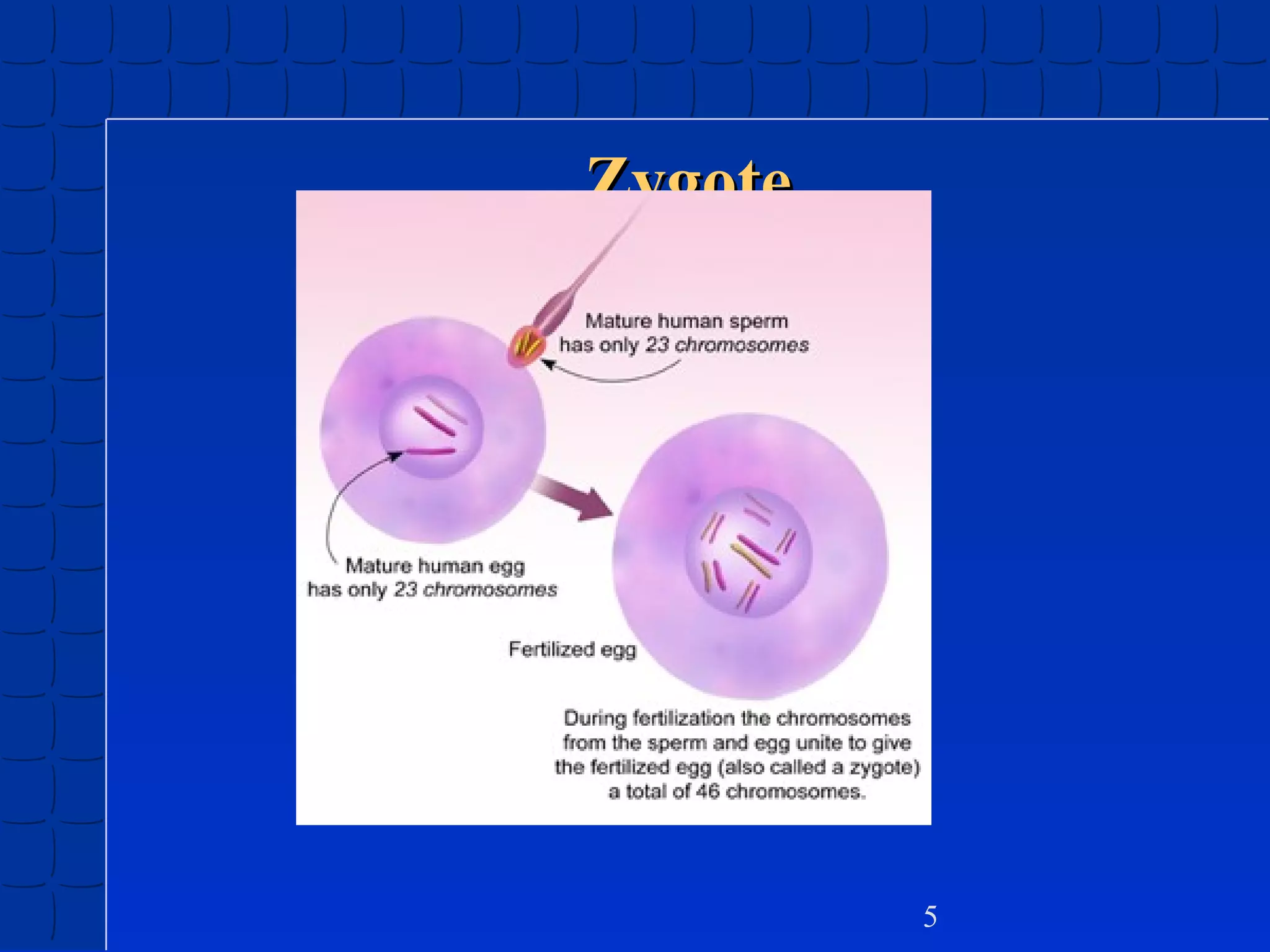
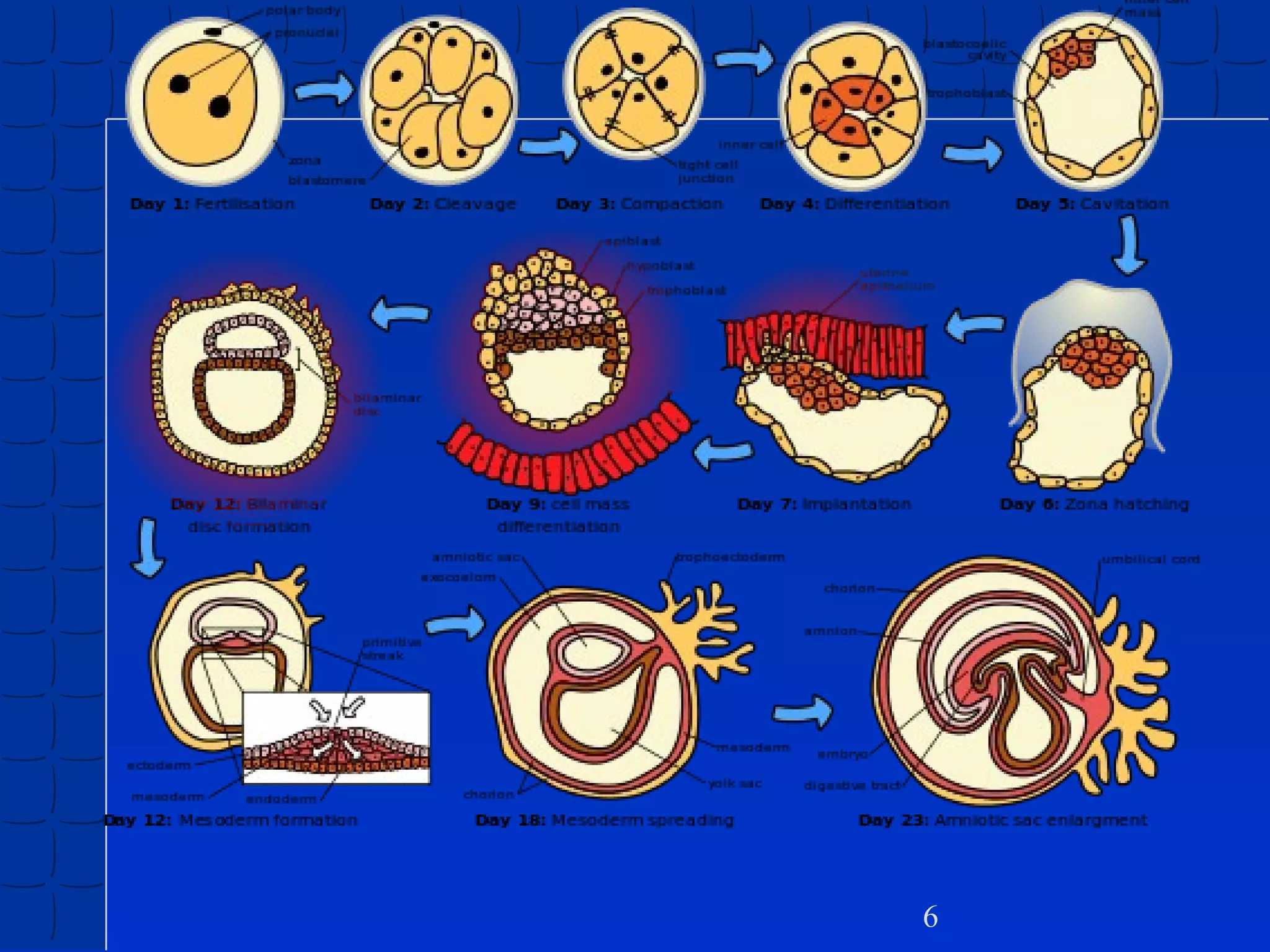
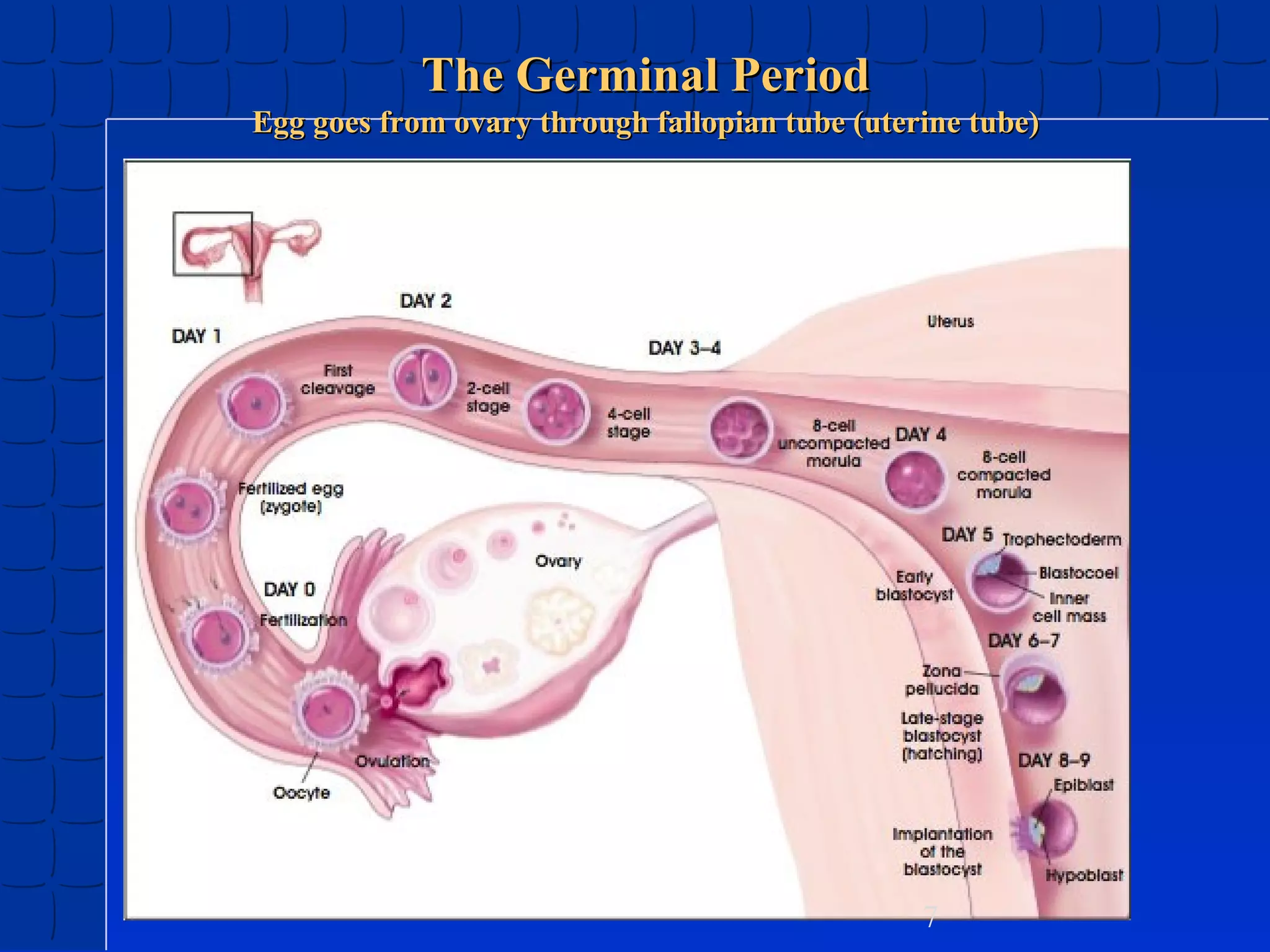
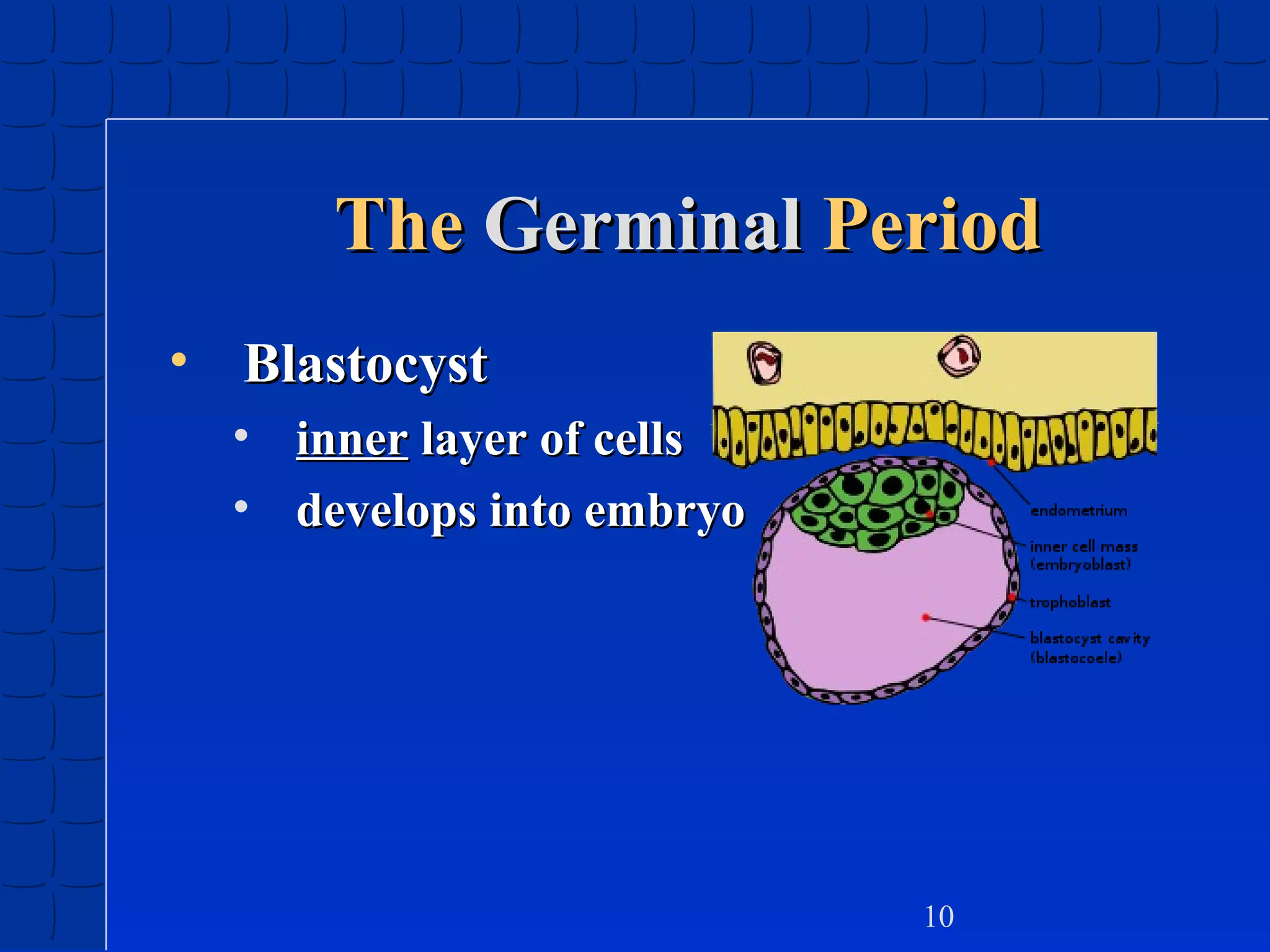
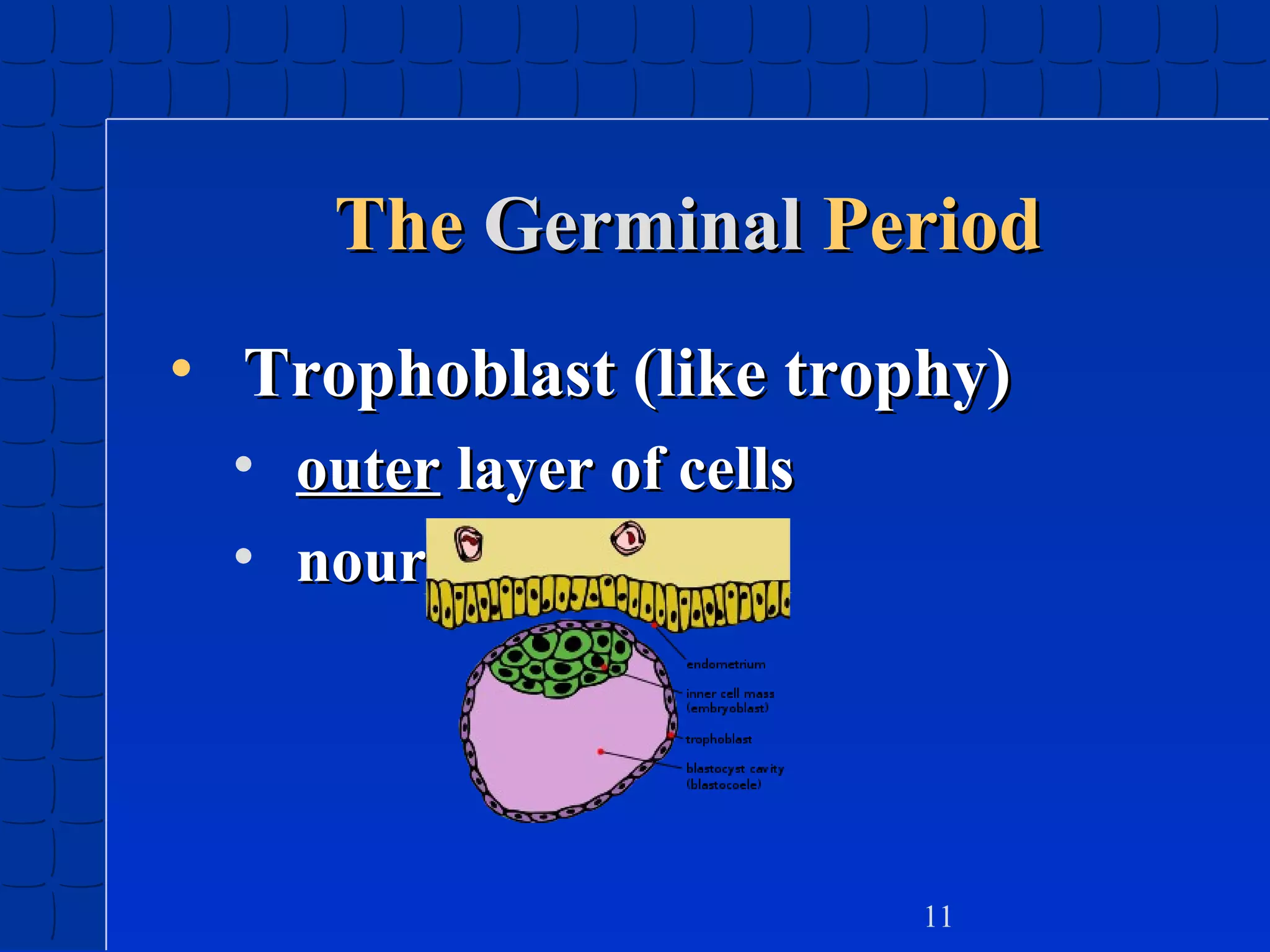
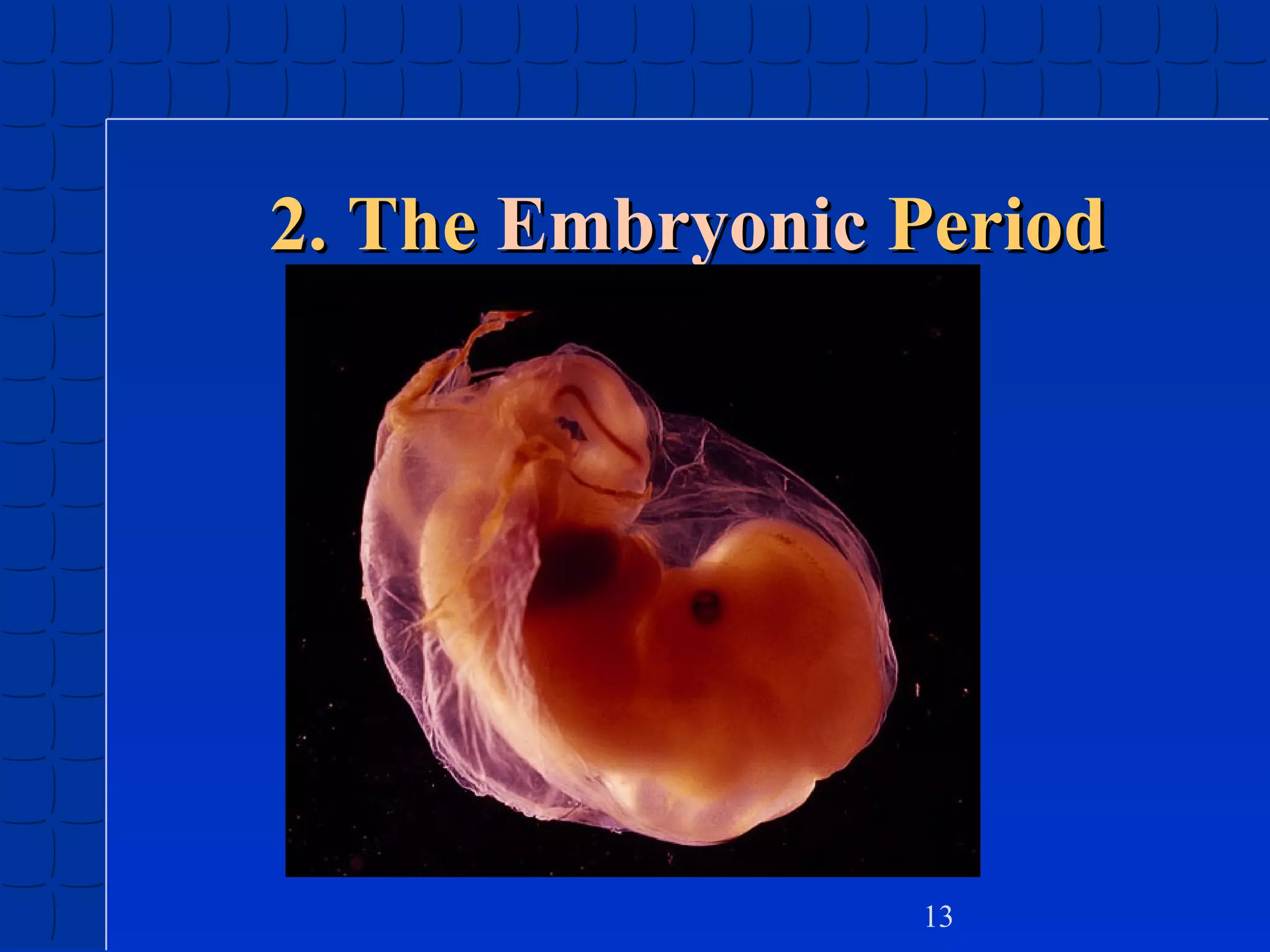
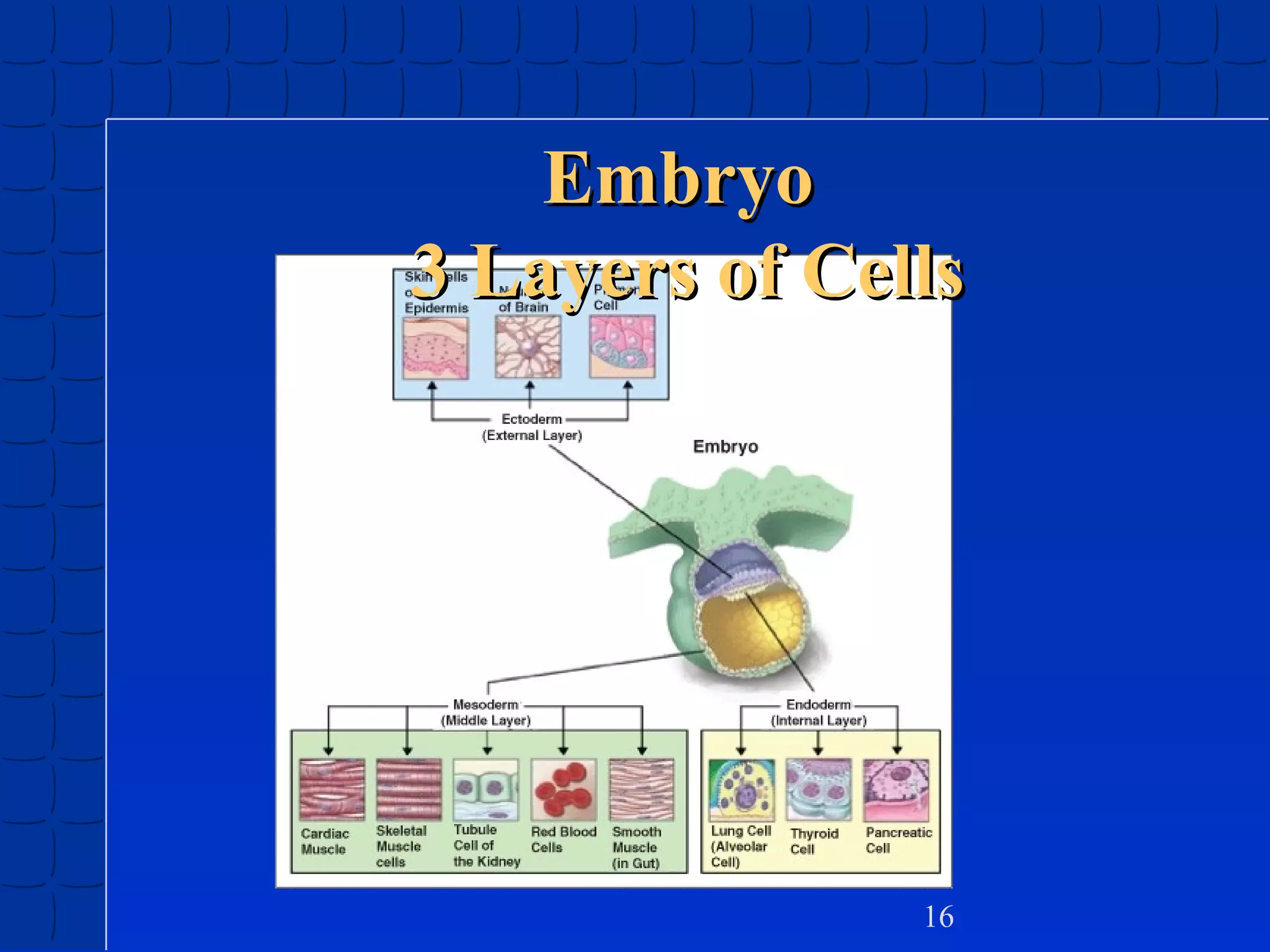
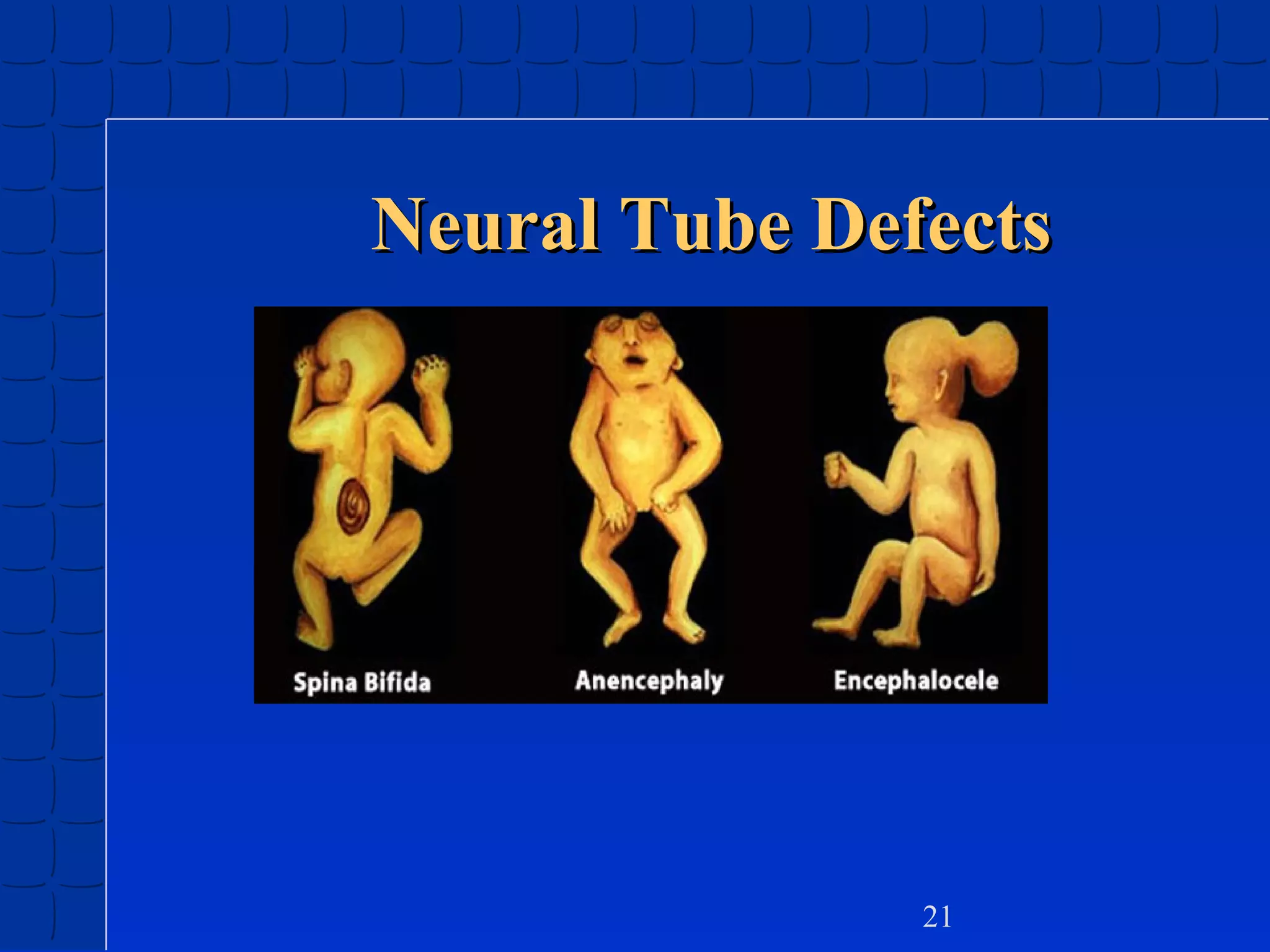
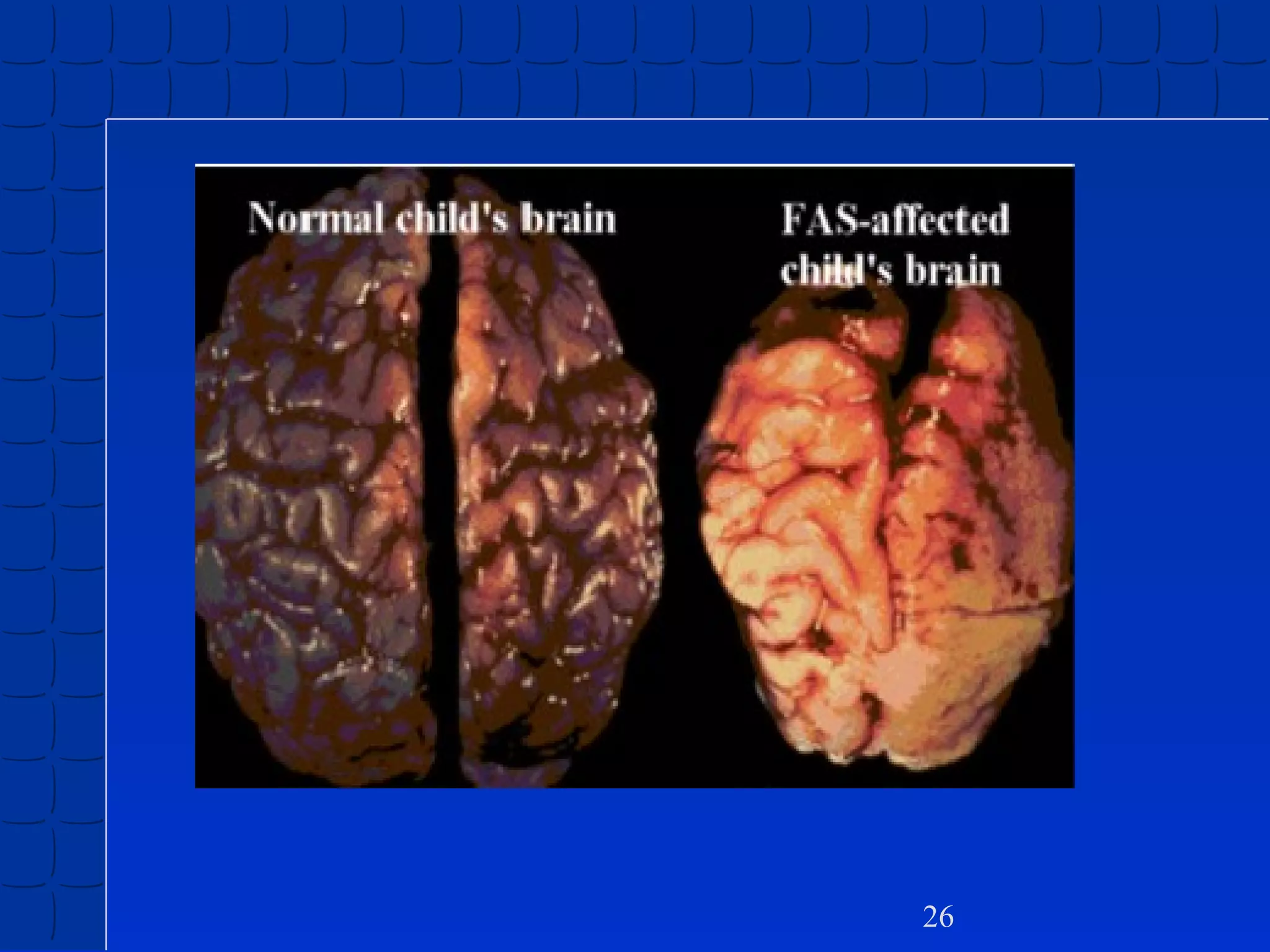
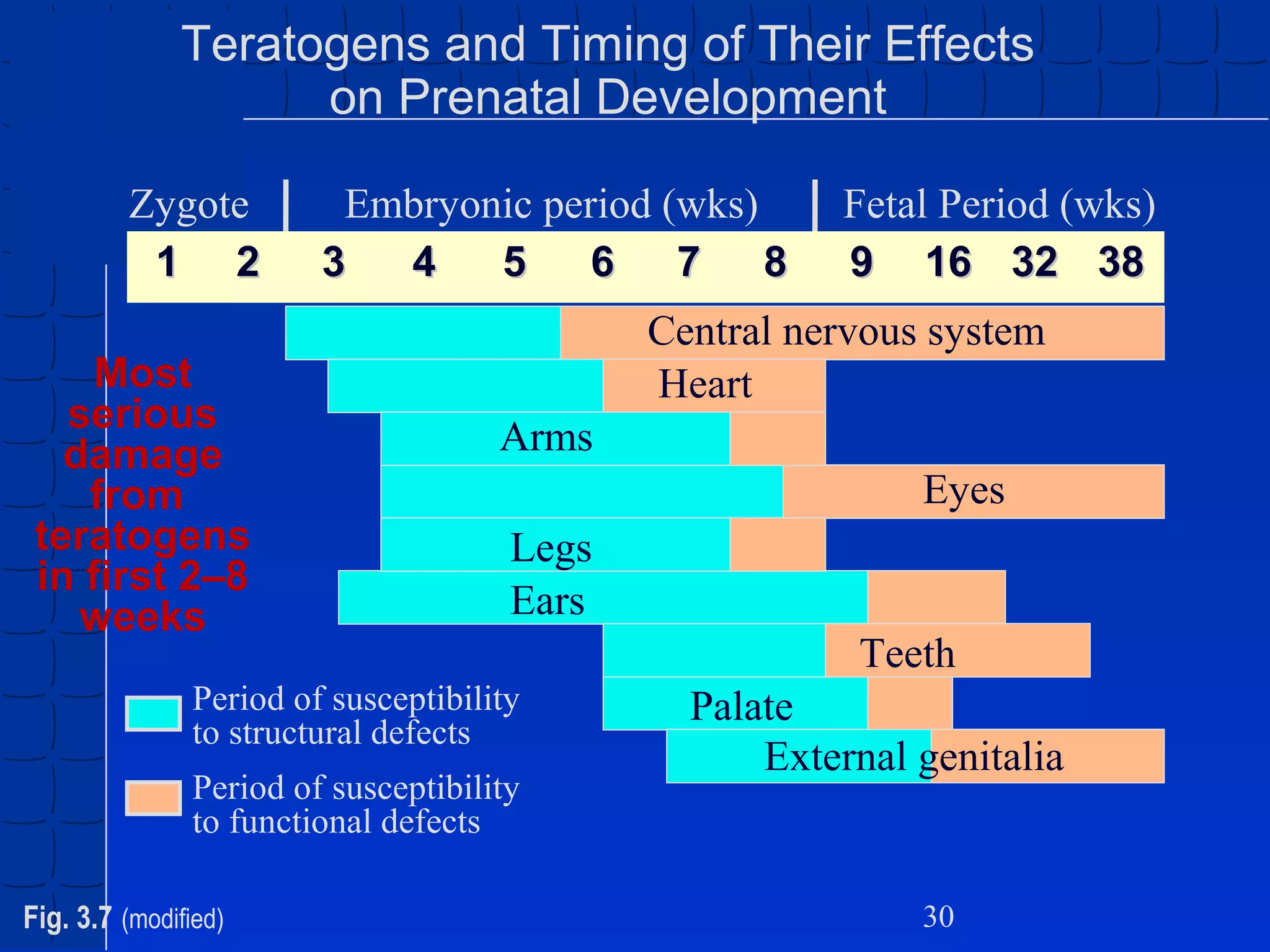
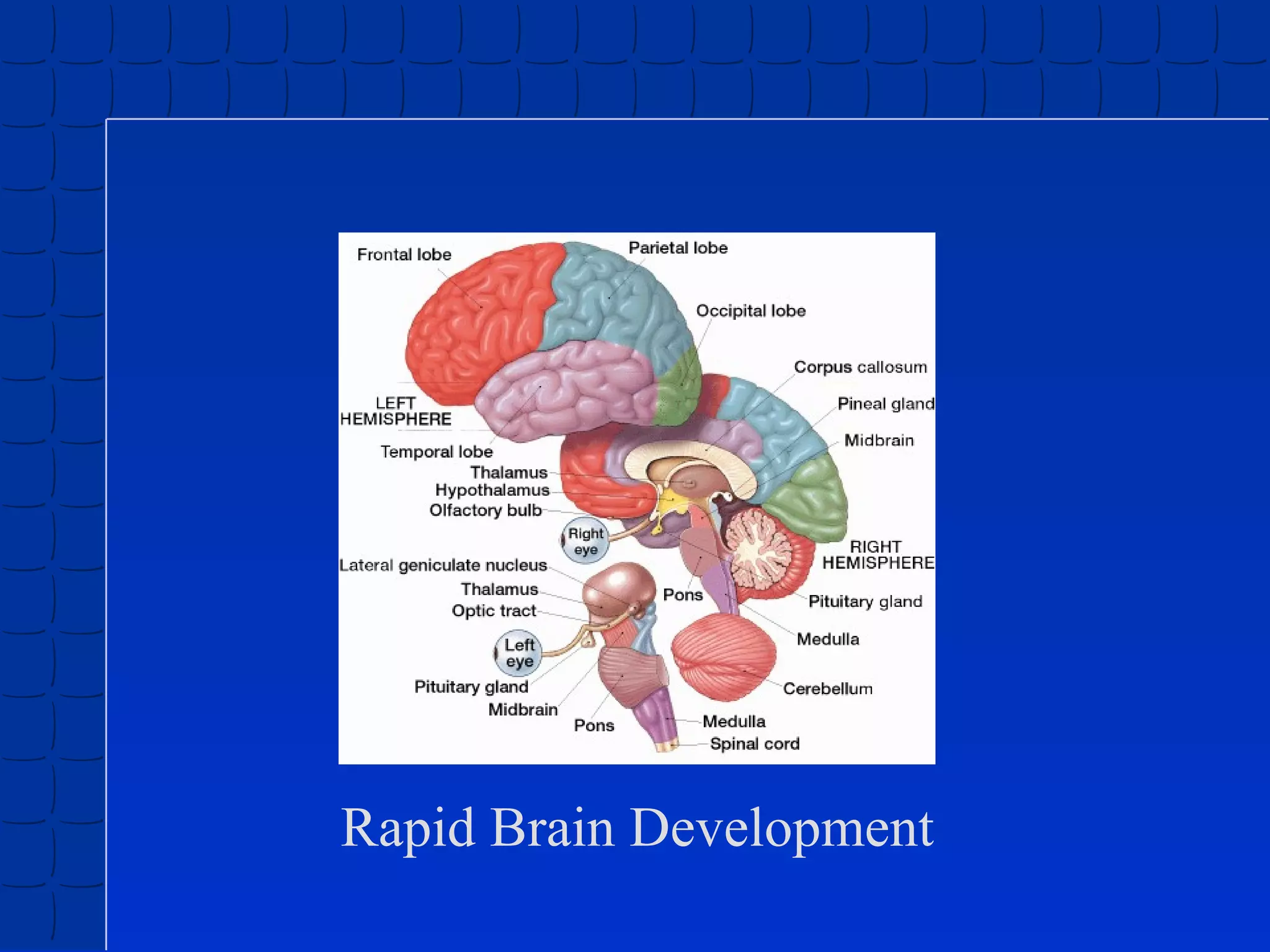
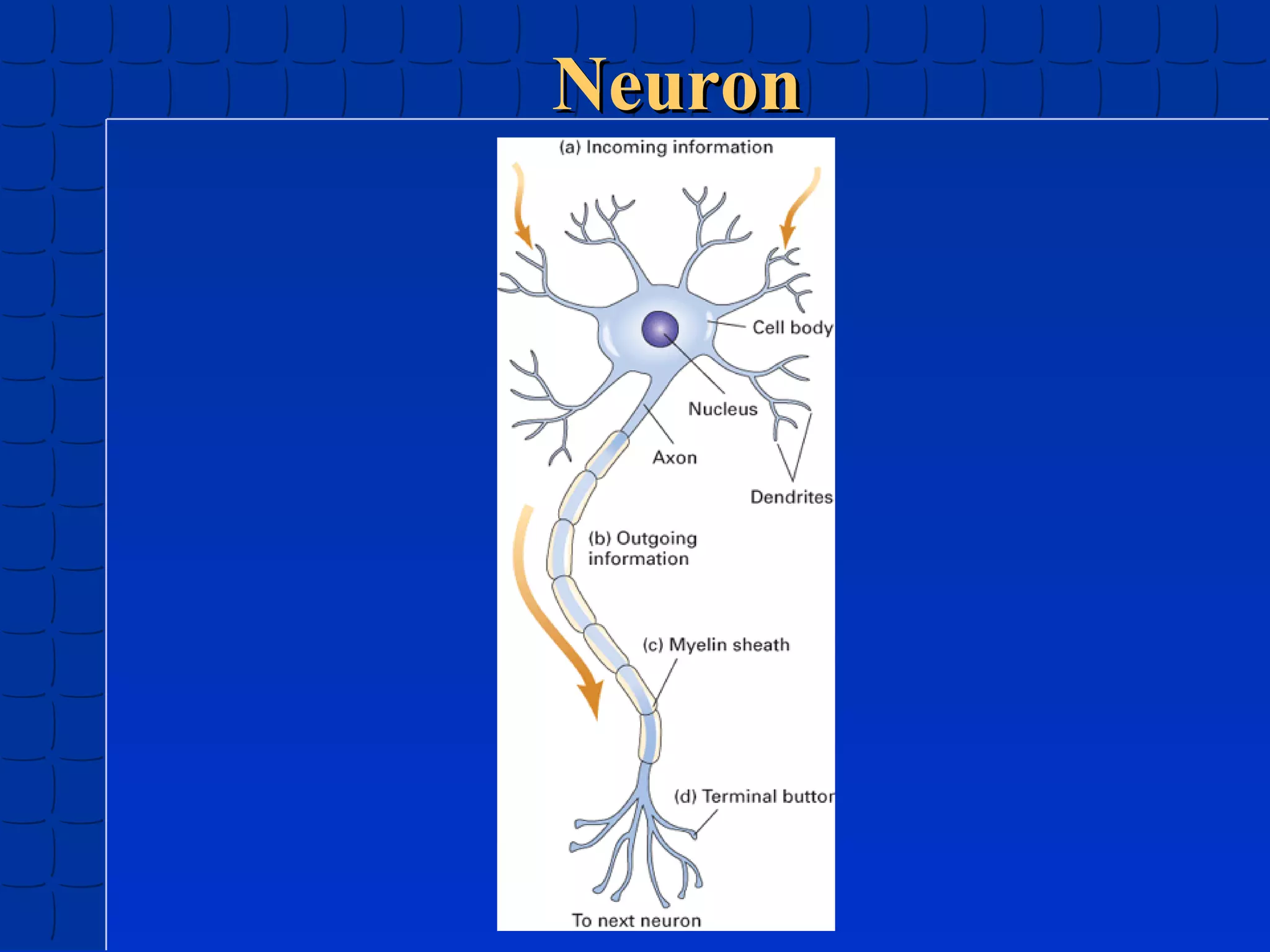
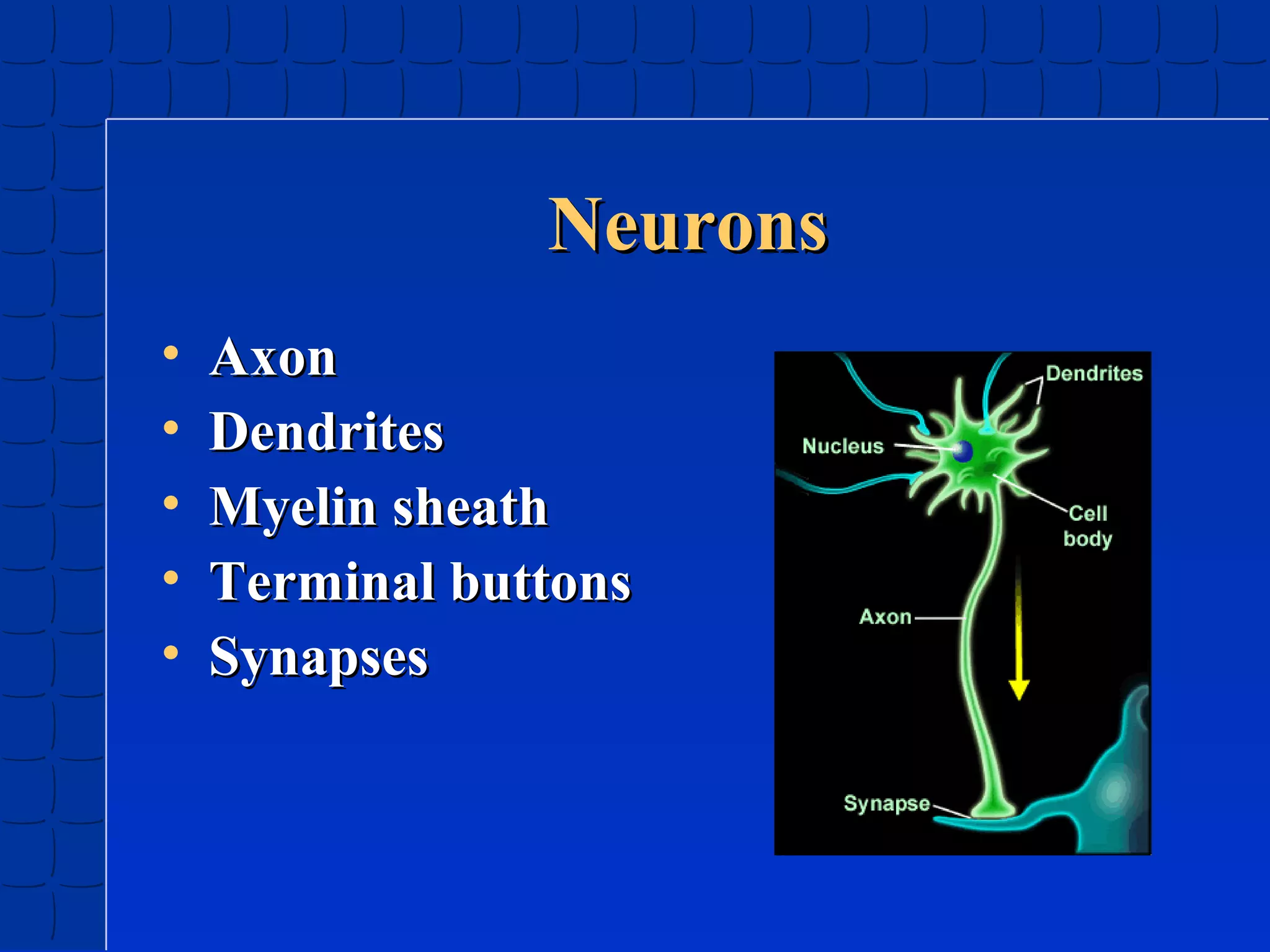
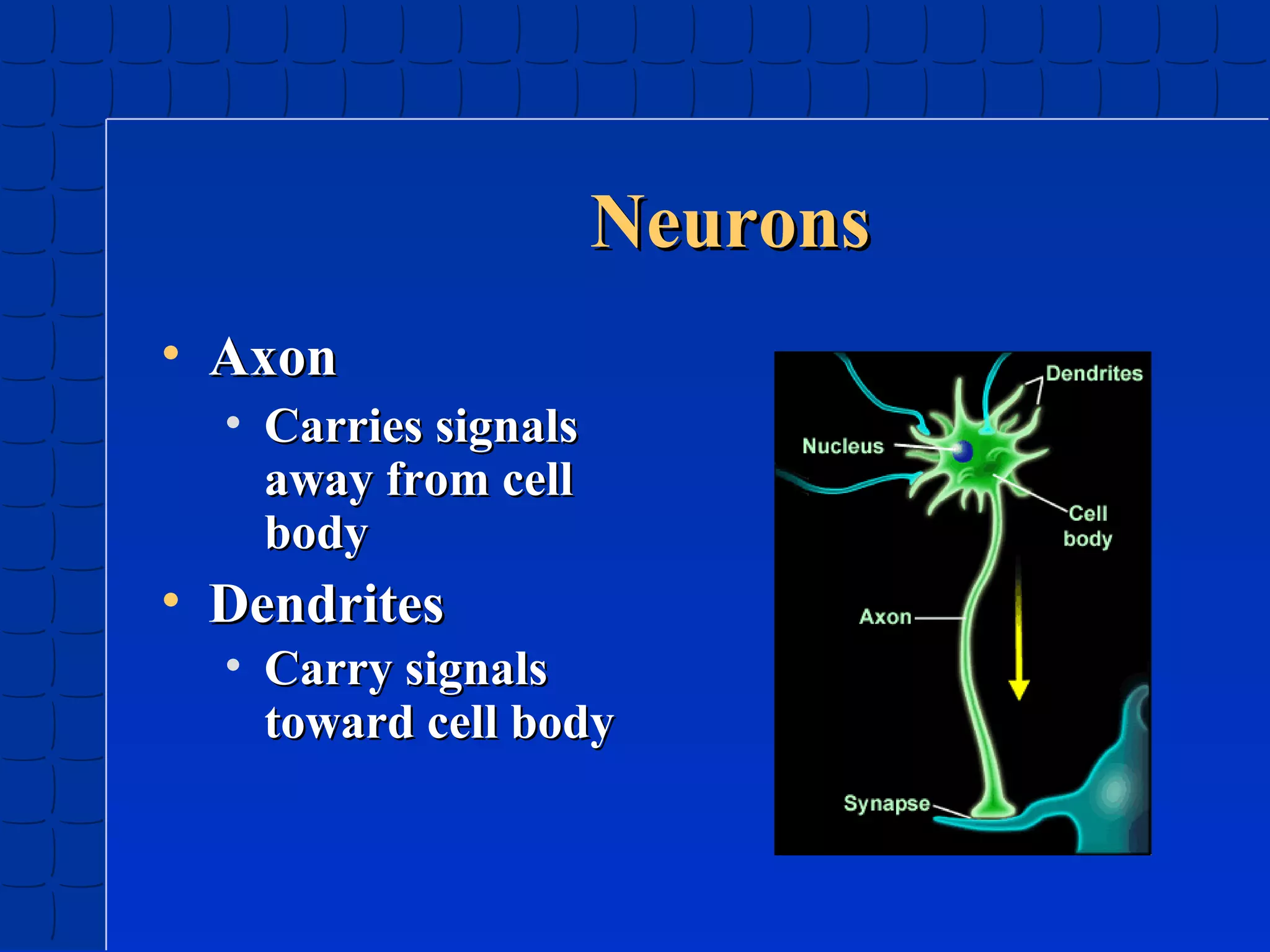
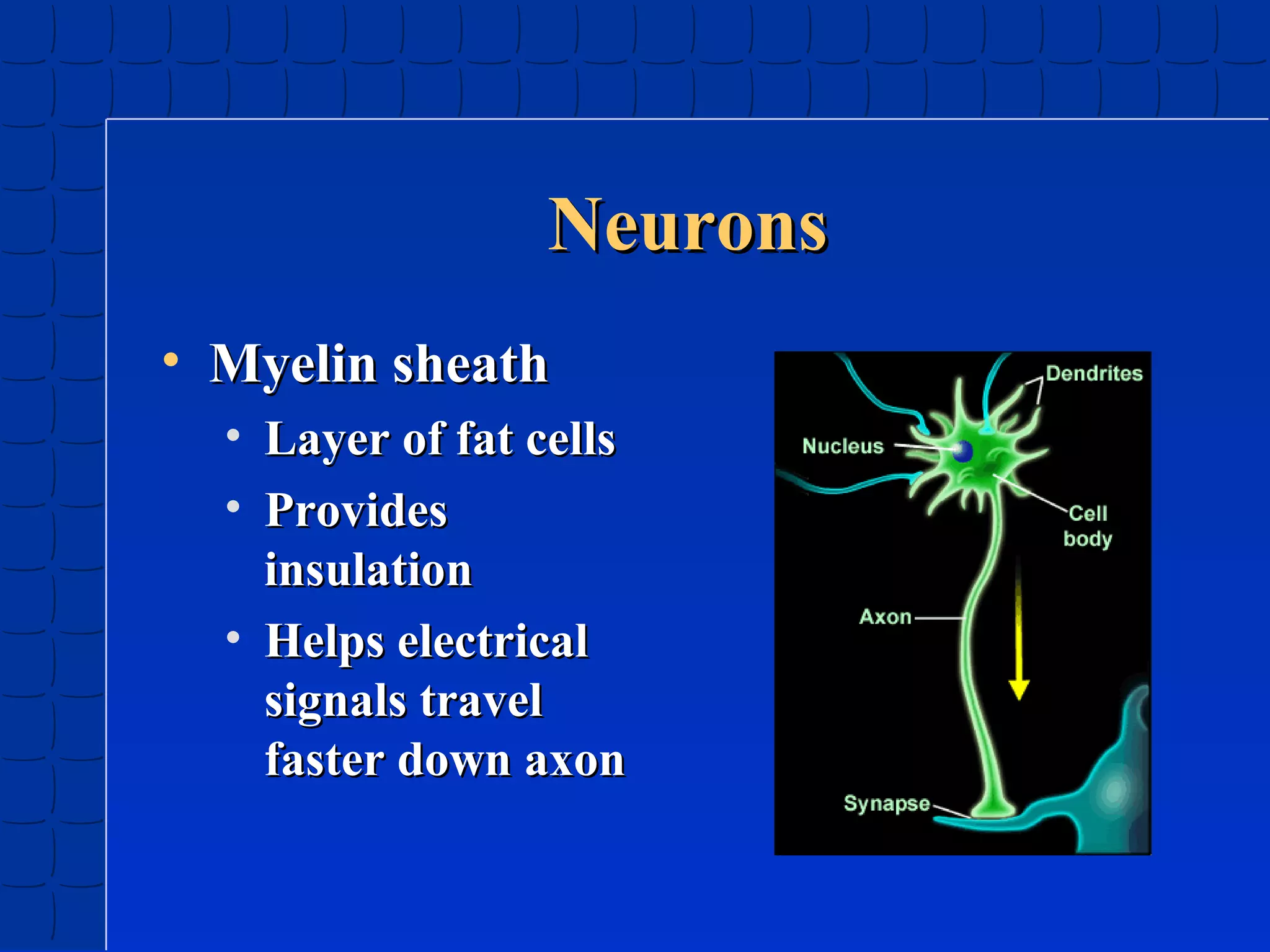
