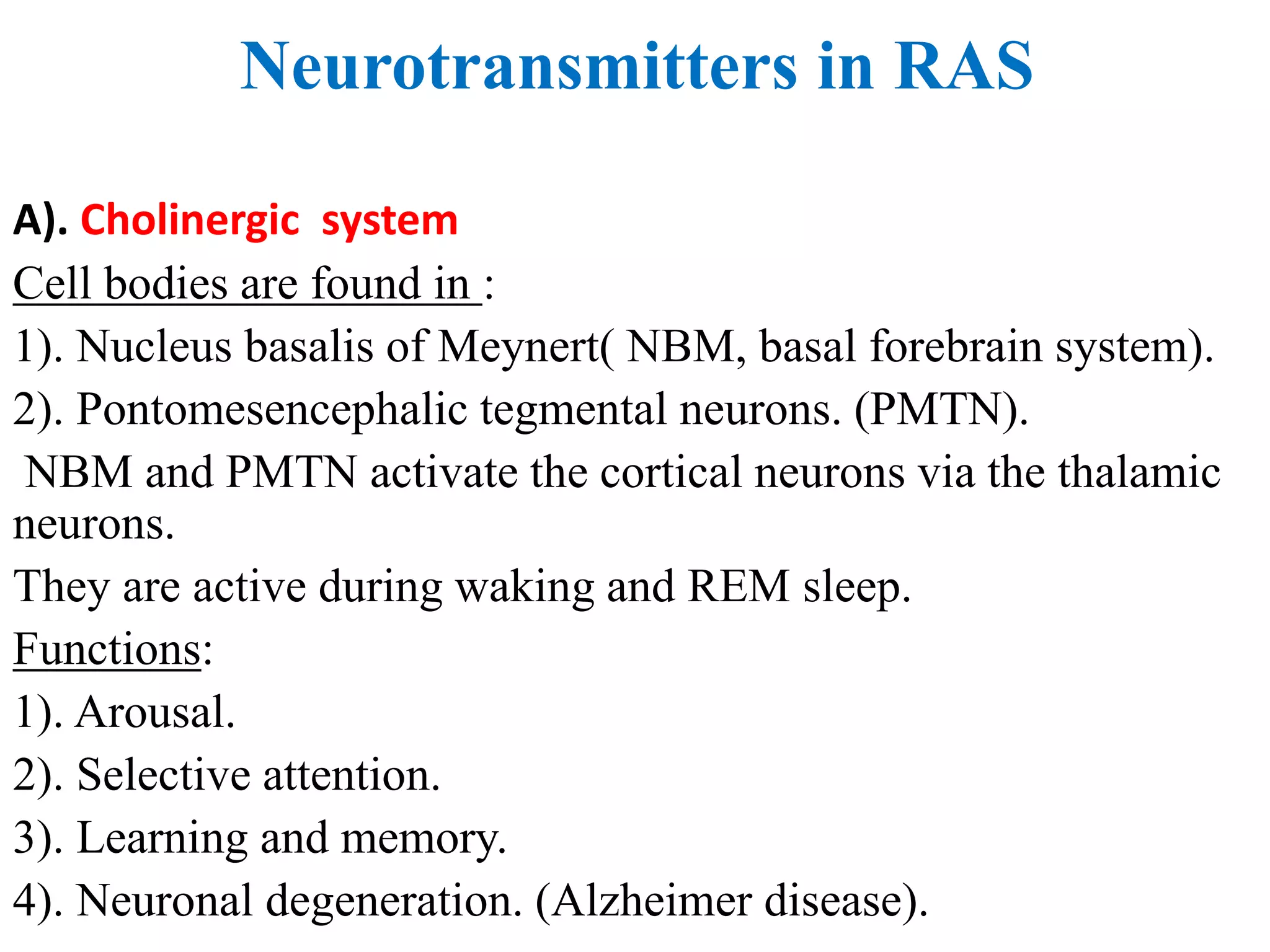
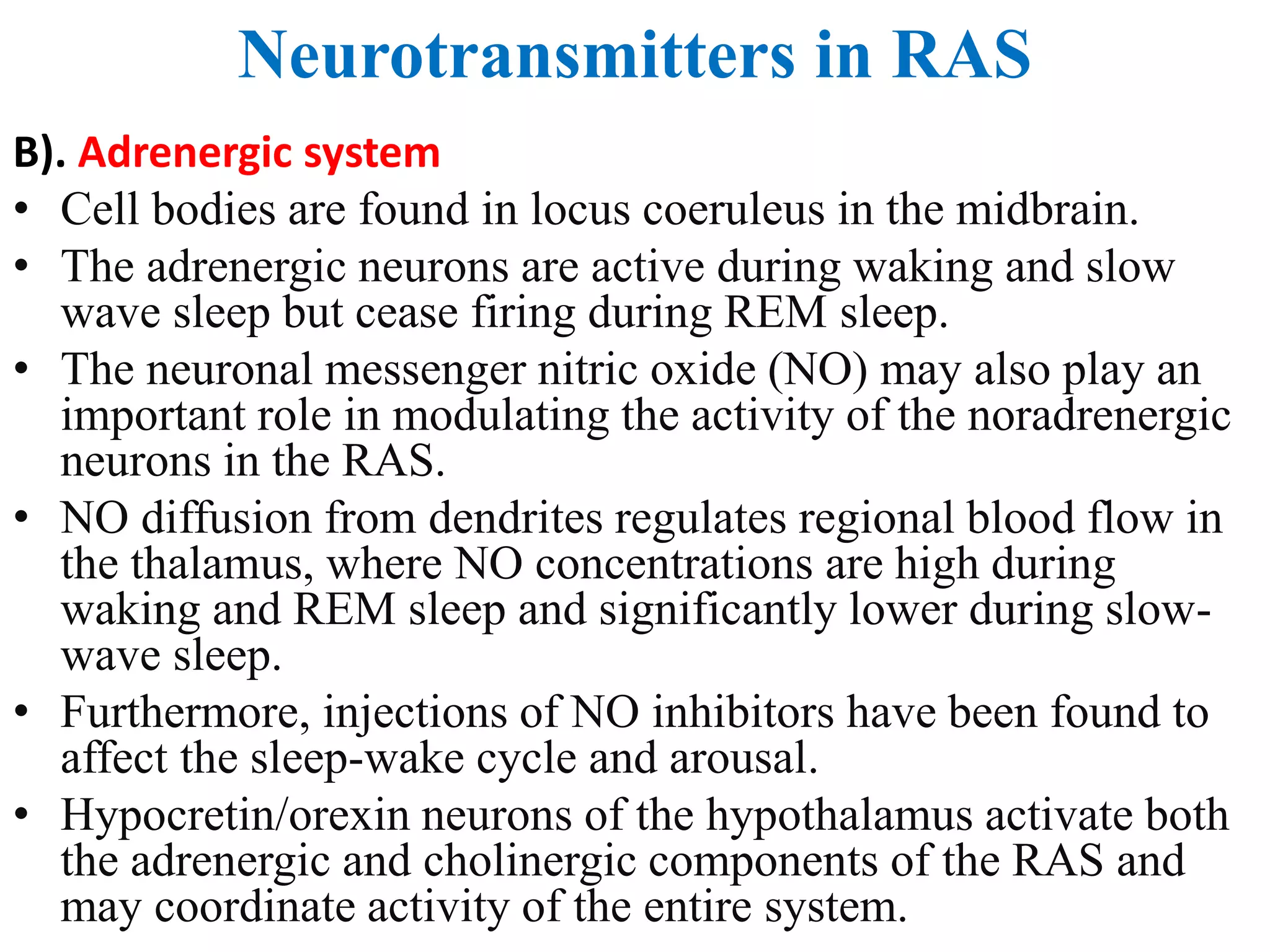
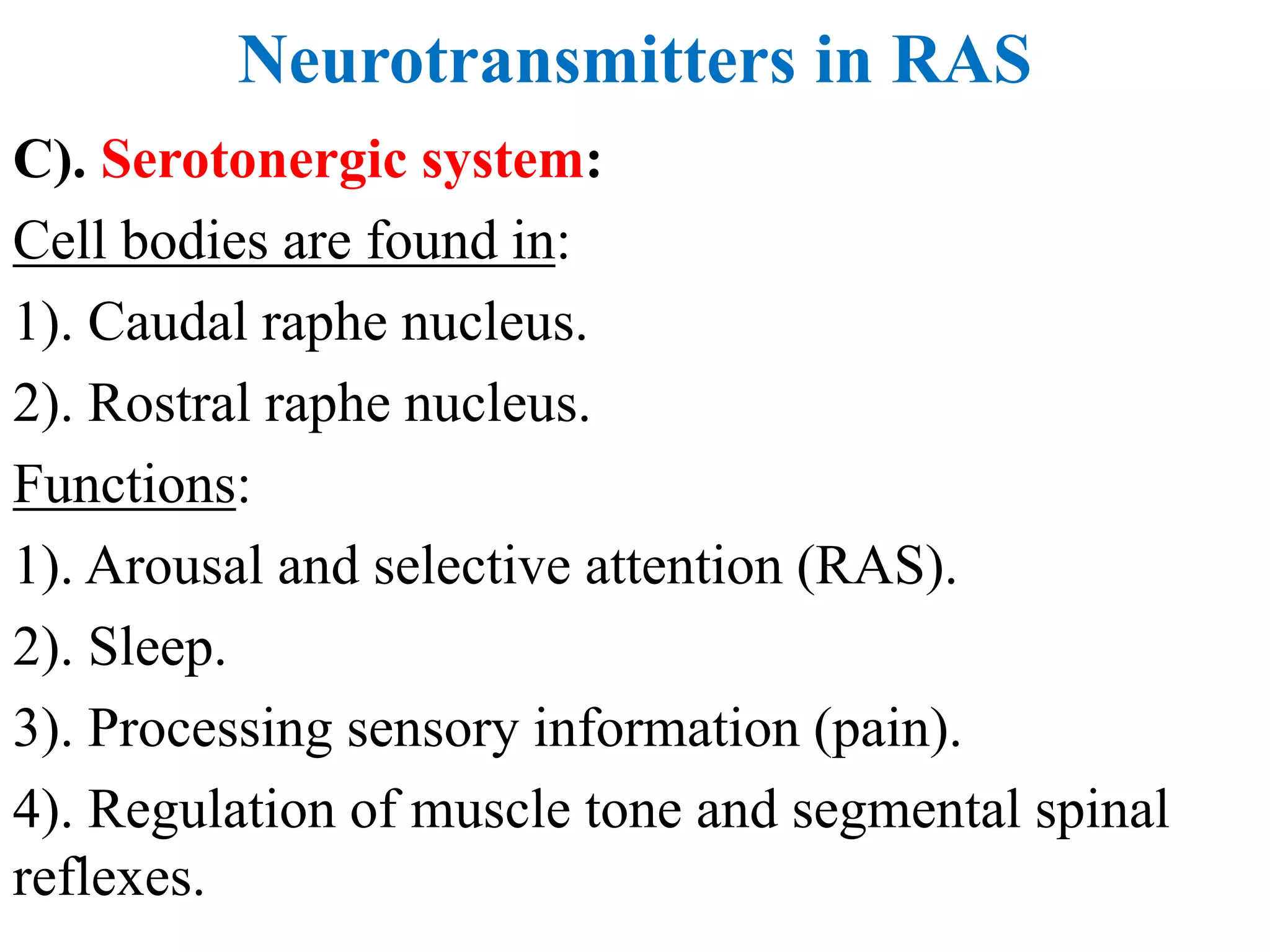
