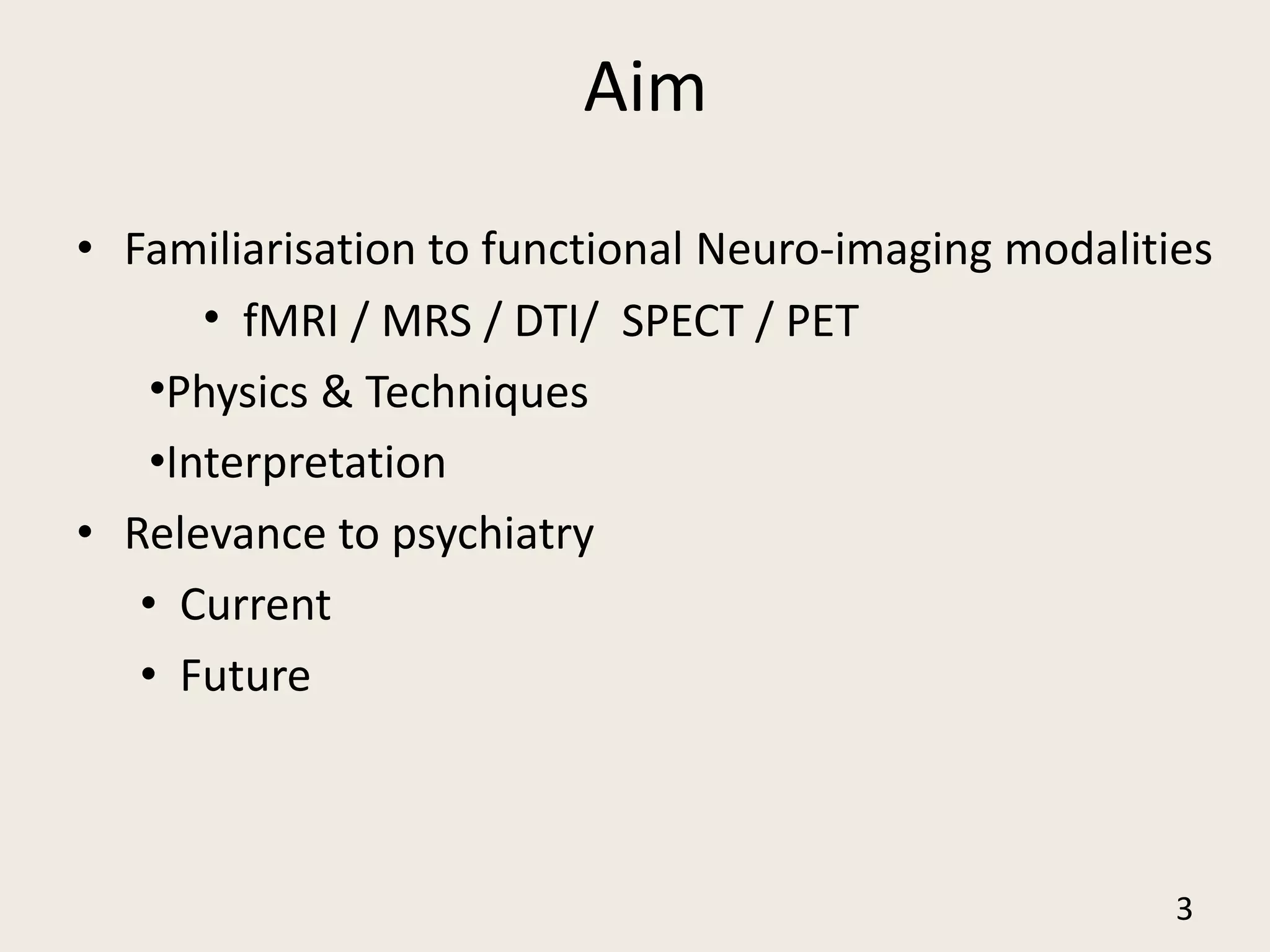
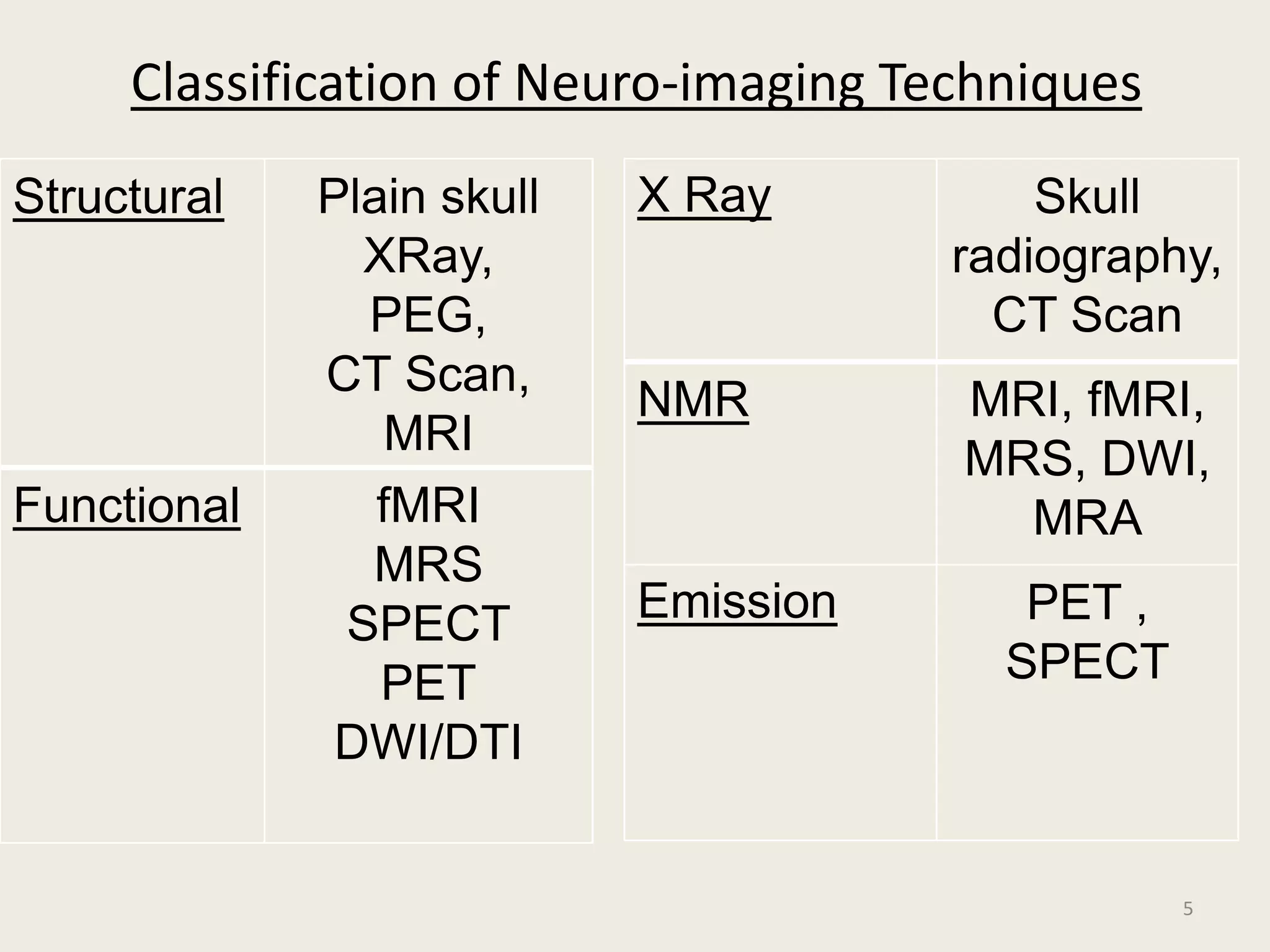
