basic terms
Cardiac output/Index
• Is the amount of blood
ejected from the ventricle in
one minute
• Two components multiply to
make the cardiac output: heart
rate and stroke volume
[amount of blood ejected with
each contraction]
• Cardiac index is the cardiac
output adjusted for body
surface area (BSI)
Vascular Resistance
• Systemic Vascular
Resistance – reflects left
ventricular afterload
• Pulmonary Vascular
Resistance – reflection of
right ventricular afterload
• Many of the drugs we
administer will affect
Preload, Afterload,
SVR/PVR, Cardiac Output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basichemodynamicmonitoring-140618171505-phpapp02/85/Basic-hemodynamic-monitoring-for-nurses-53-320.jpg)

![Equipment Needed
7. Set up pressure lines and transducers
8. Please level pressure flush monitoring system and transducers to
the
phlebostastic axis. Zero the transducers. Also check to make sure
all connections are secure.
9. Connect tubings to patient [PA port and CVP port] when
physician
is ready to flush the swann. Flush all ports of swann before
inserting.
10. While floating the swann, observe for ventricular ectopy on the
monitor, and make physician aware of frequent PVC’s or runs of
VT !
11. After swann is in place, assist with cleanup and let patient know
procedure is complete.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basichemodynamicmonitoring-140618171505-phpapp02/85/Basic-hemodynamic-monitoring-for-nurses-57-320.jpg)
![Measuring Cardiac output
11. Obtain your RA [CVP], PAS/D, PAM, and
wedge.
For Cardiac Outputs, inject 10 mLs of D5W
after pushing the start button, repeat X 3.
Delete outputs not within 1 point of the
mean value.
Can use 0.9% NS instead, but affects the
accuracy of the output reading.
12. Before obtaining the cardiac output, please
check the computation constant [should
read 0.692 for regular yellow swans; 0.692
for SVO2 or blue swanns]
13. Perform hemocalculations
(enter today’s height and weight).
14. Document findings on the ICU flowsheet.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basichemodynamicmonitoring-140618171505-phpapp02/85/Basic-hemodynamic-monitoring-for-nurses-58-320.jpg)