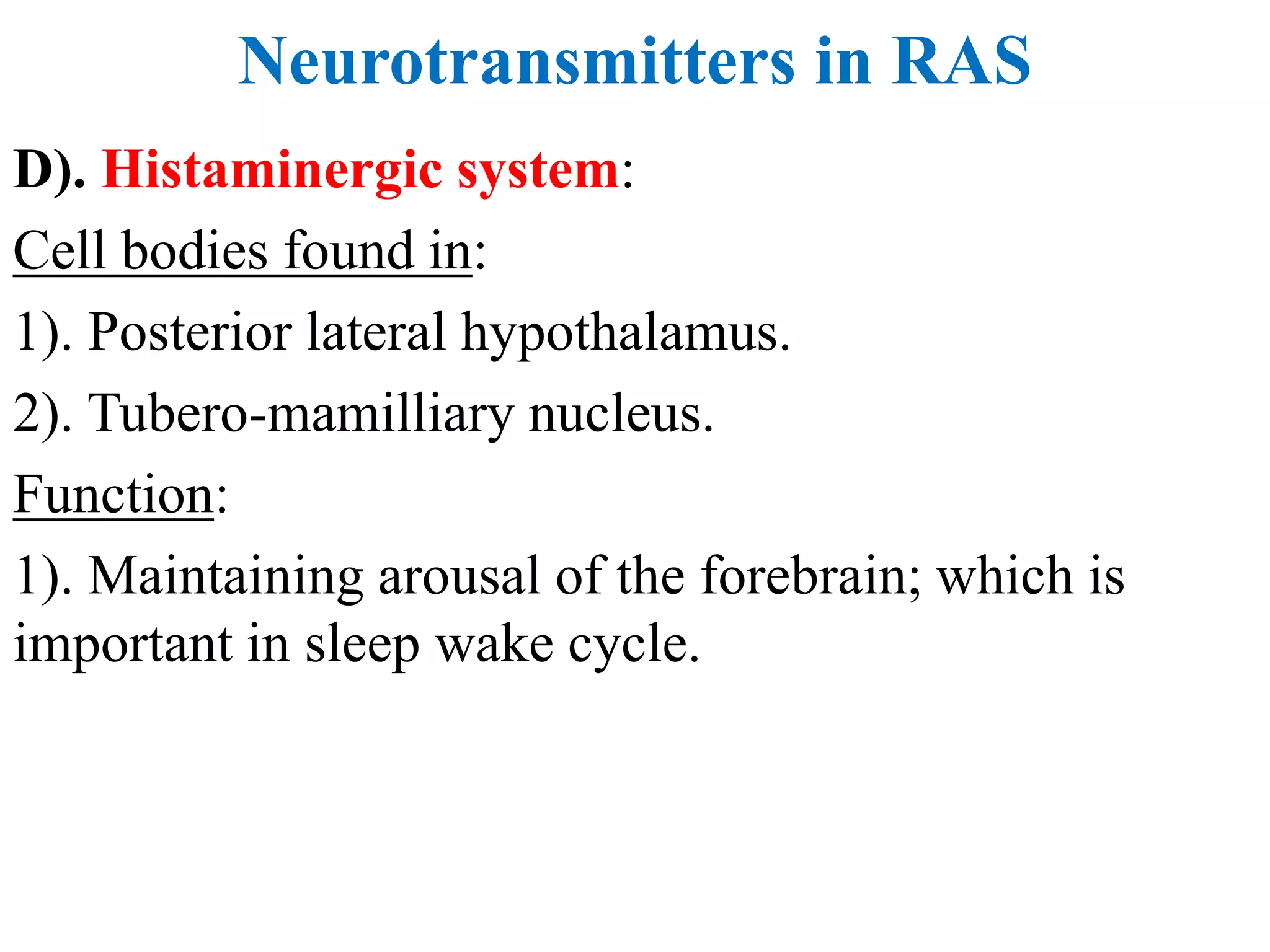
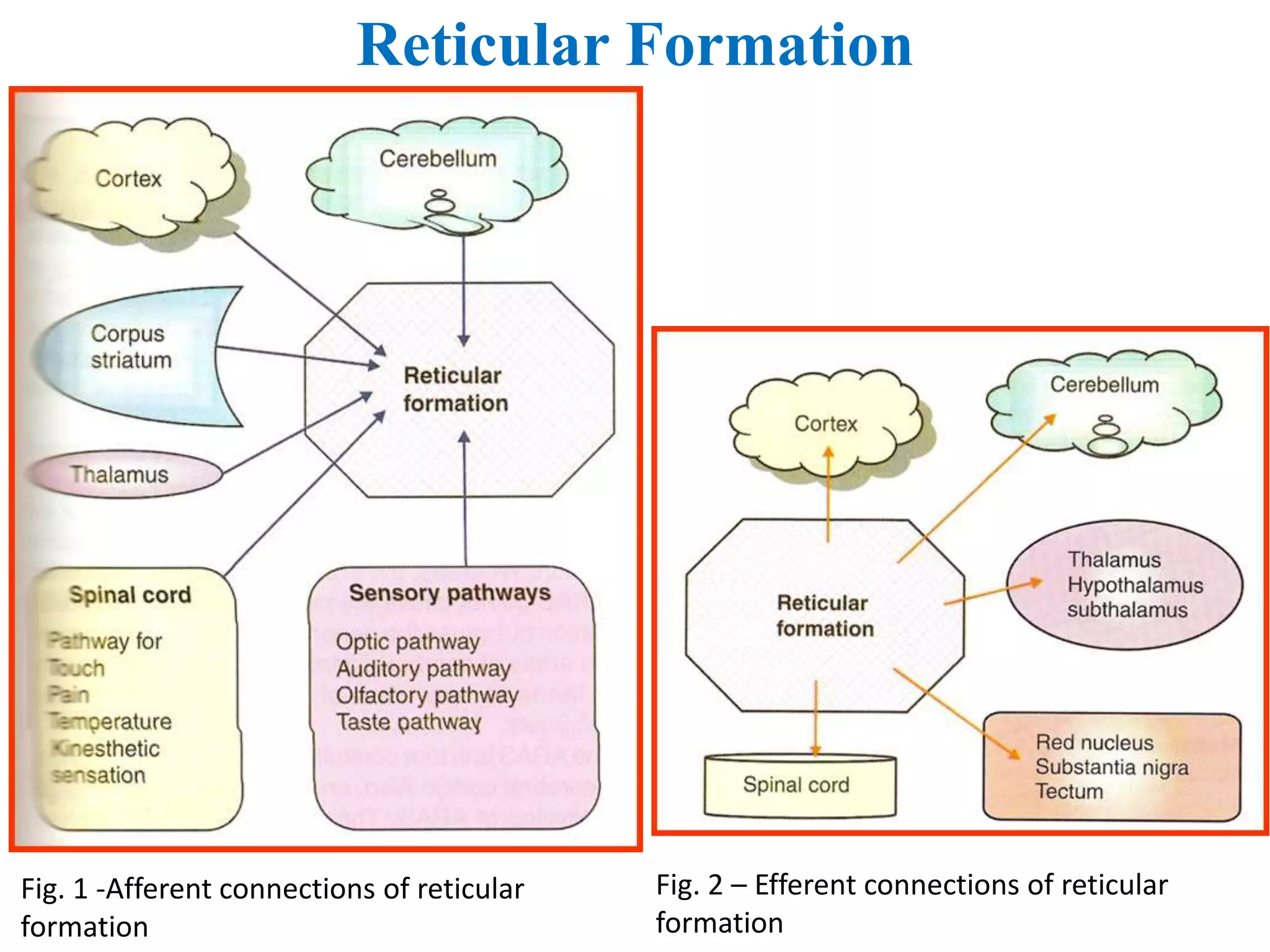
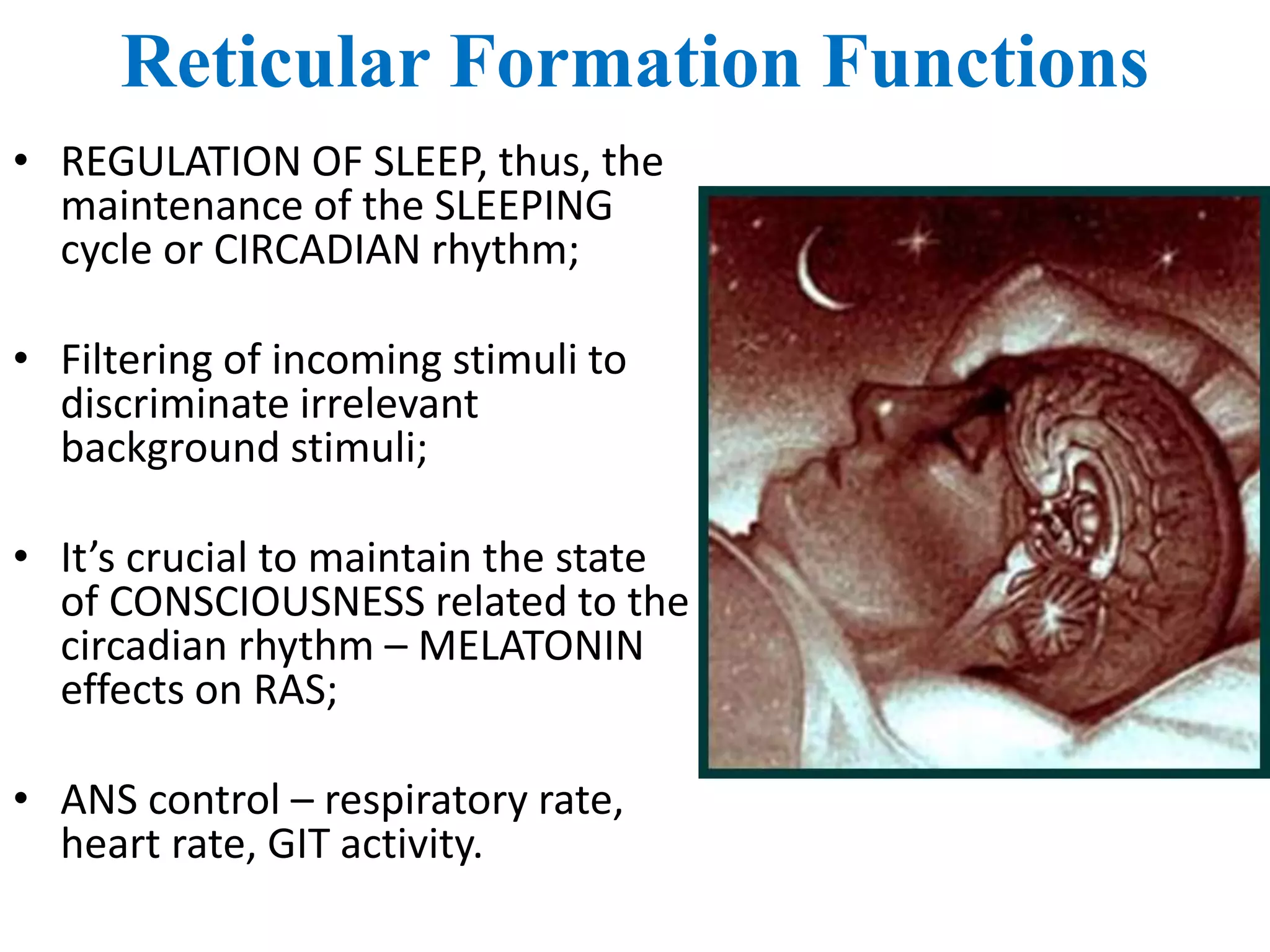