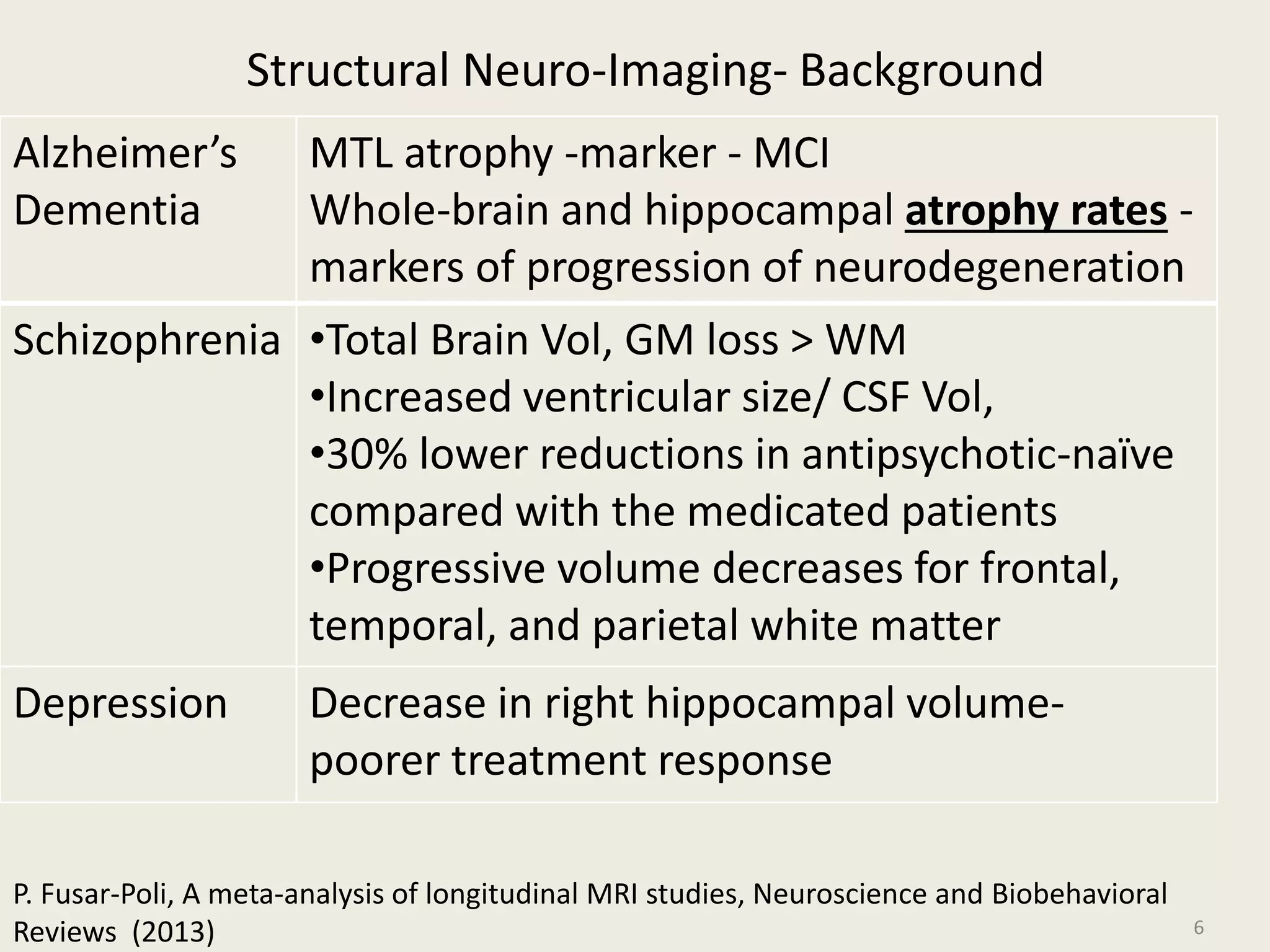
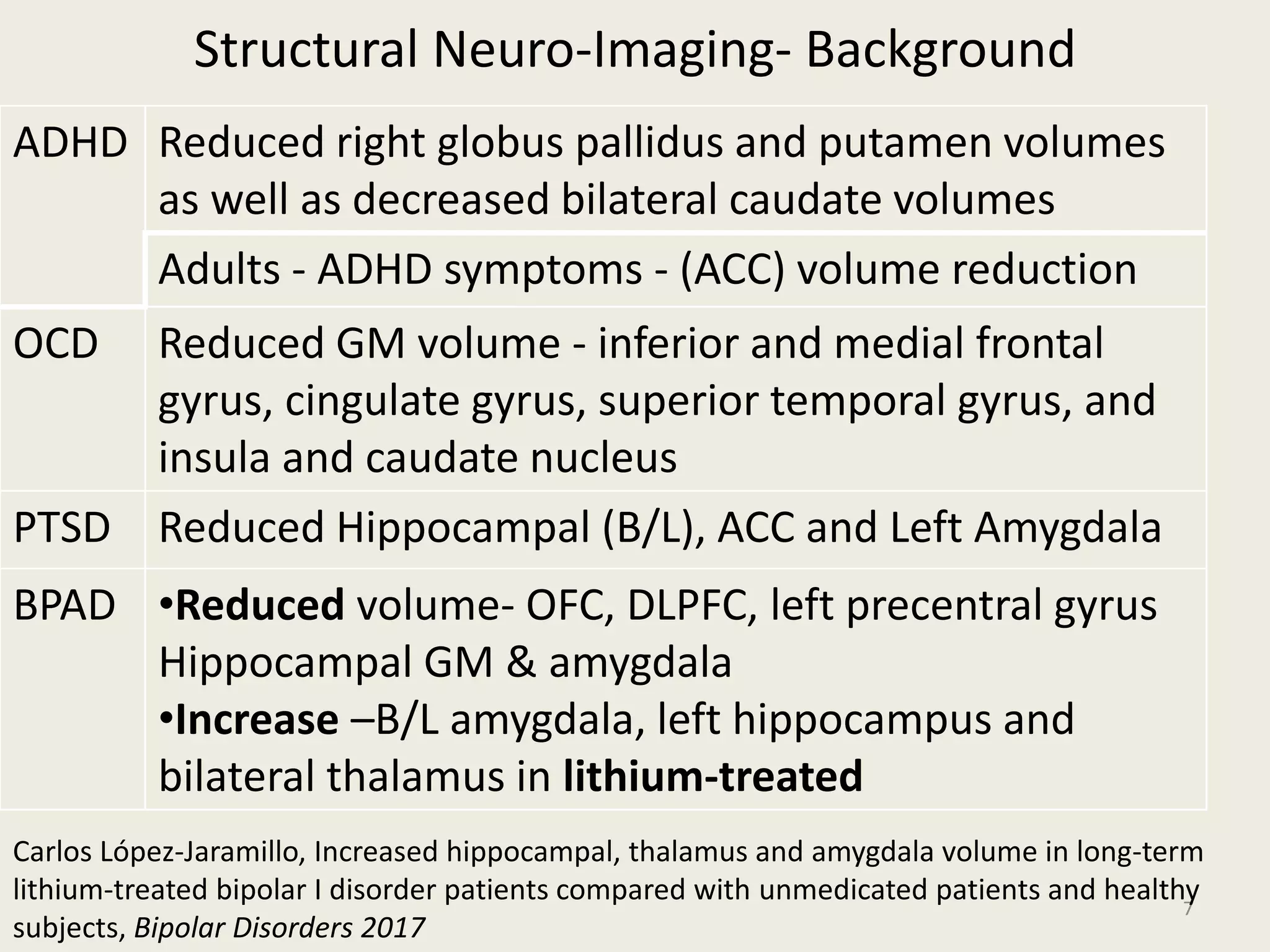
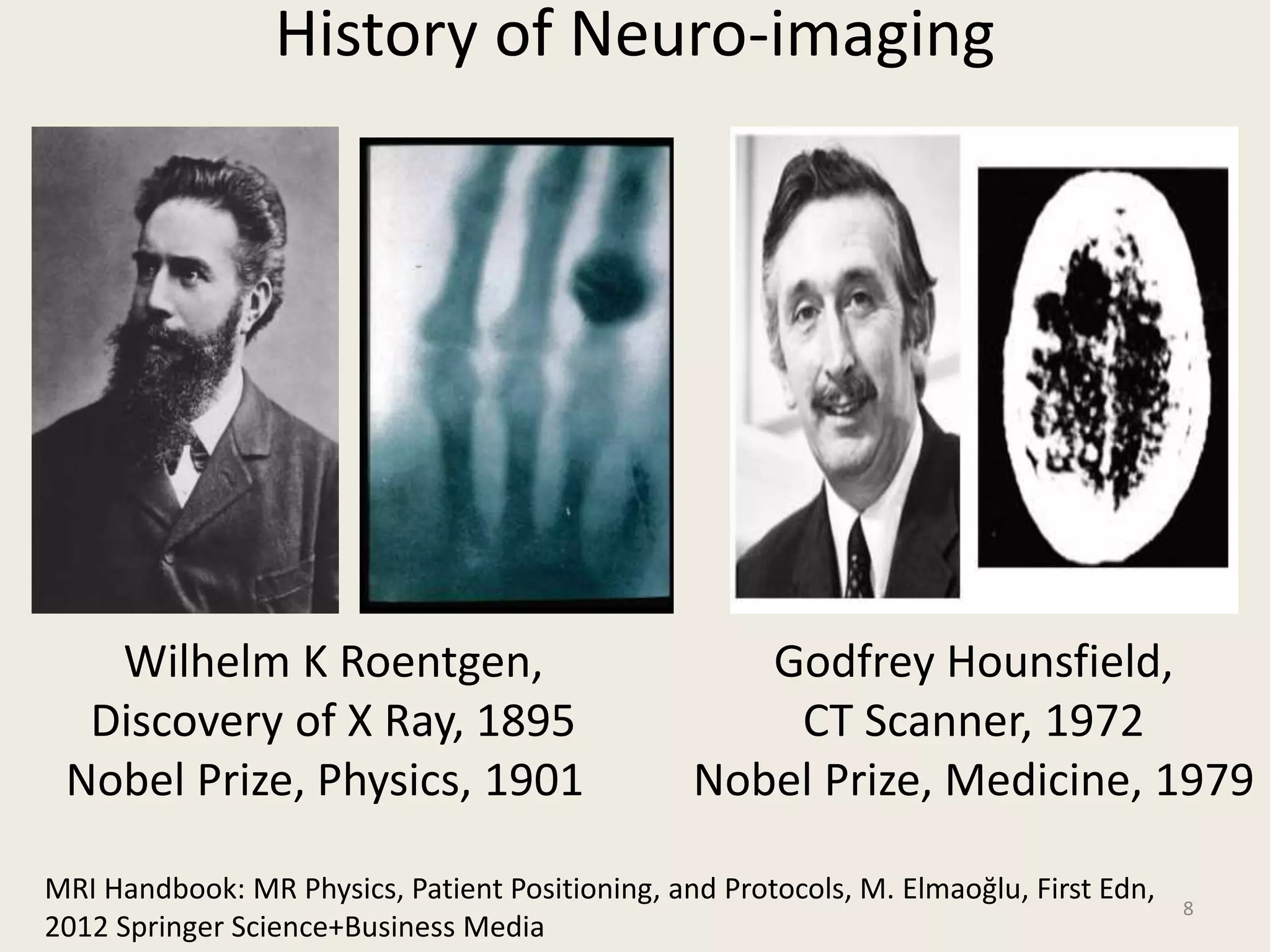
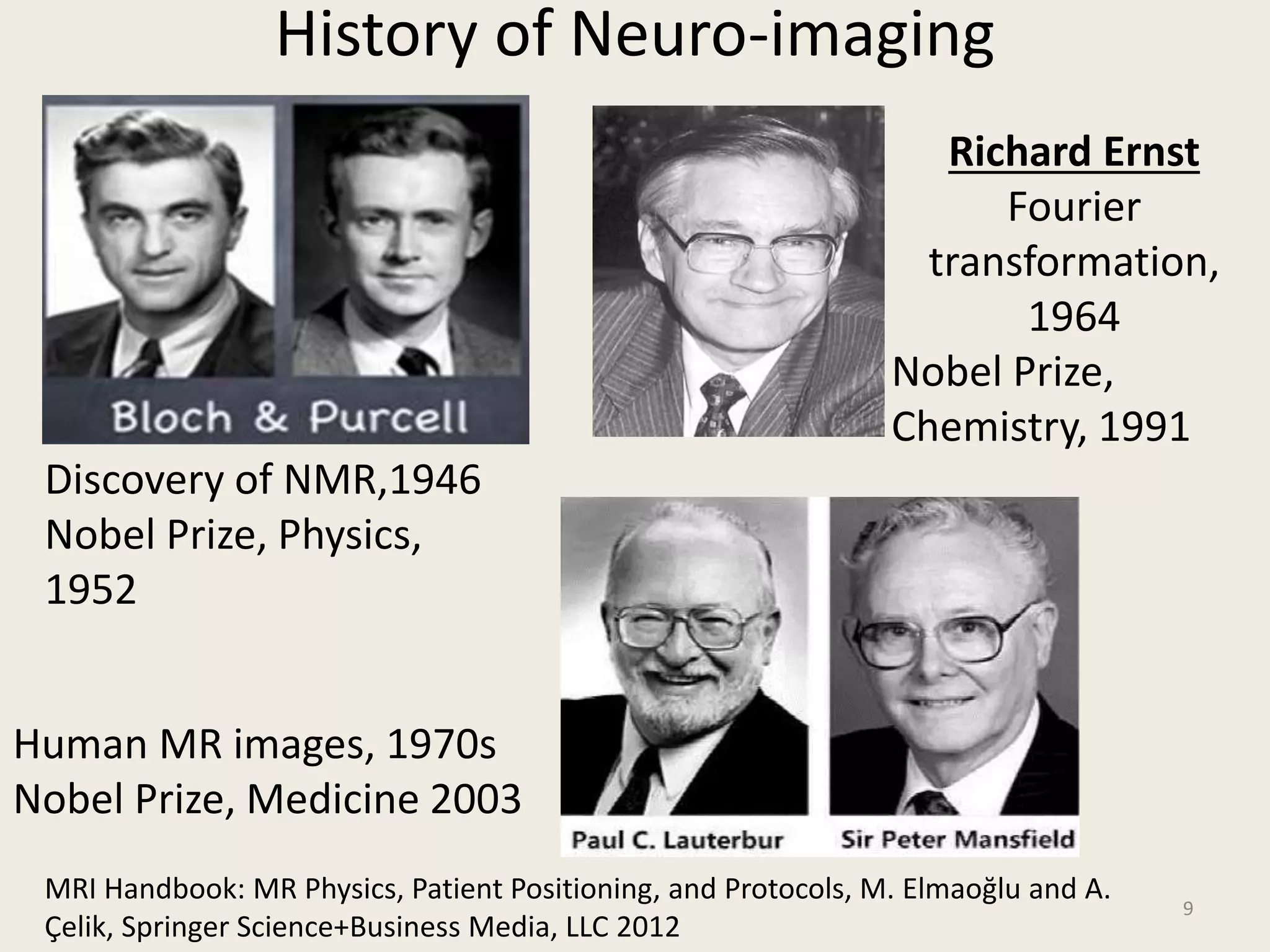
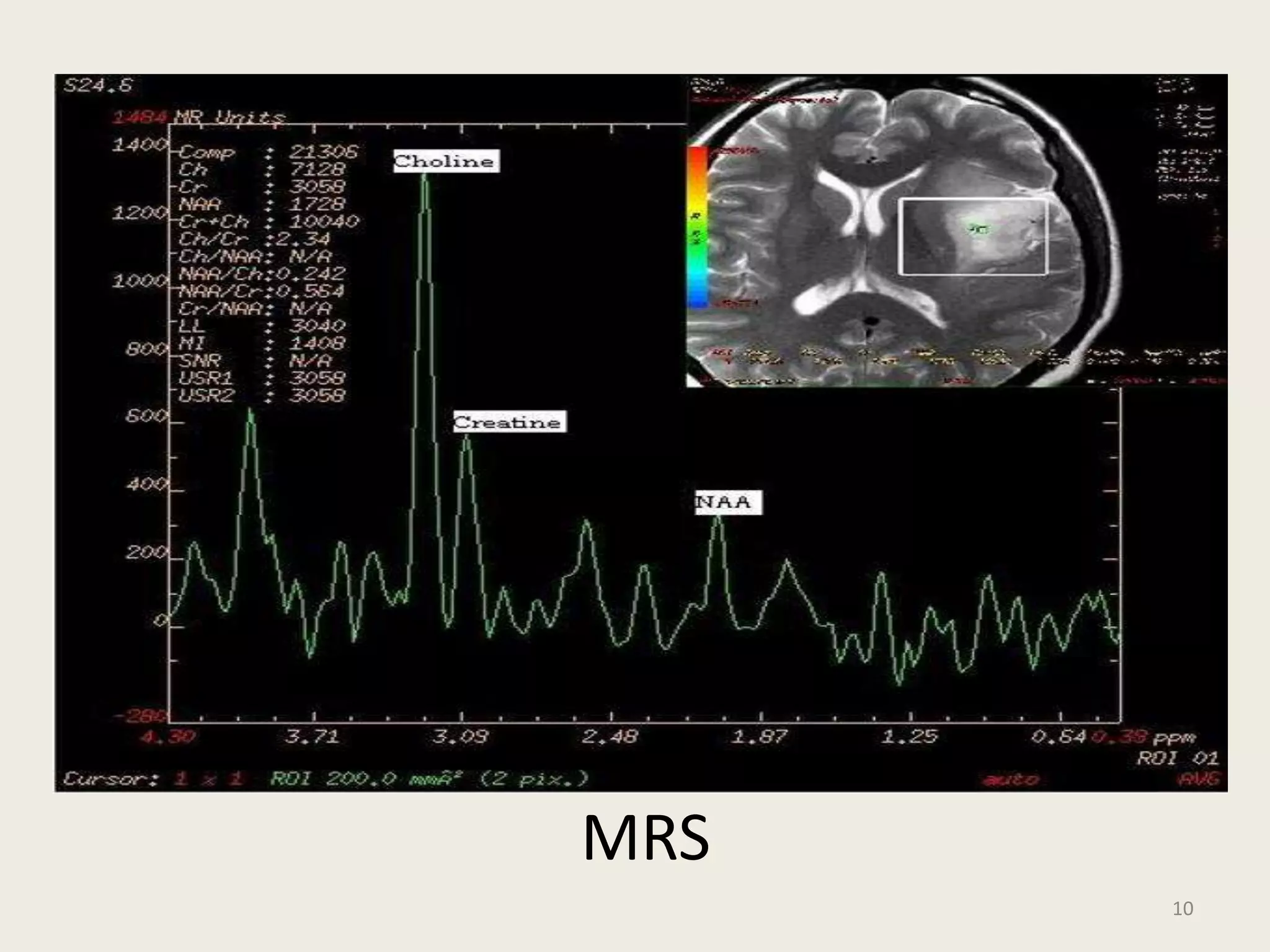
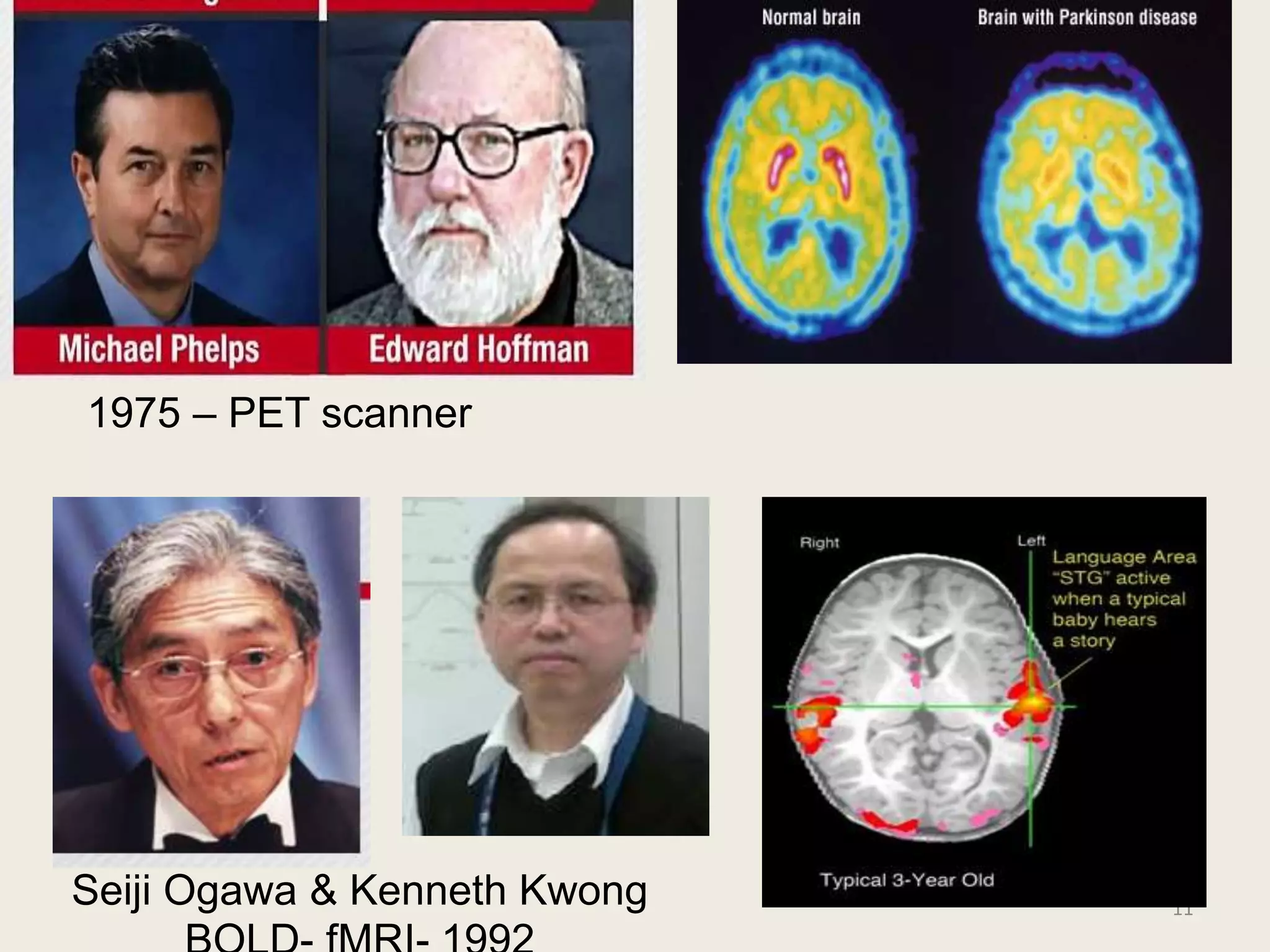
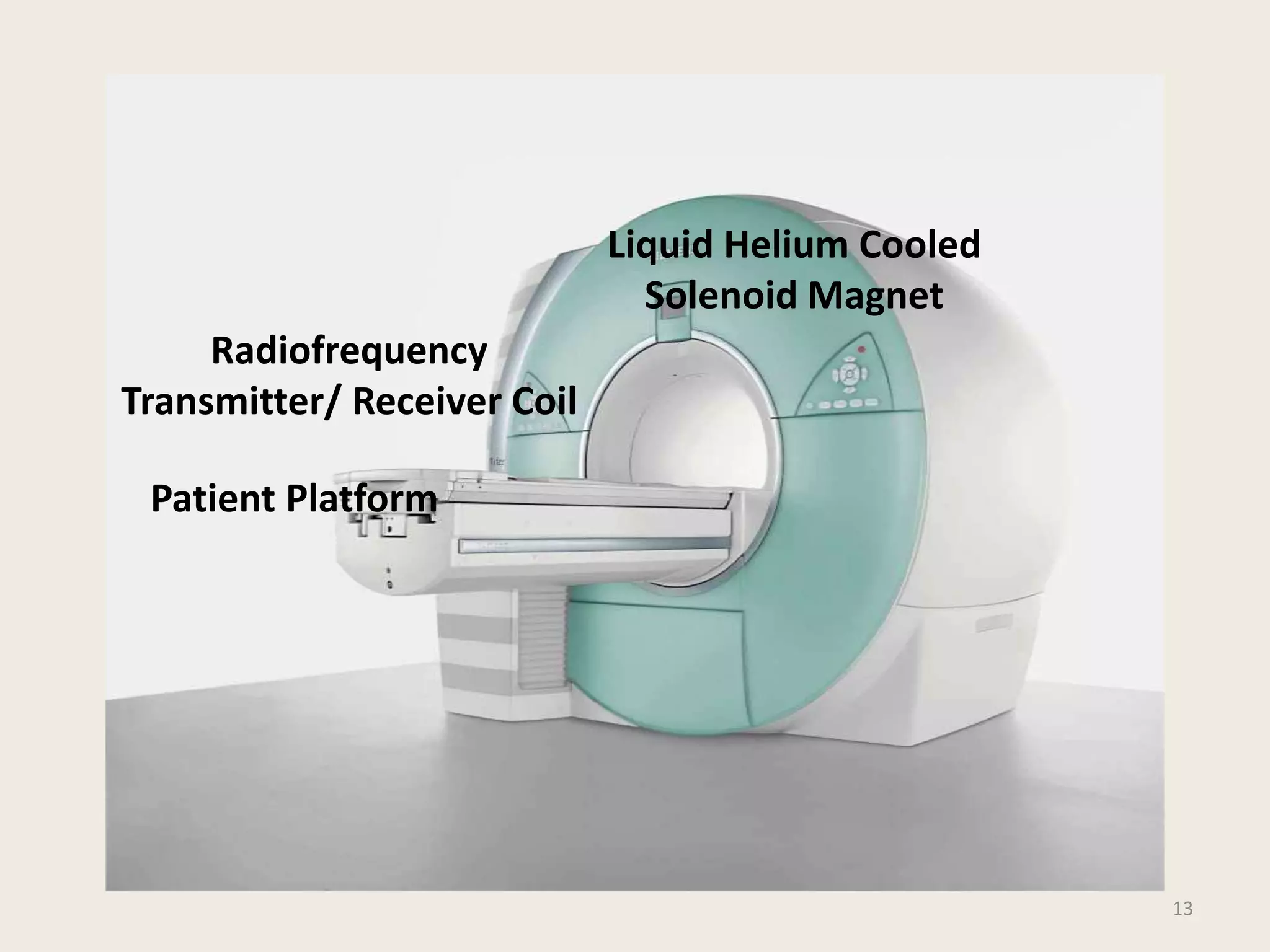
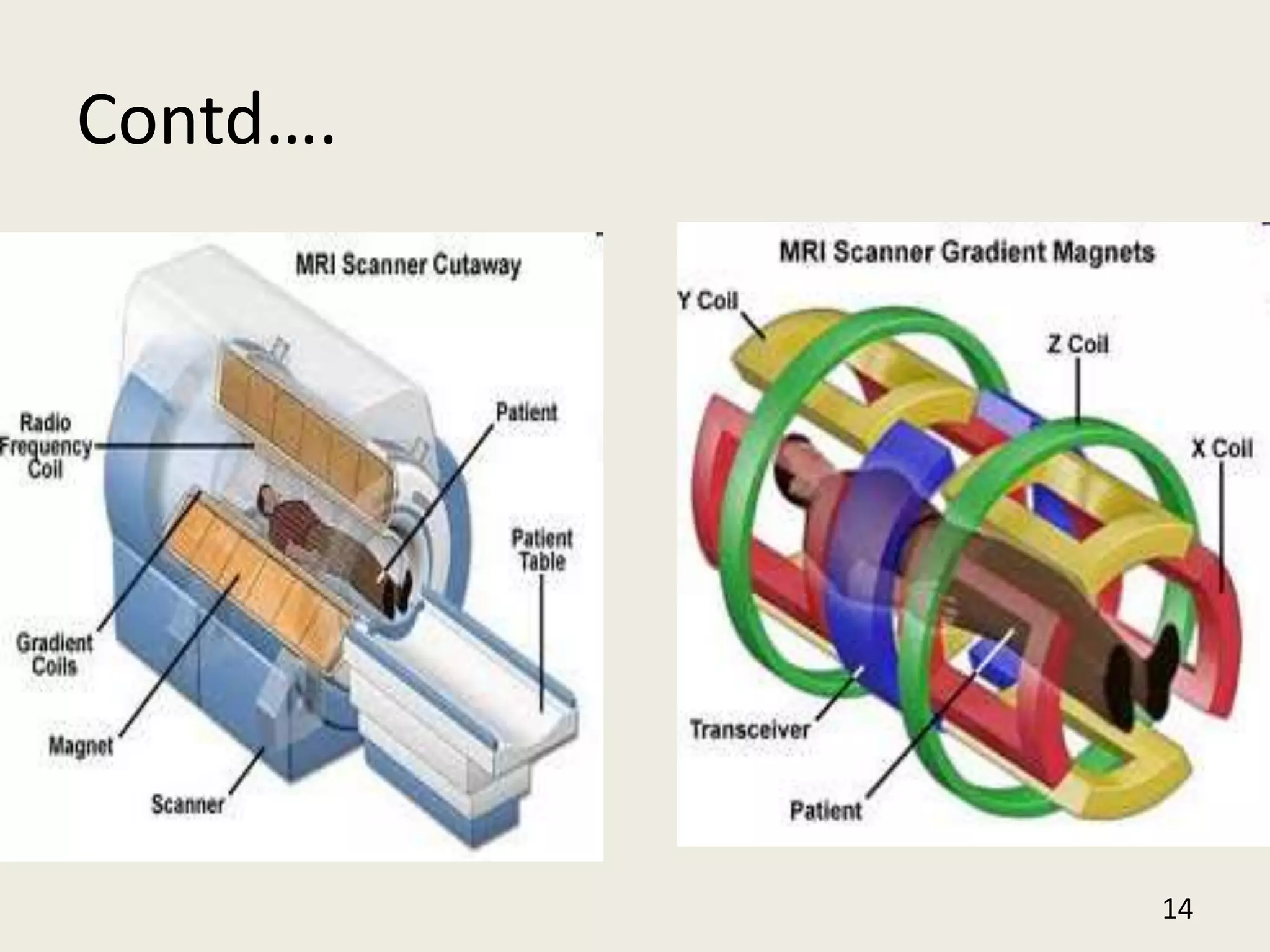
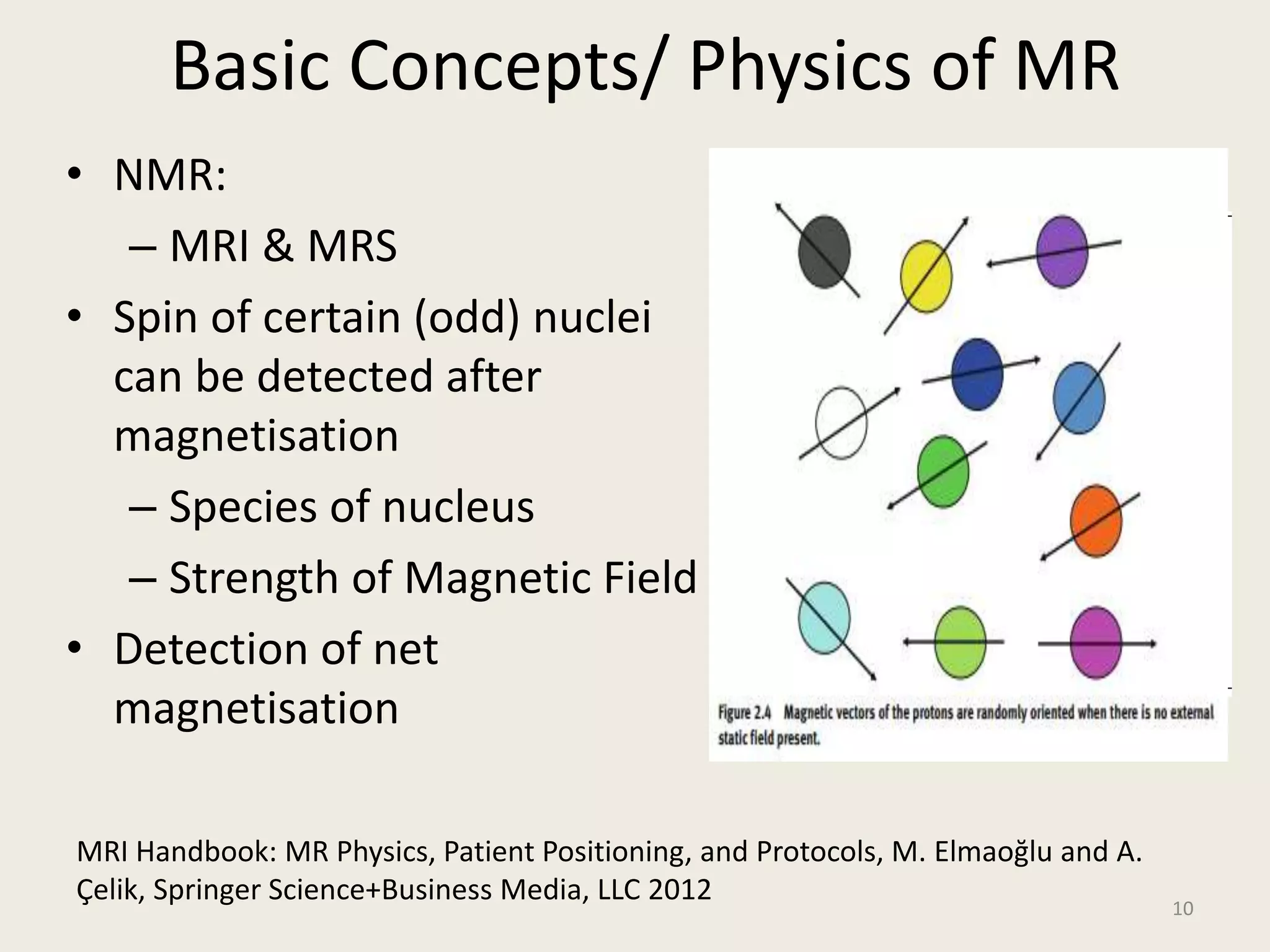
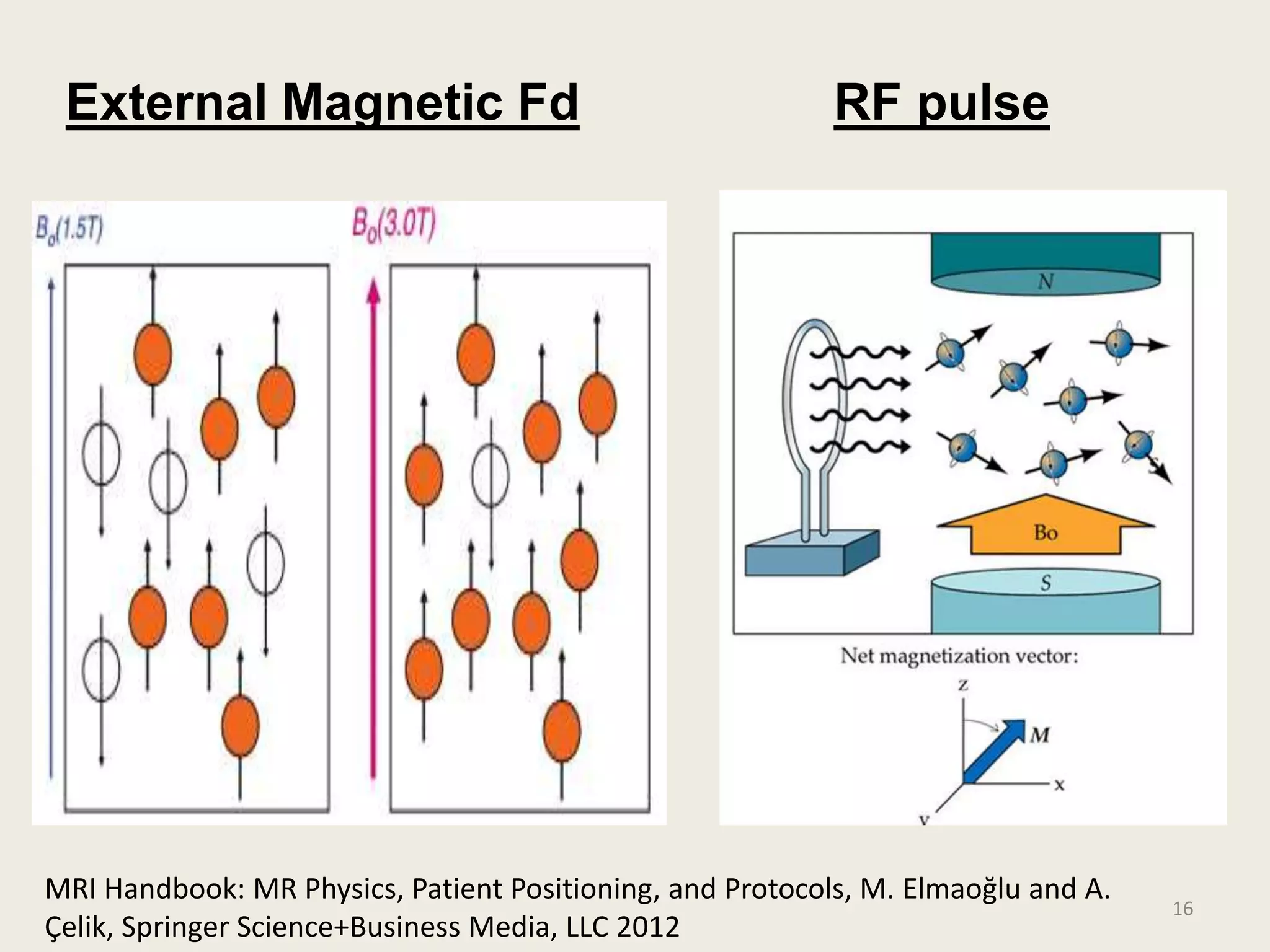
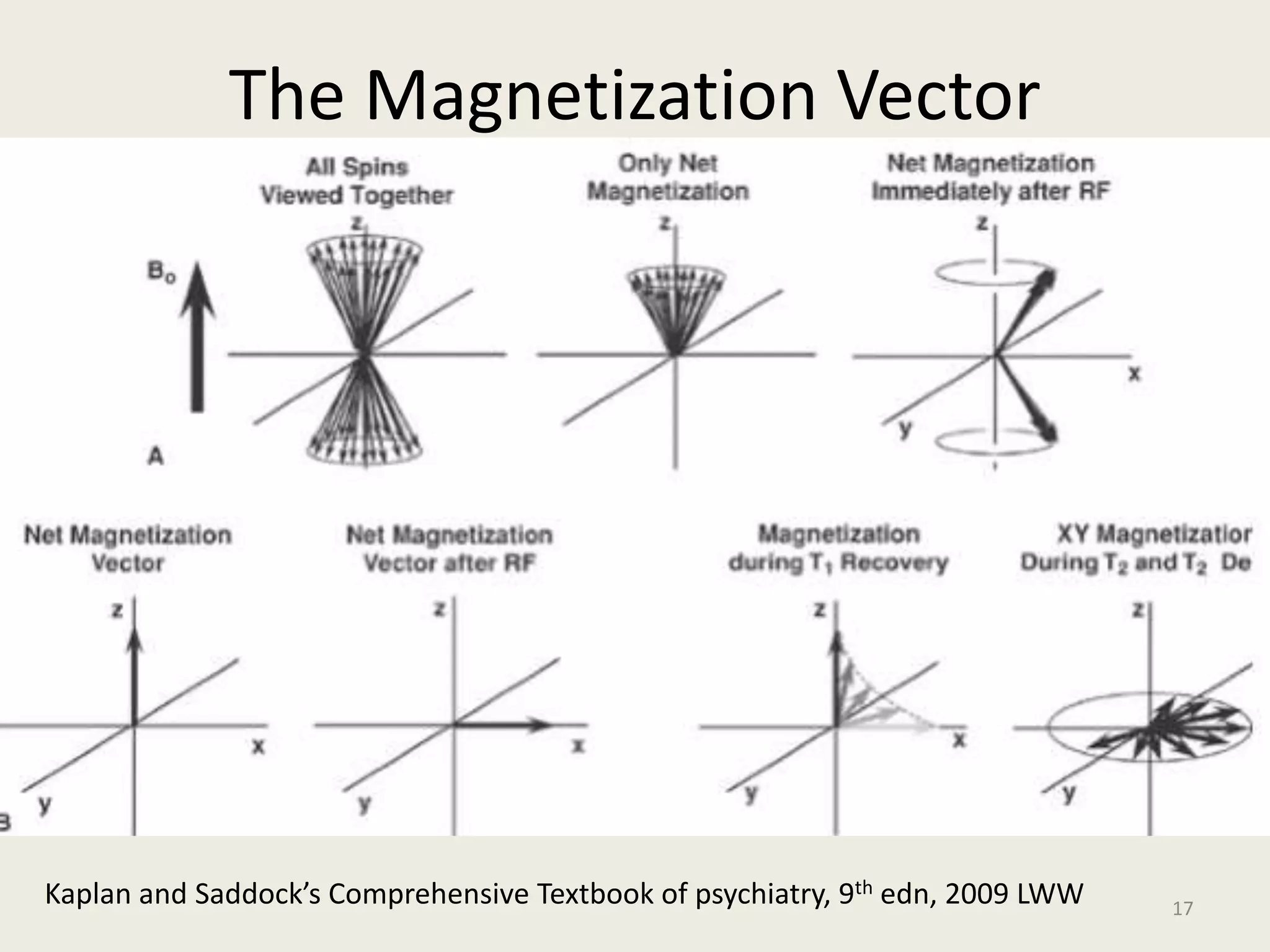
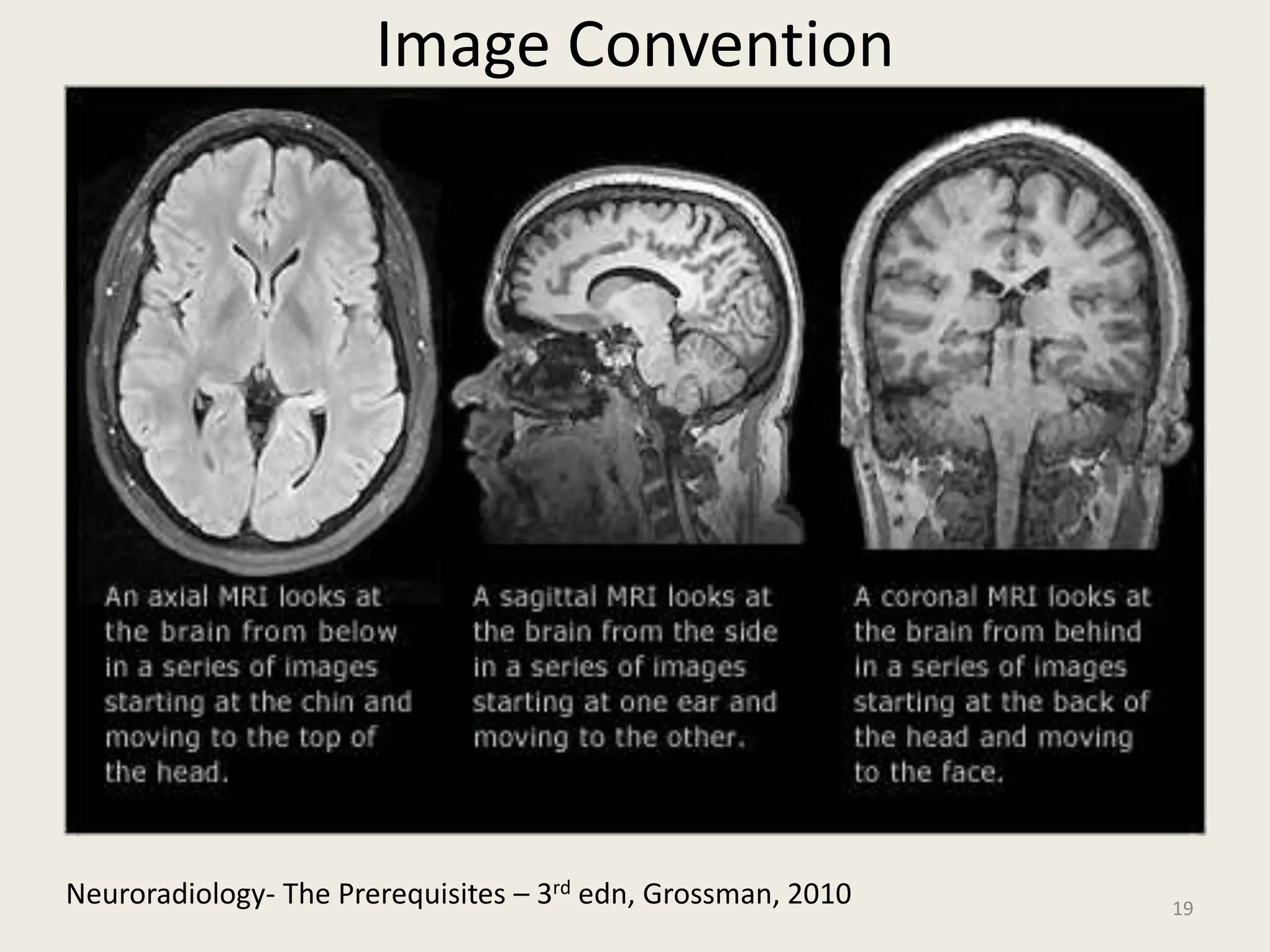
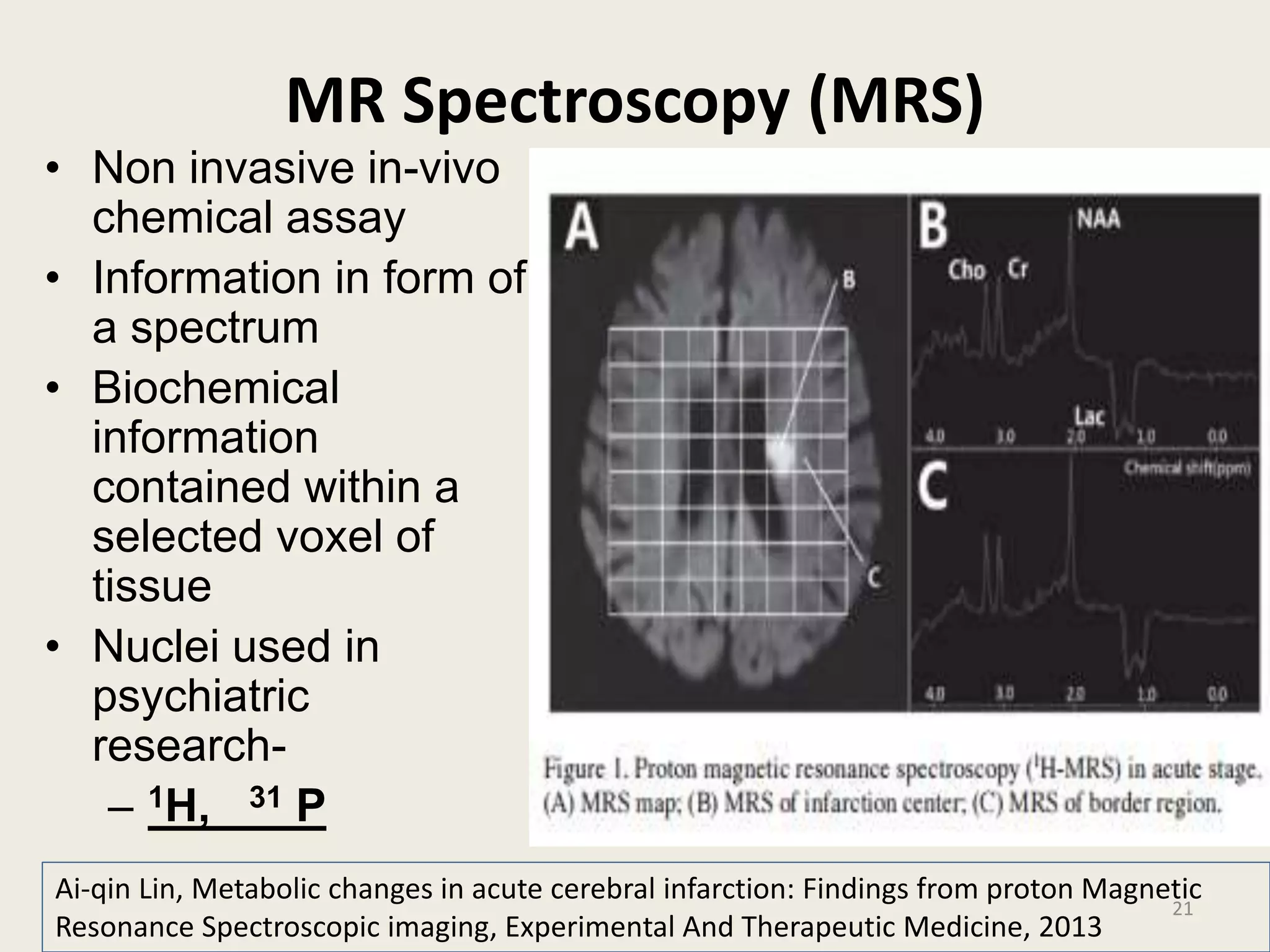
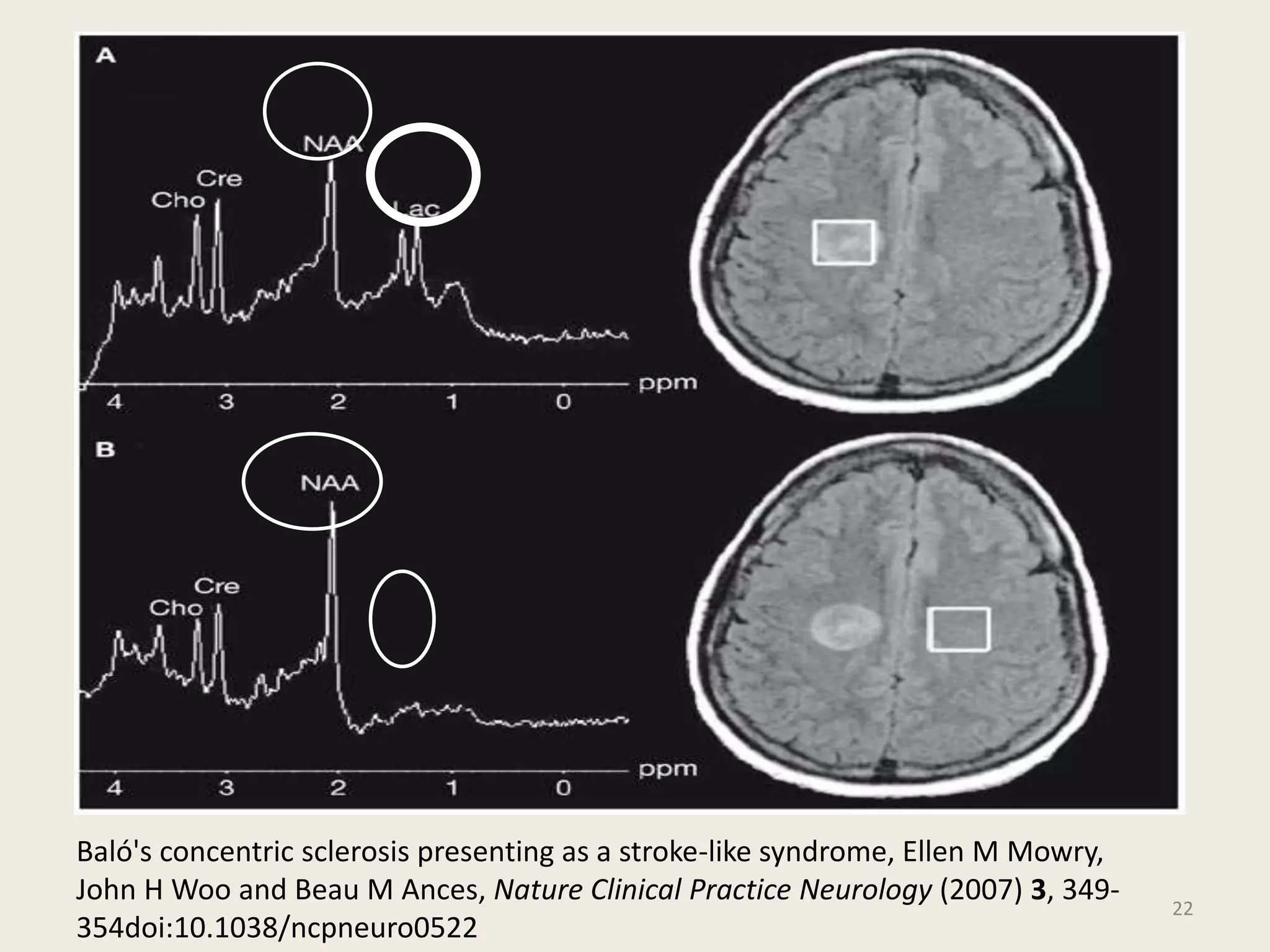
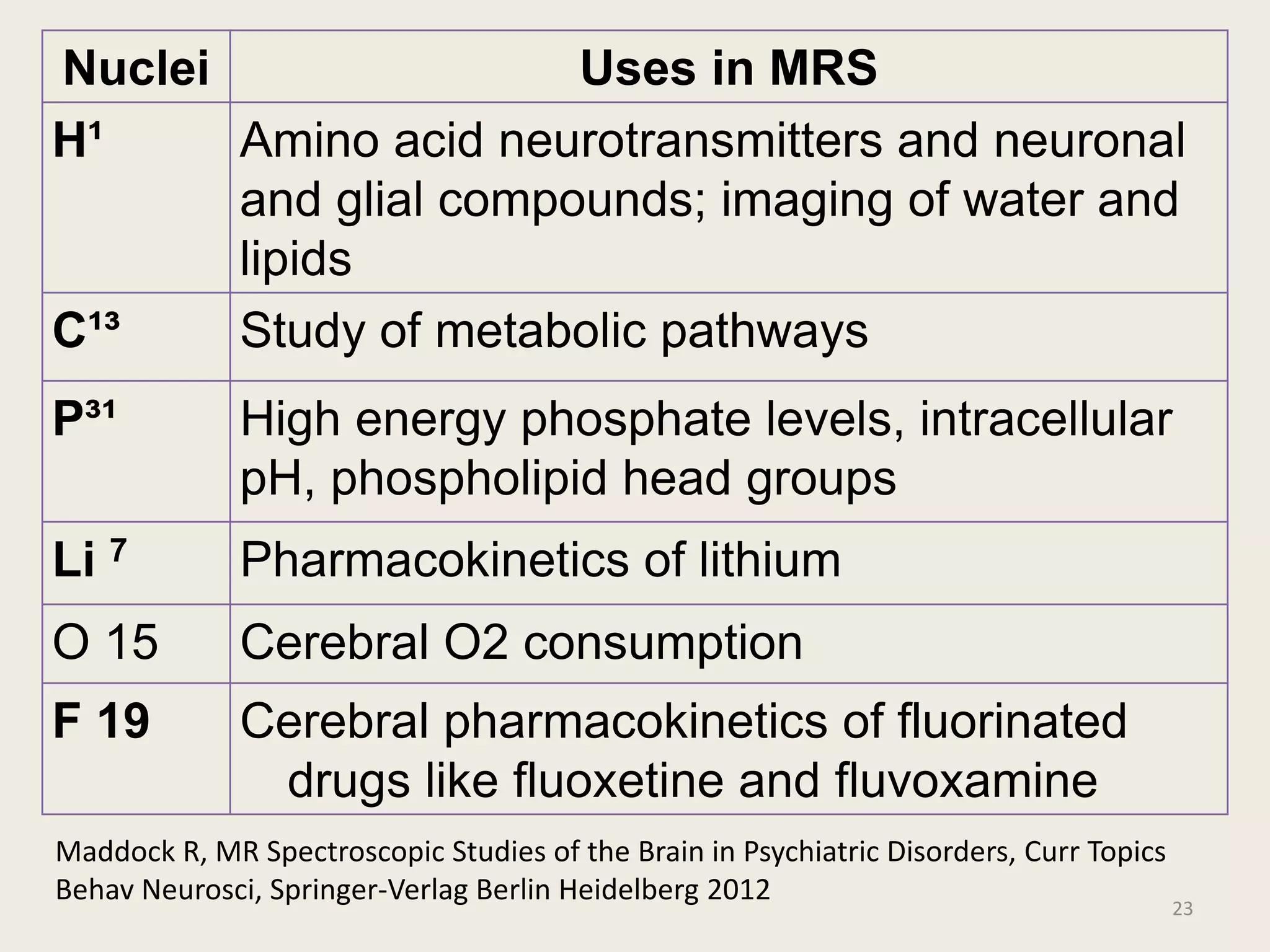
