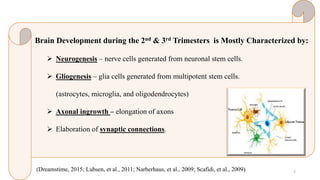
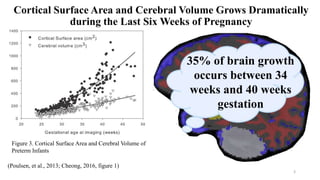
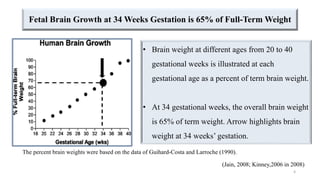
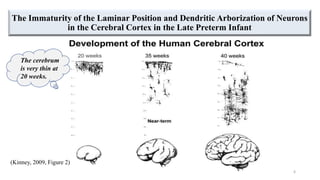
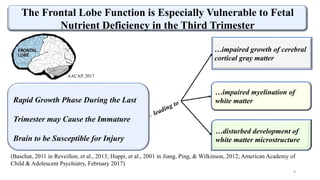
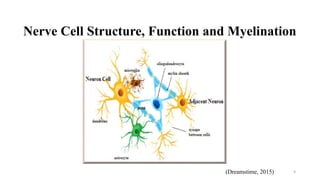
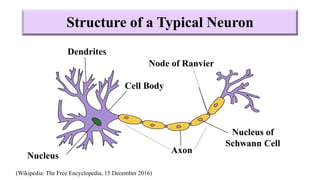
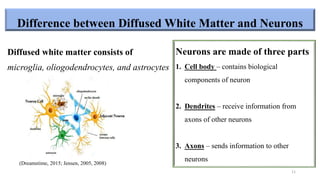
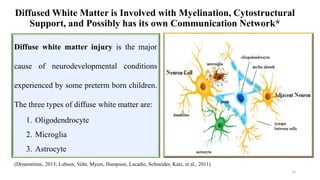
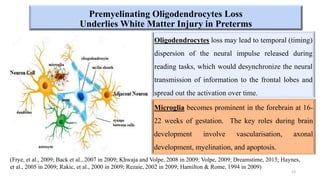
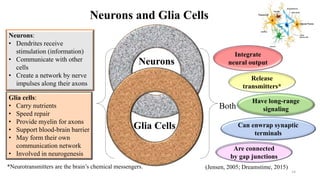
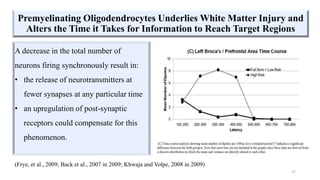
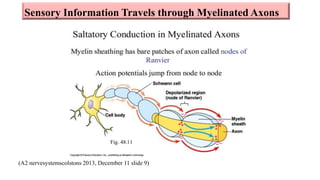
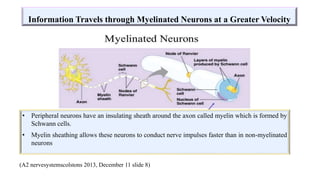
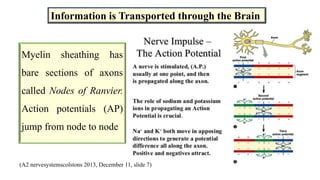
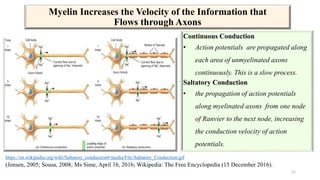
Fetal brain development is characterized by neurogenesis, gliogenesis, and the growth of axons and synaptic connections, particularly during the third trimester. Key processes, including myelination and neuronal connectivity, continue into early adulthood and are critical for cognitive development, with growth of gray and white matter peaking before term. Premature birth can disrupt this critical growth phase, leading to long-term neurological deficits such as reduced gray matter density and impaired cognitive functions.