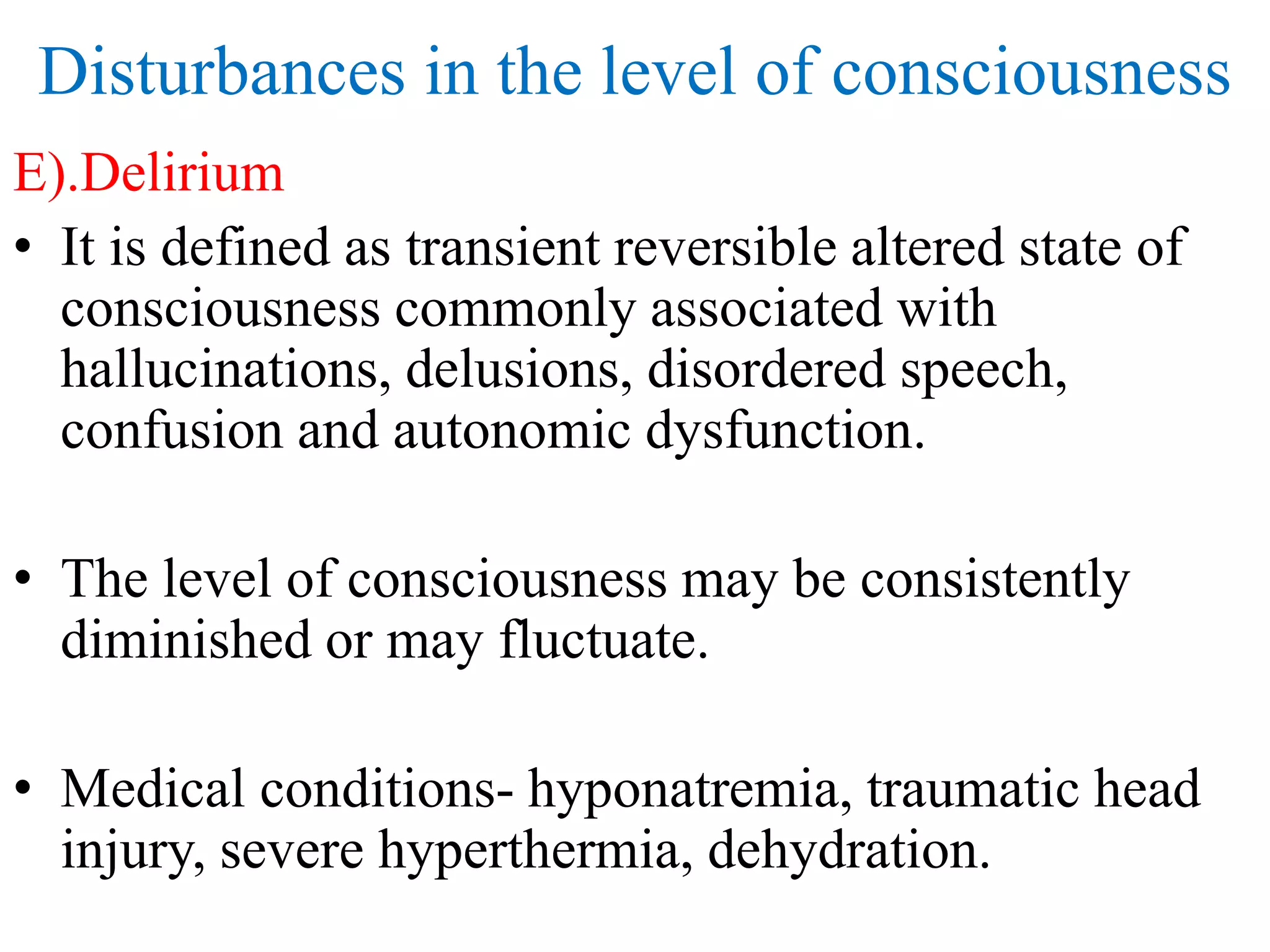
The reticular activating system (RAS) is a complex network of neurons located in the brainstem that regulates states of consciousness such as sleep and wakefulness. It is composed of neurotransmitter systems including cholinergic, adrenergic, serotonergic, and histaminergic neurons. The RAS maintains arousal and attention by transmitting signals from the brainstem to the thalamus and cortex. Disruptions in the RAS can result in disturbances of consciousness and sleep-wake cycles, and have been implicated in disorders such as schizophrenia, PTSD, Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease.