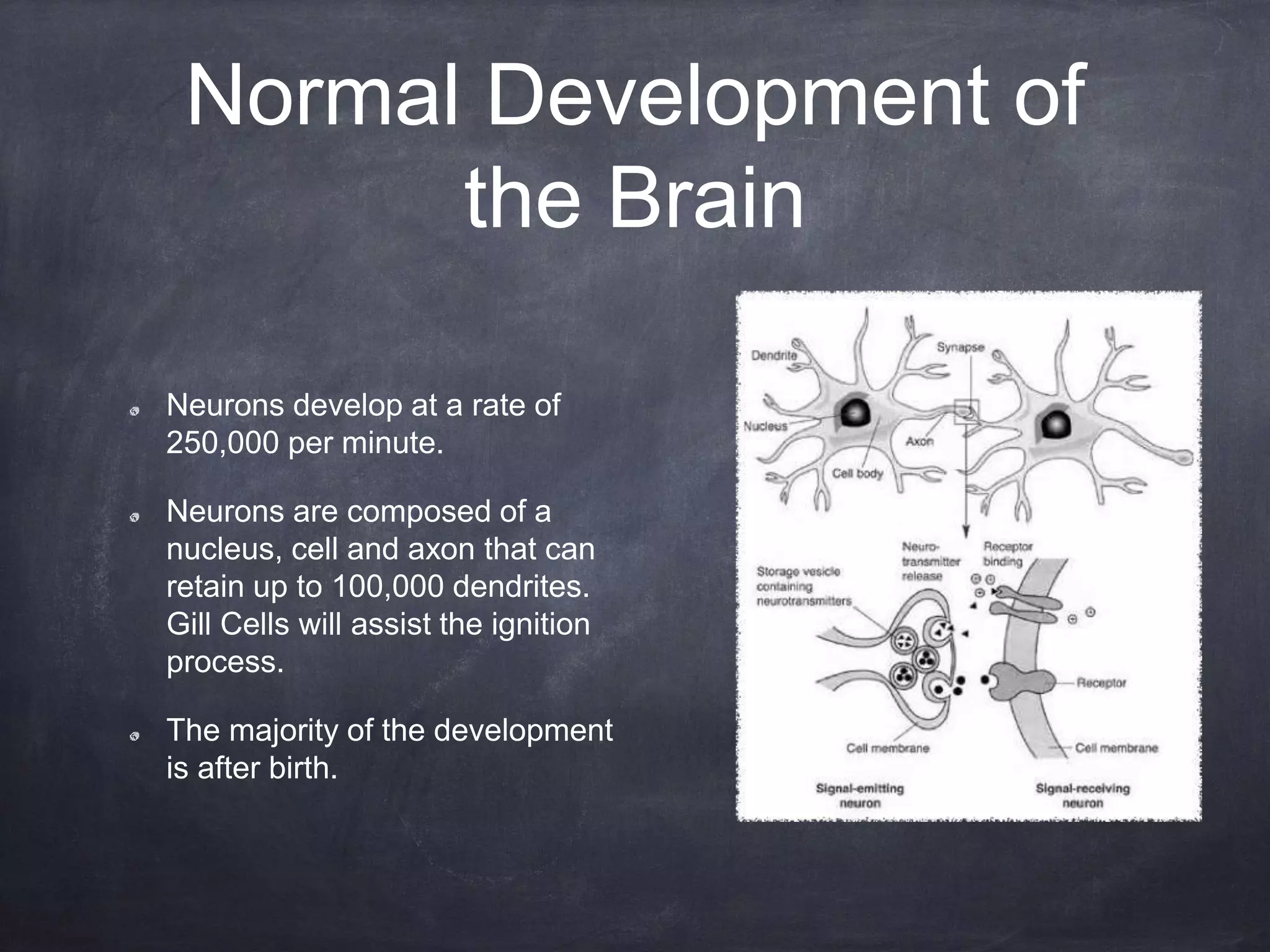
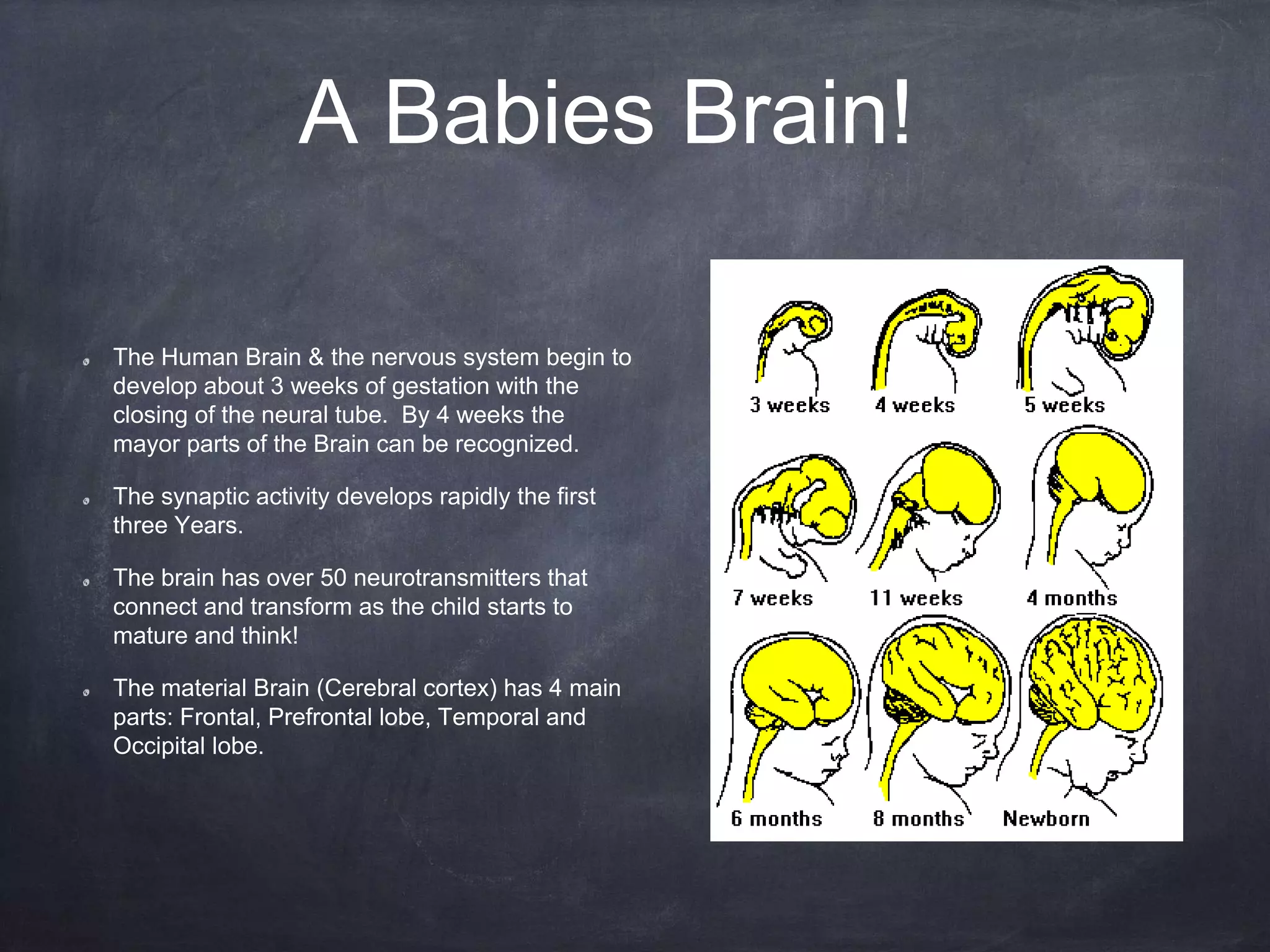
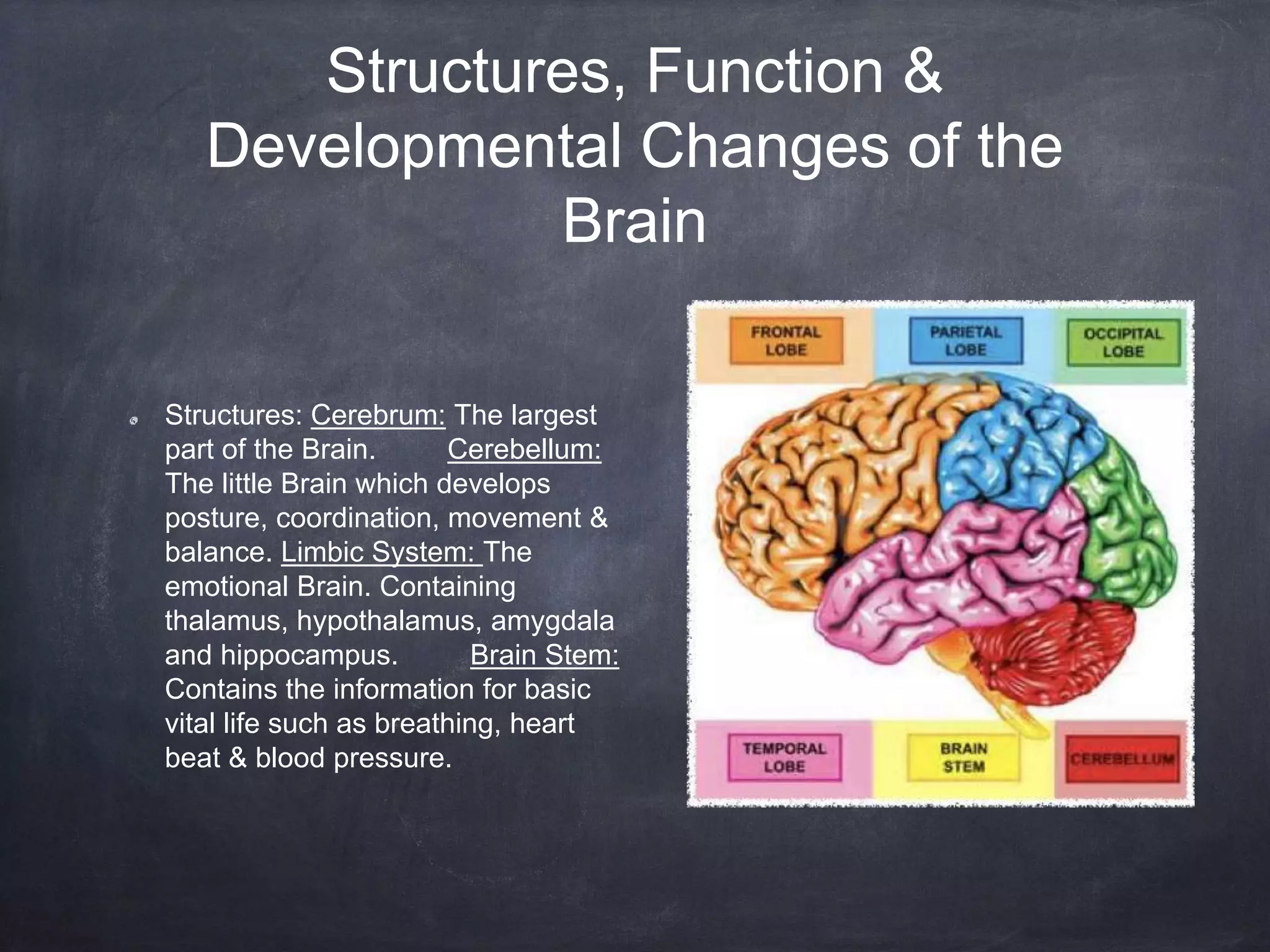
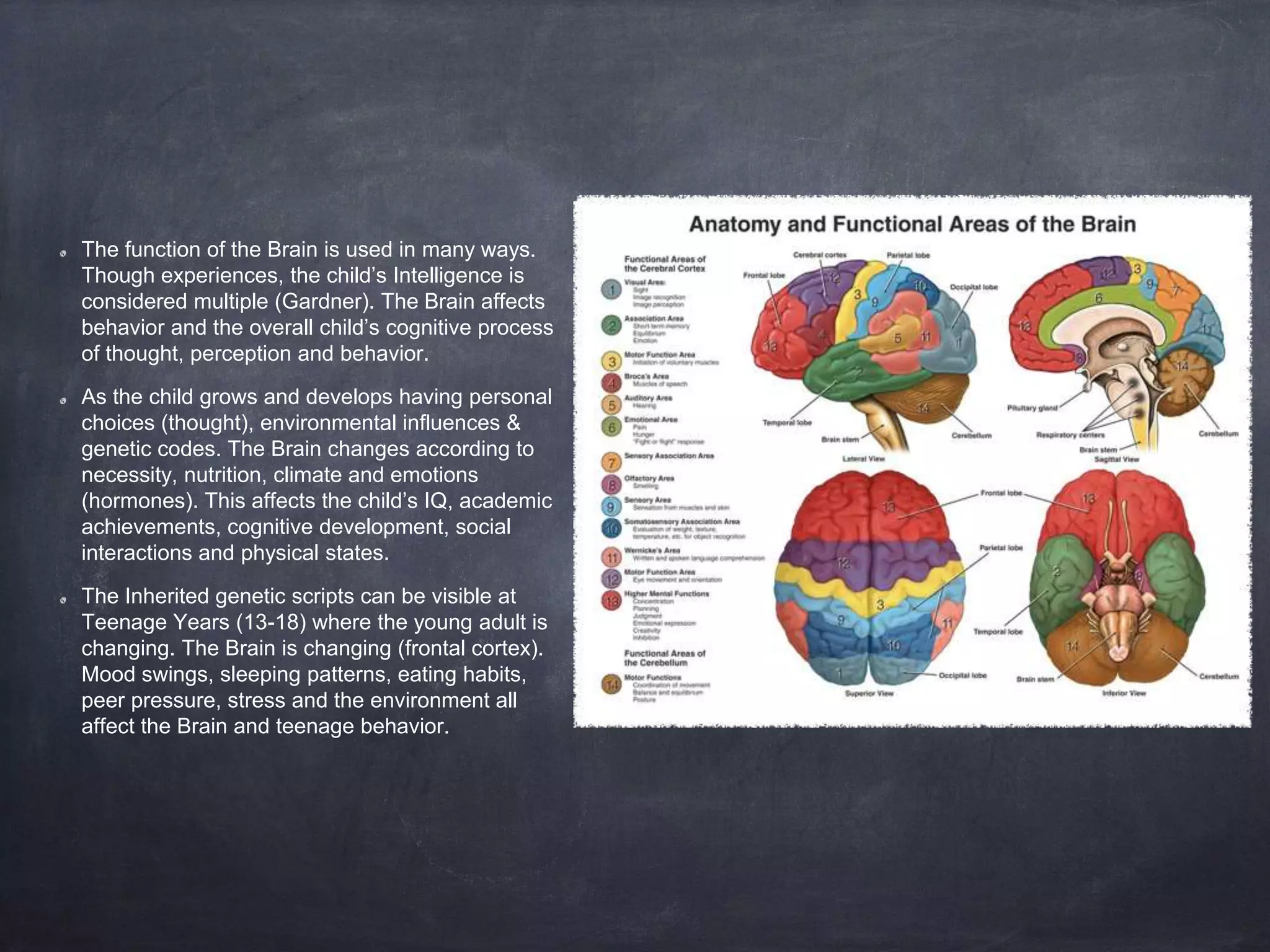
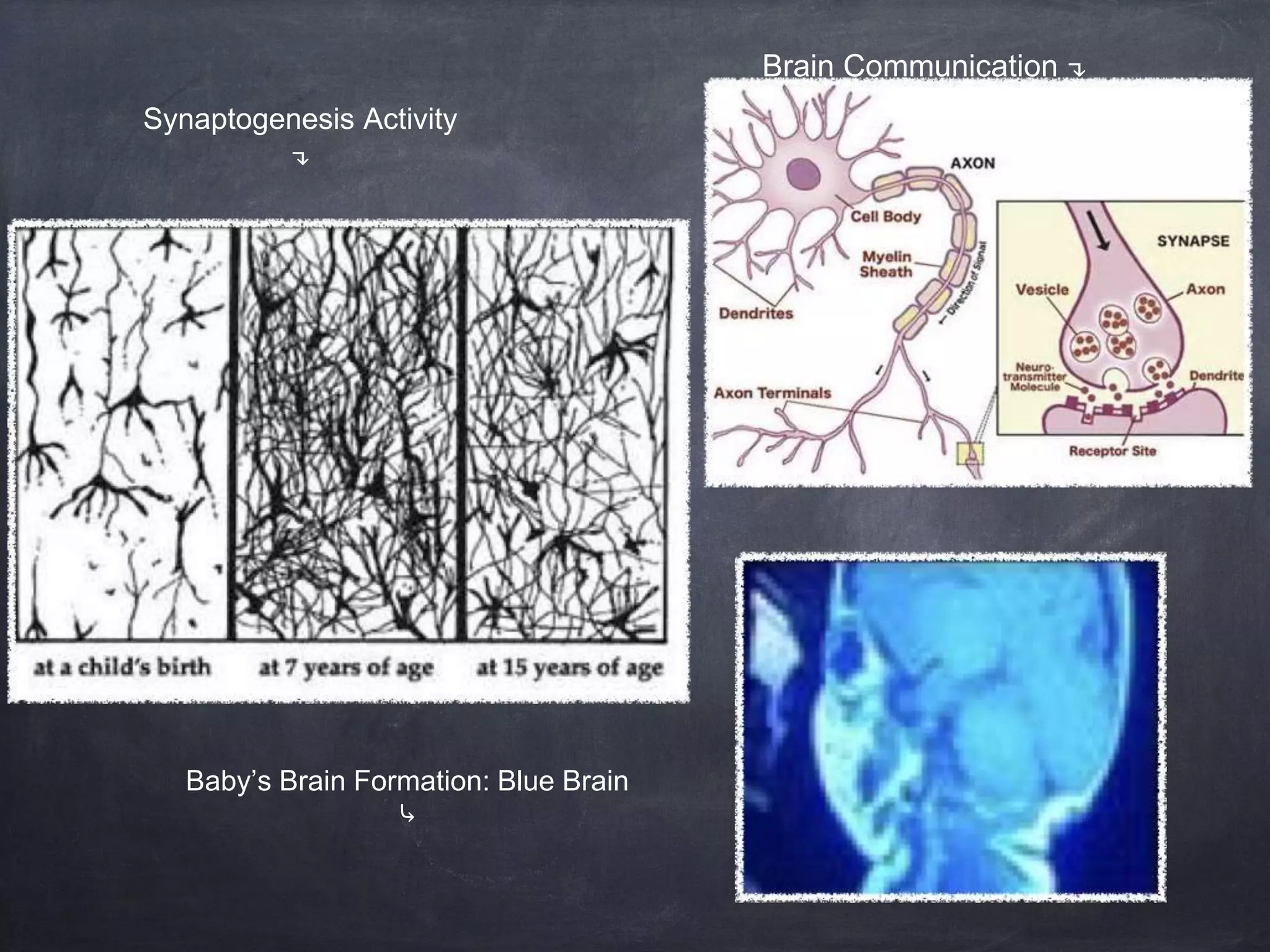
The brain develops rapidly before and after birth, with neurons developing at 250,000 per minute before birth and synapses forming most rapidly in the first three years of life. The brain's structures such as the cerebrum, cerebellum, and limbic system develop specialized functions. Teratogens like drugs, alcohol, infections and environmental toxins can harm the developing brain before birth and influence later cognitive, social and physical development.