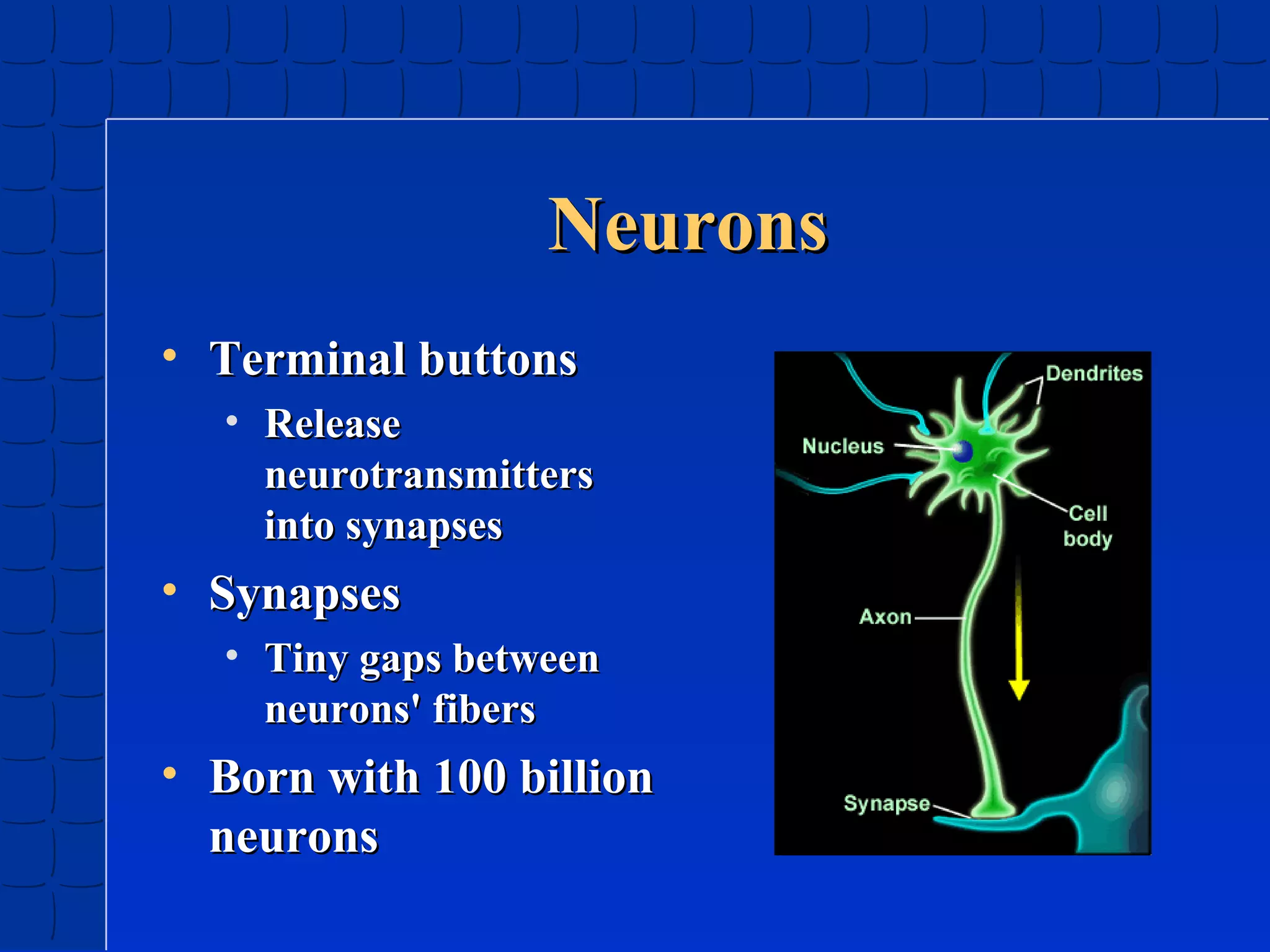
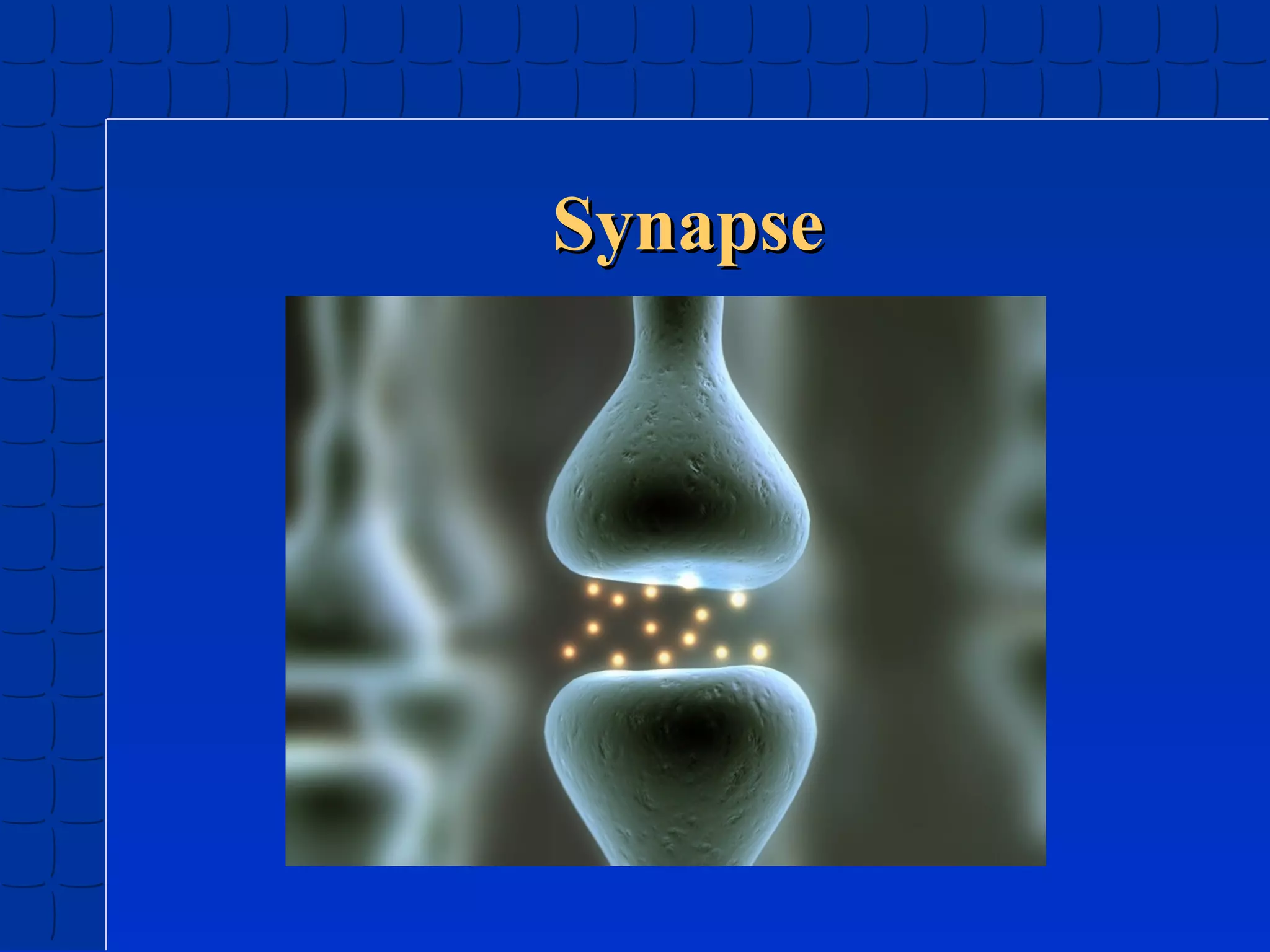
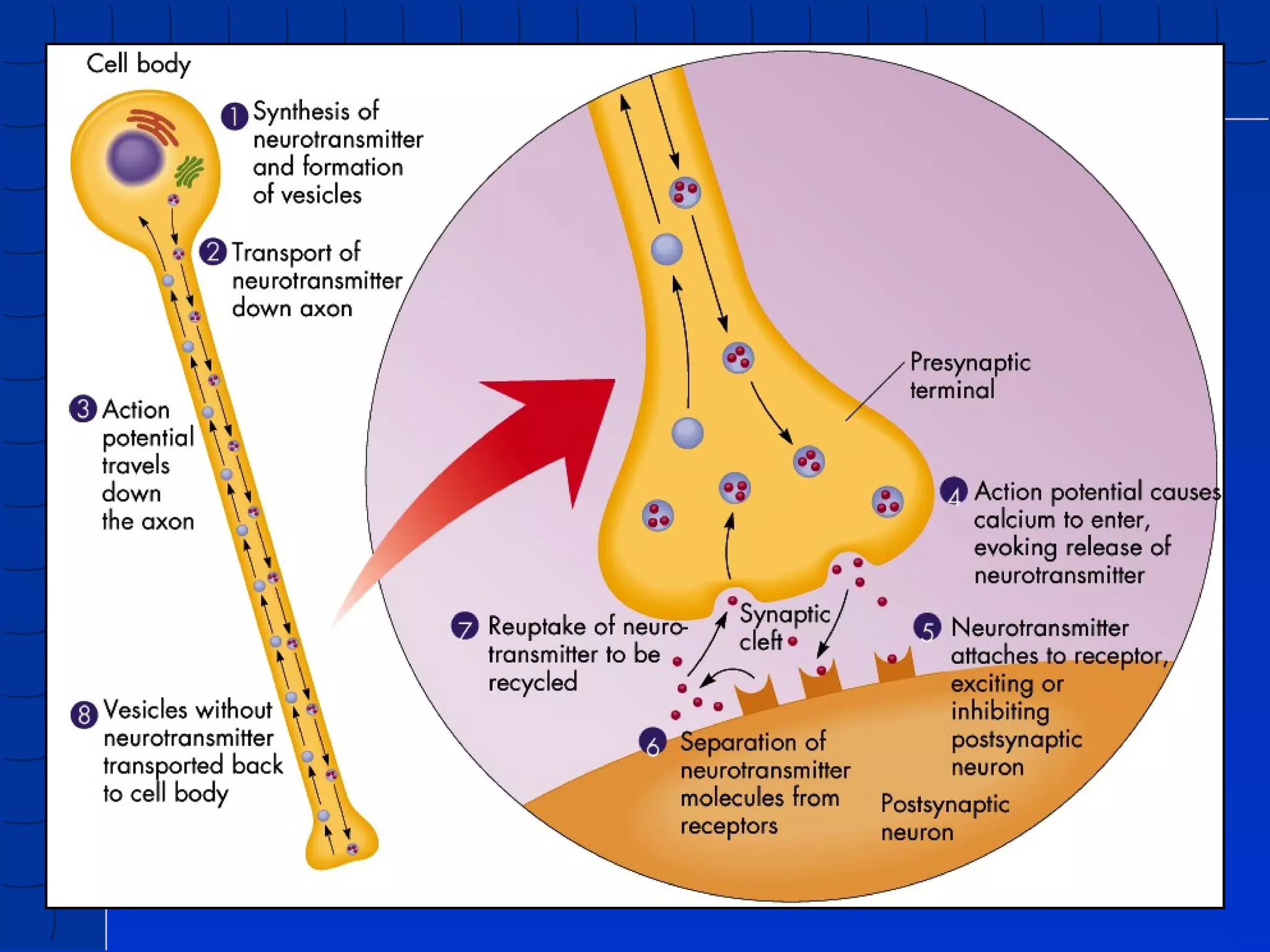
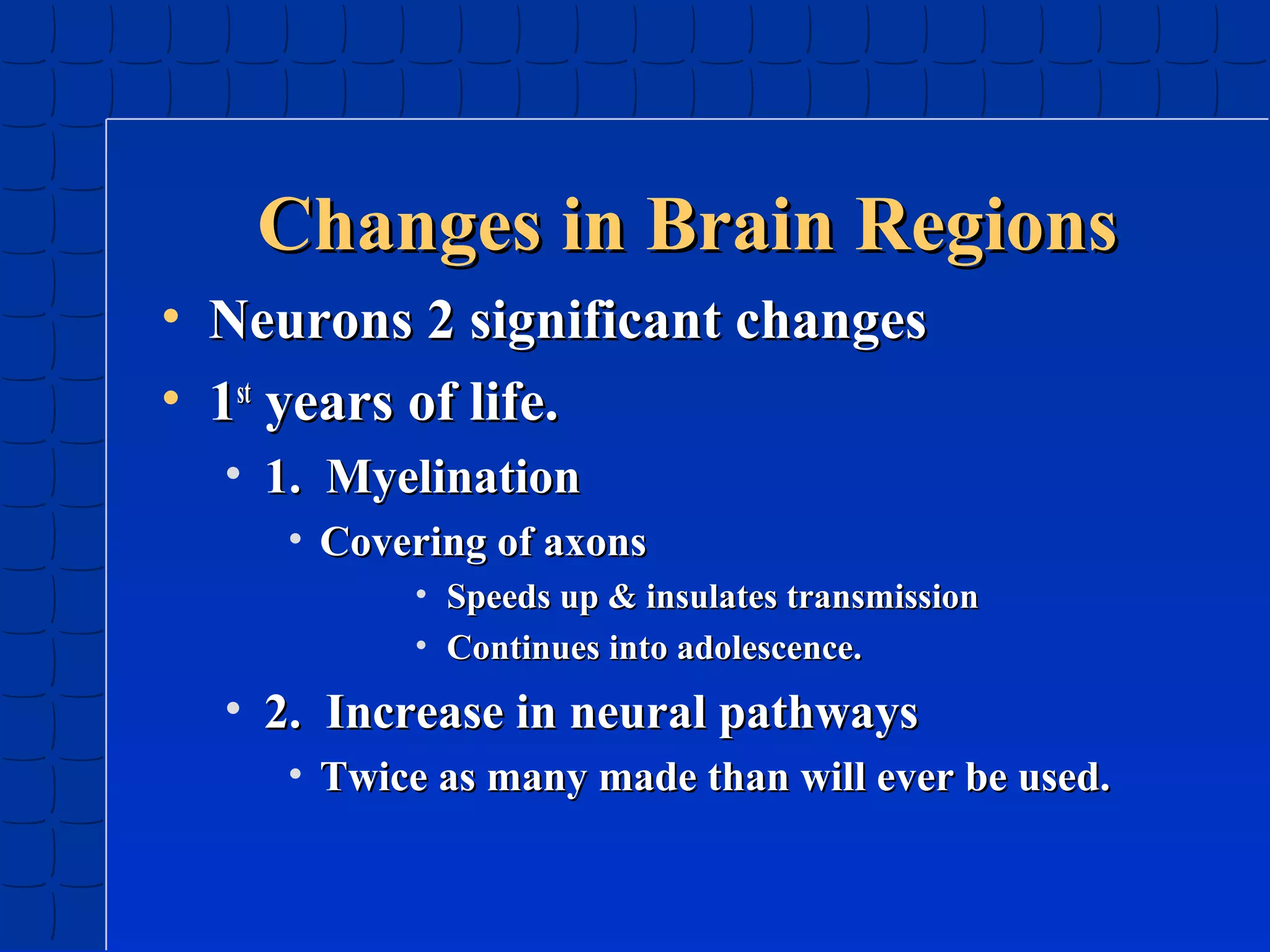
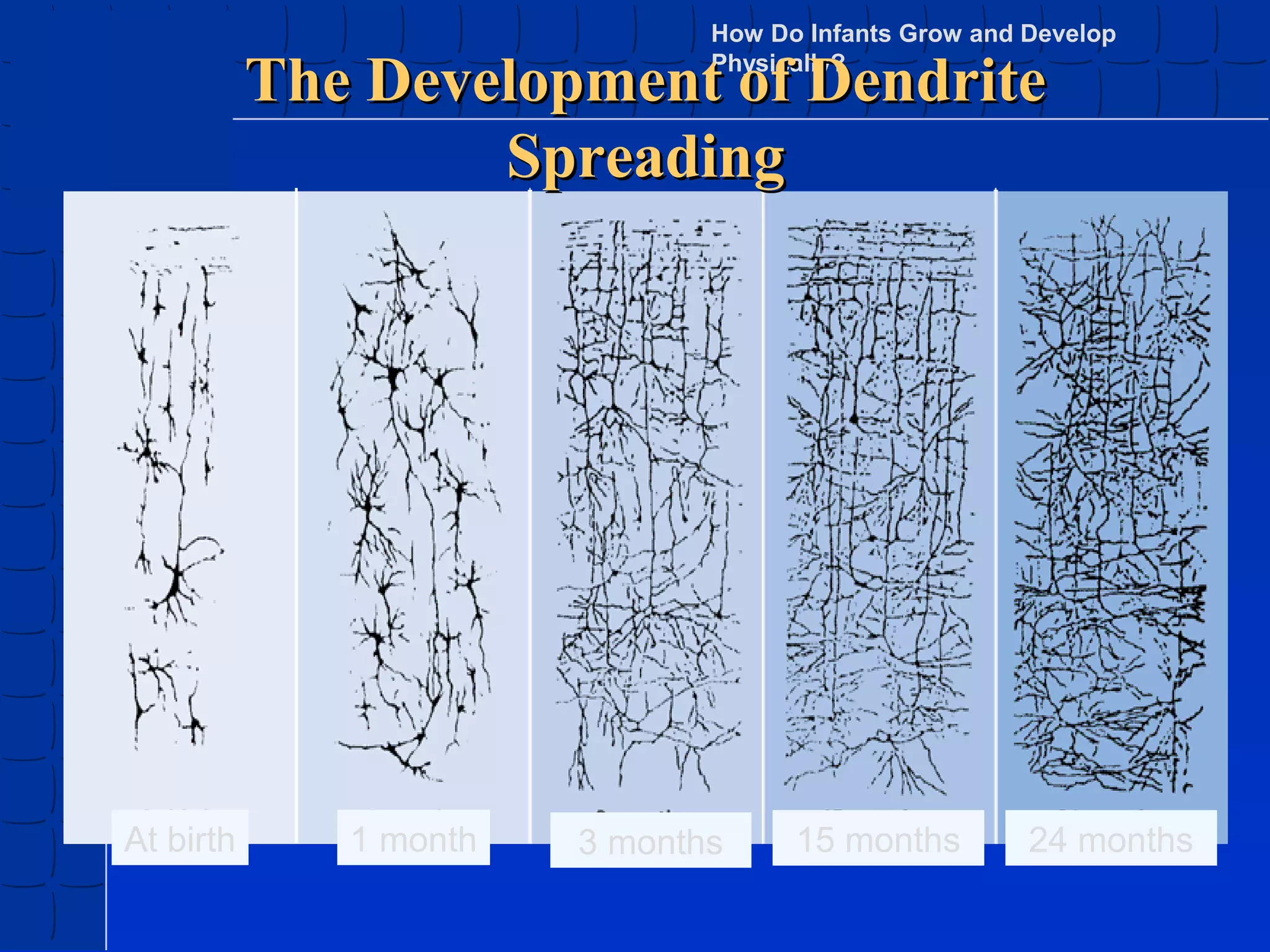
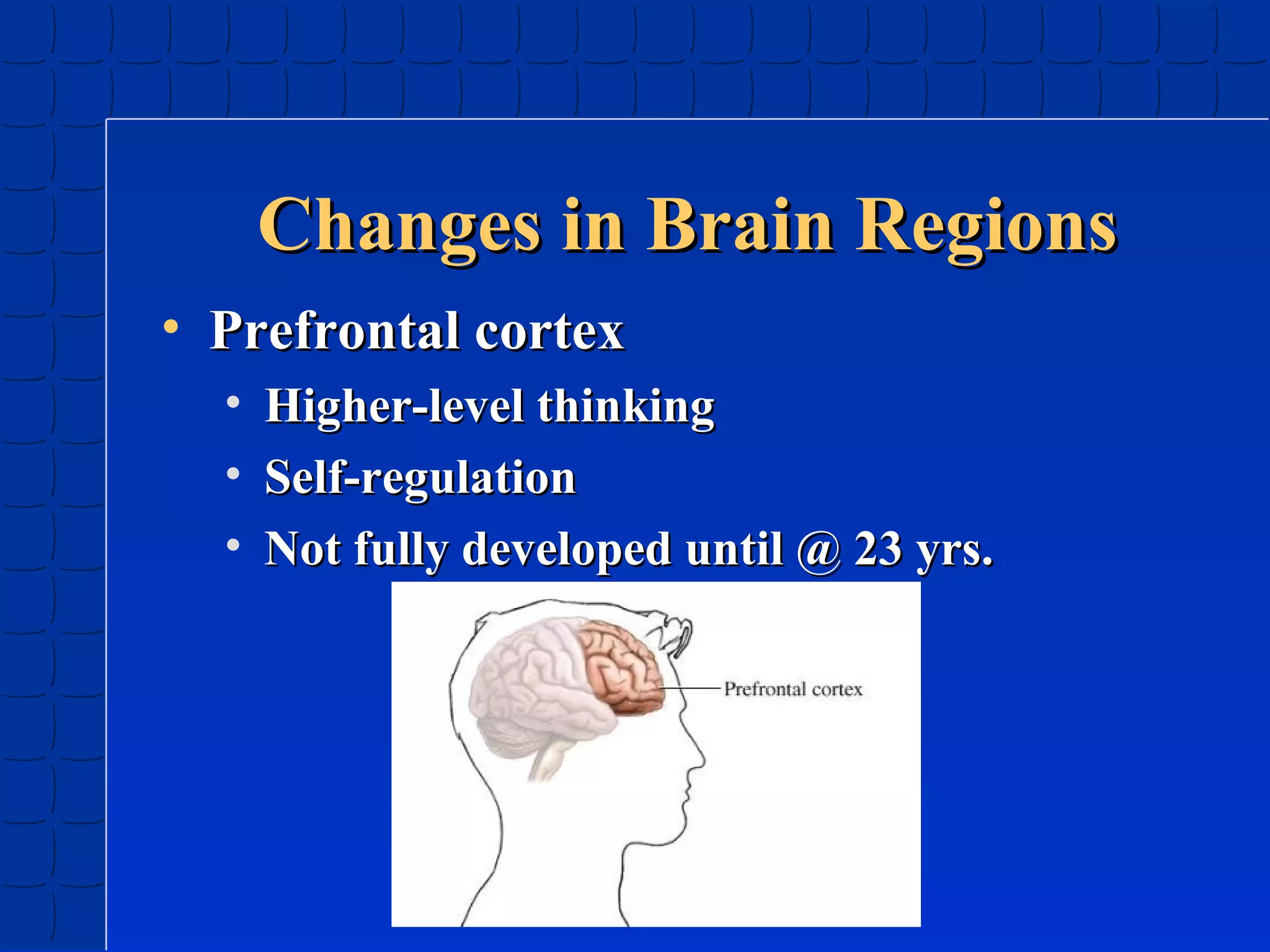
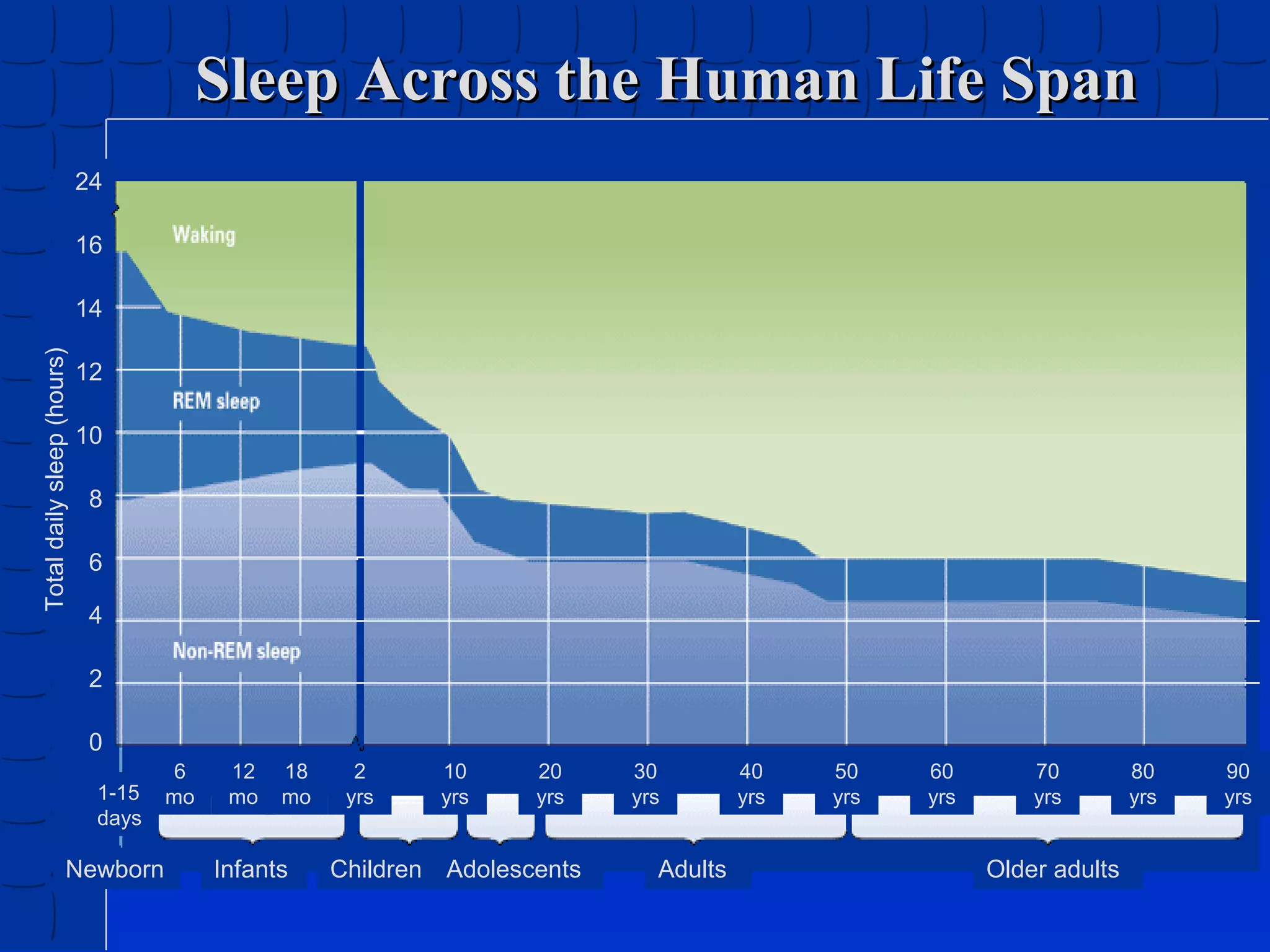
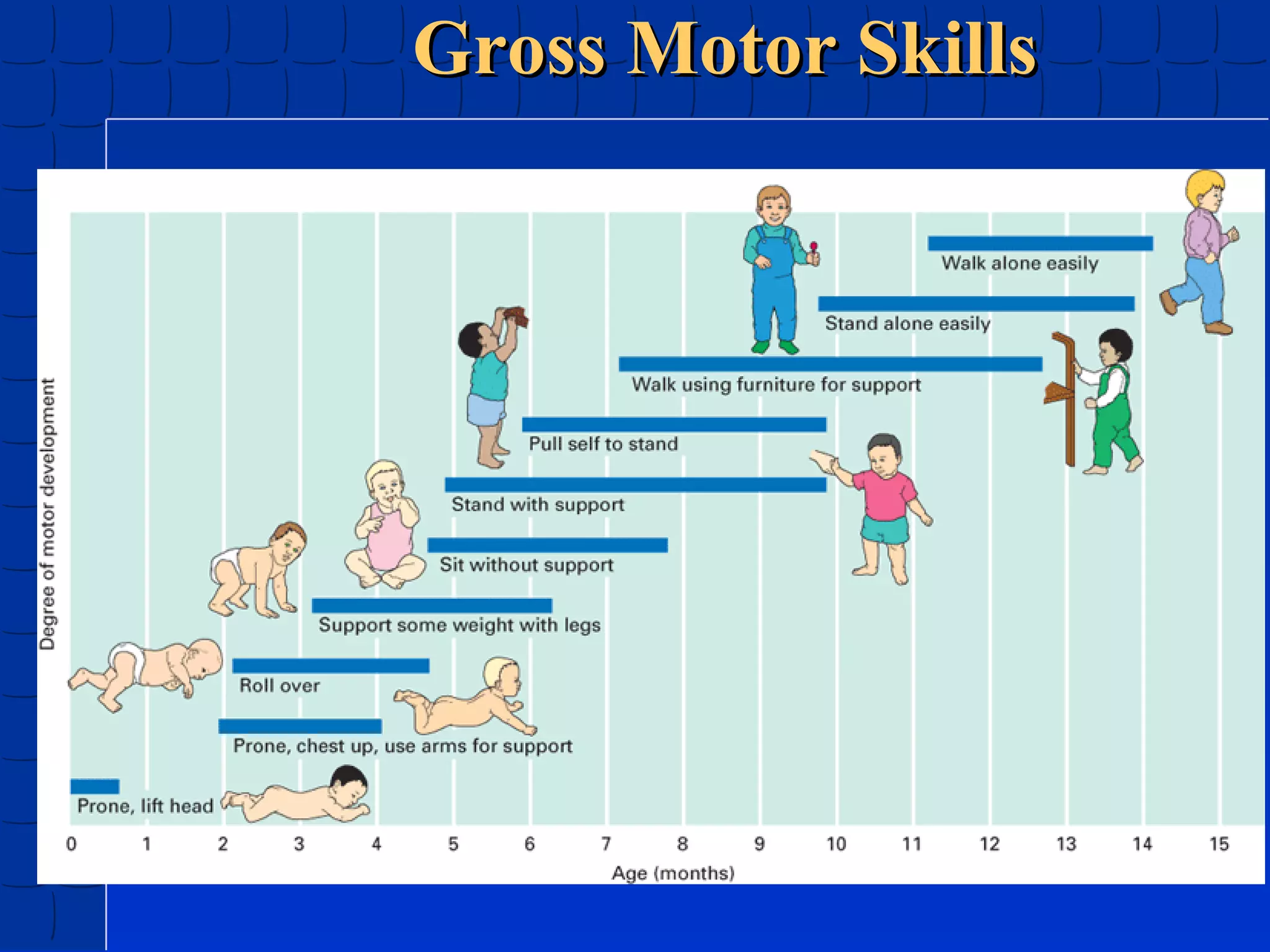
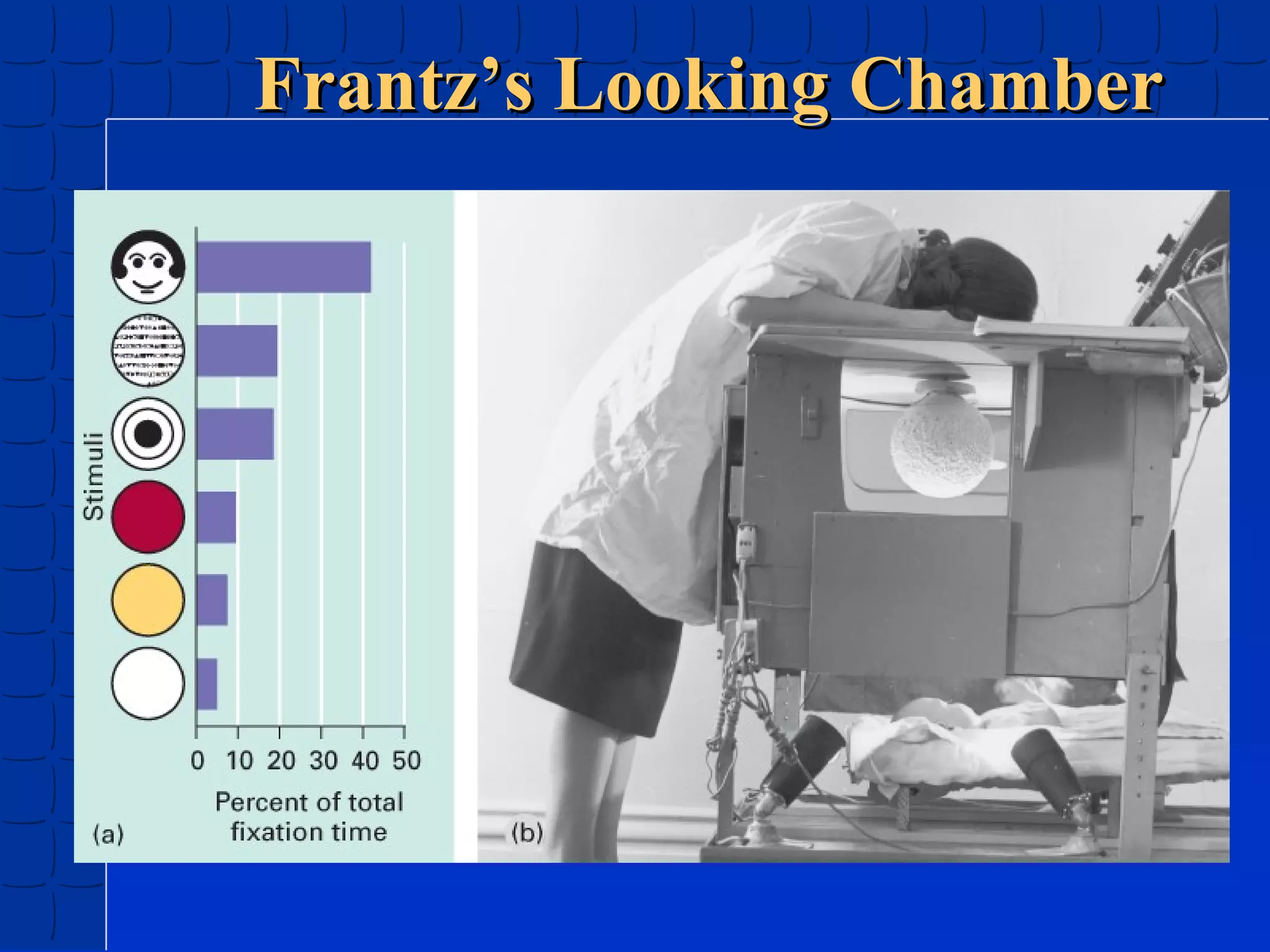
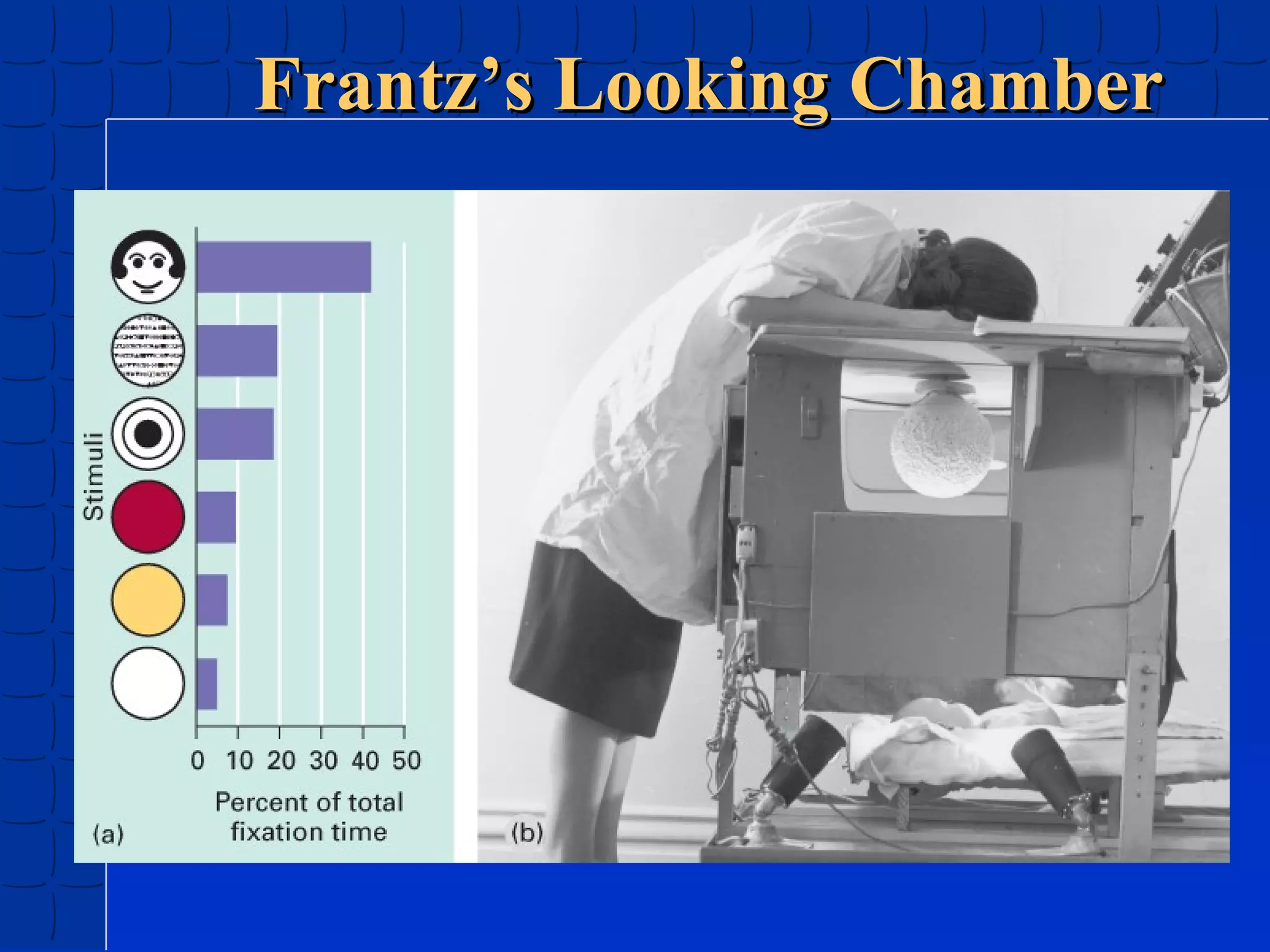
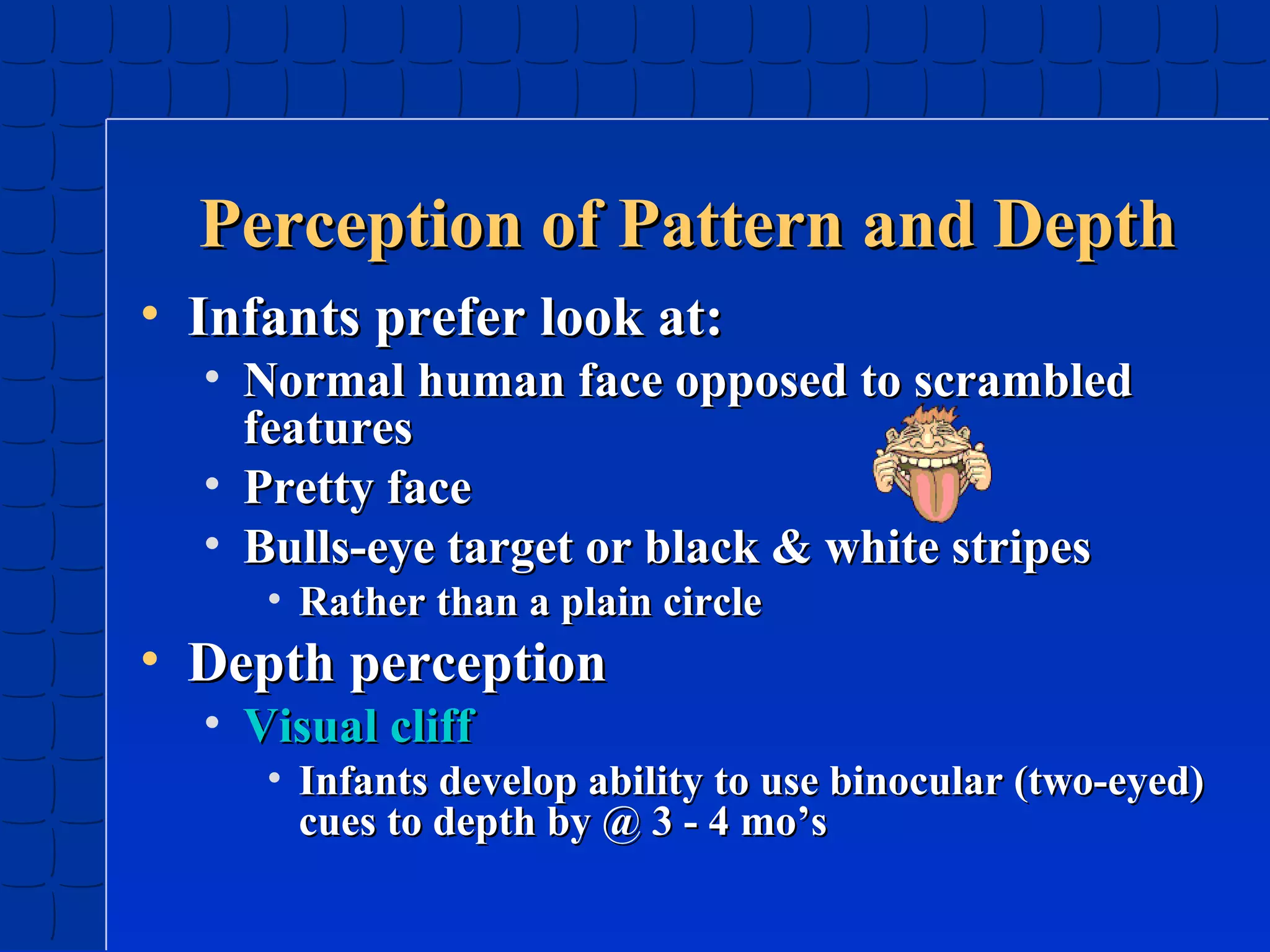
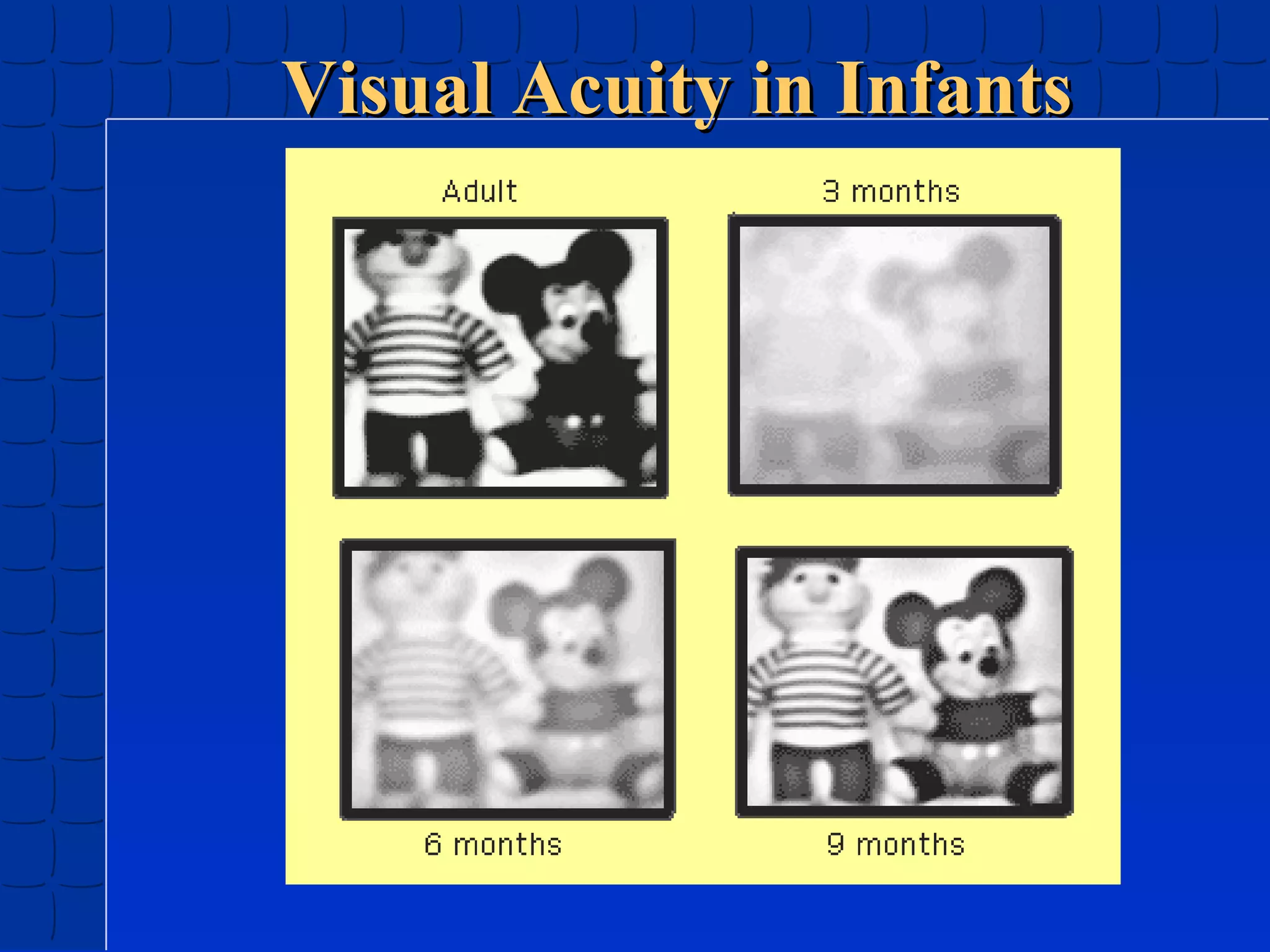
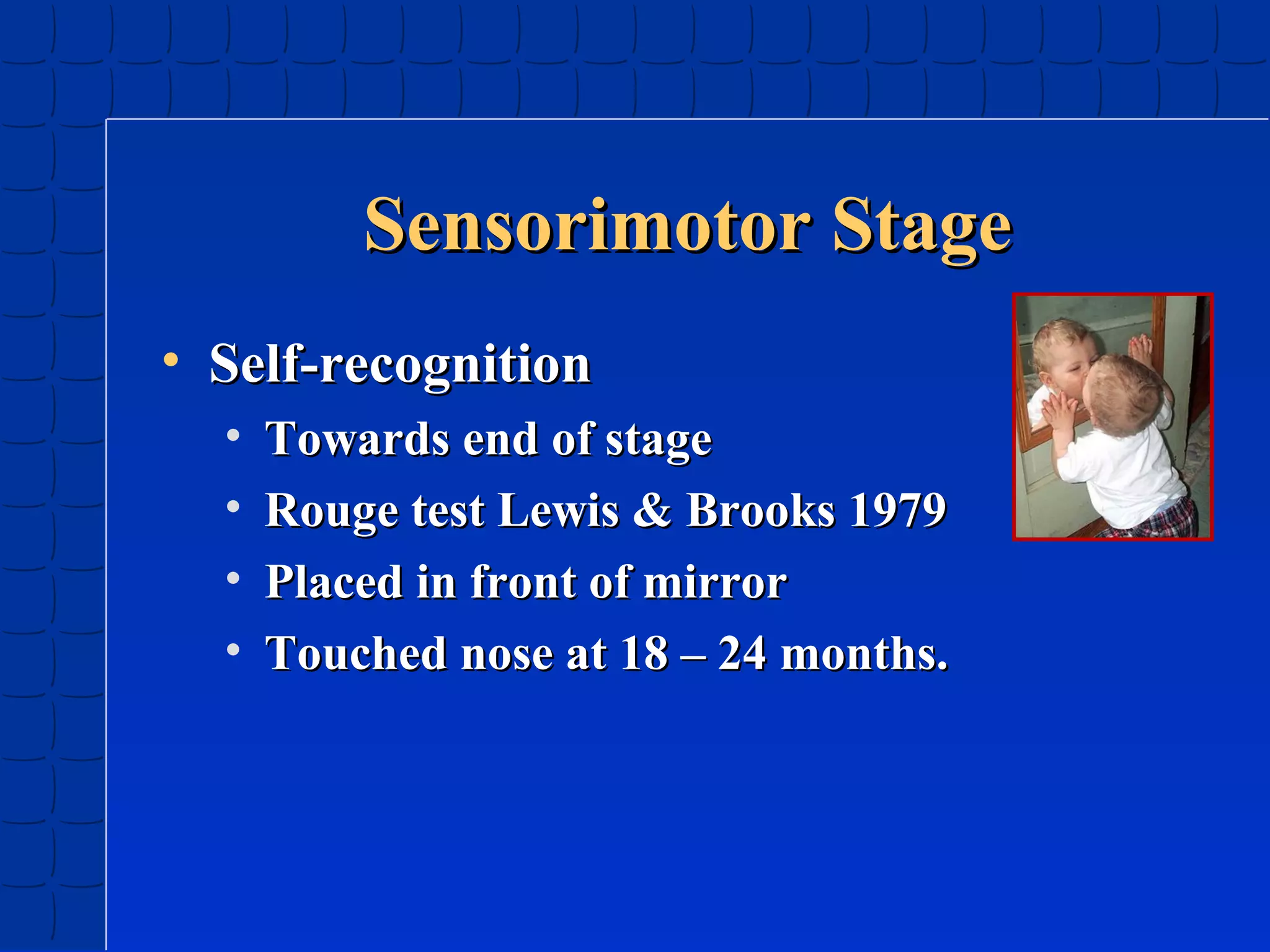
Prenatal development begins at fertilization and continues through birth. Major stages include the germinal period, embryonic period, and fetal period. The embryo develops from three germ layers into all body systems. The brain develops rapidly during prenatal development and early childhood. Infants progress through gross and fine motor skill milestones. Language develops from crying and cooing to first words and combining words. Cognitive development is characterized by the sensorimotor stage from birth to age 2.