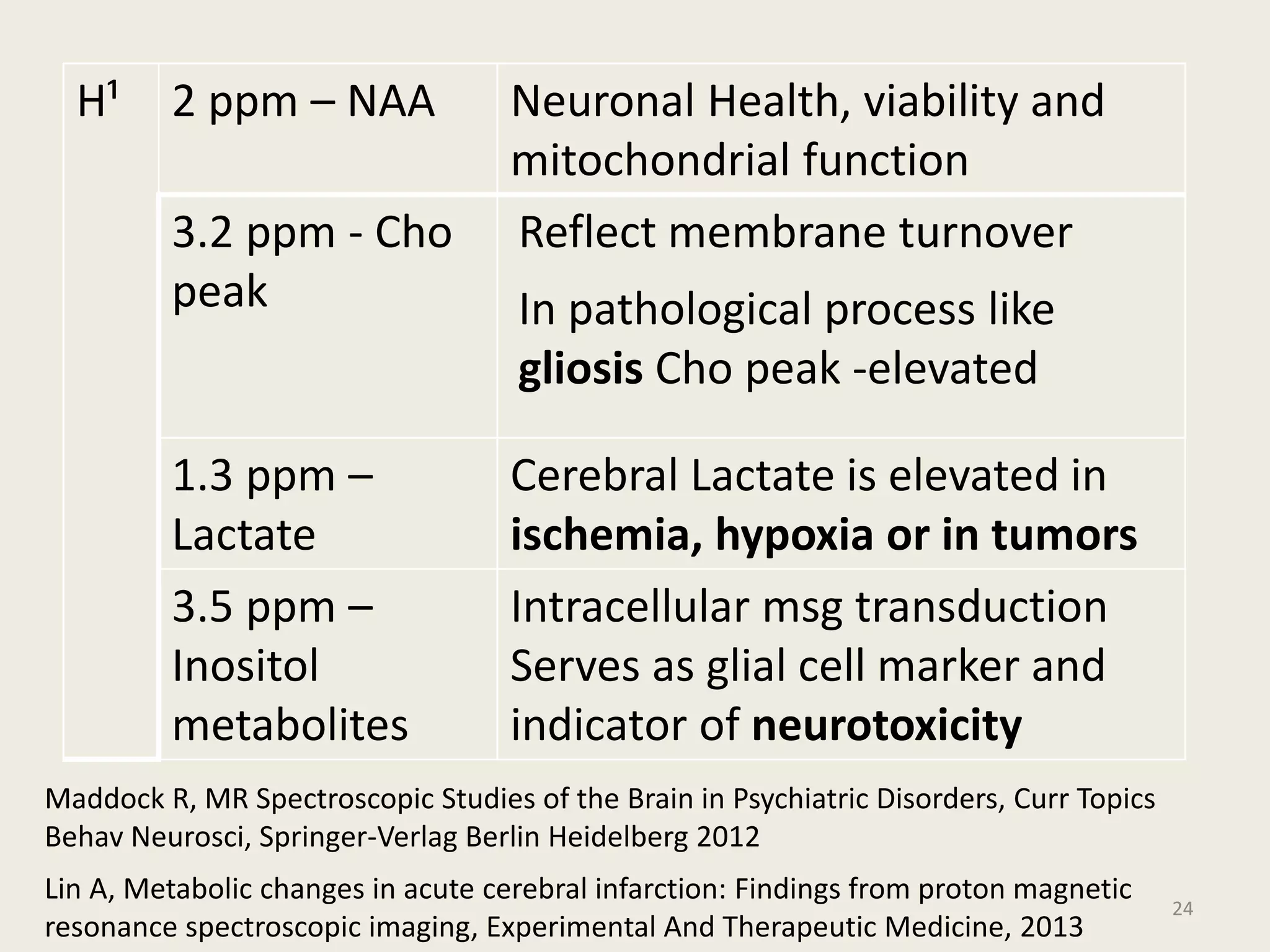
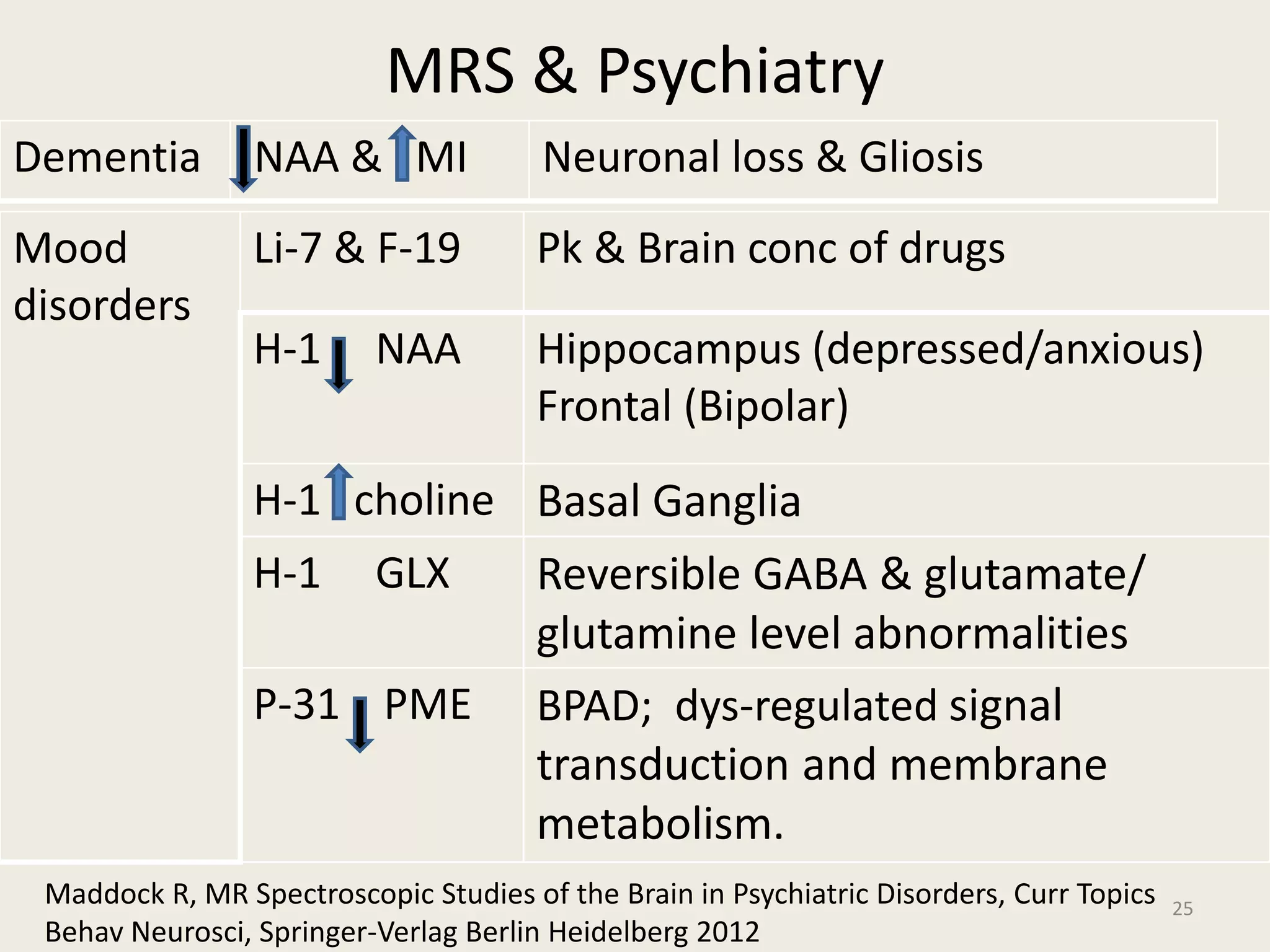
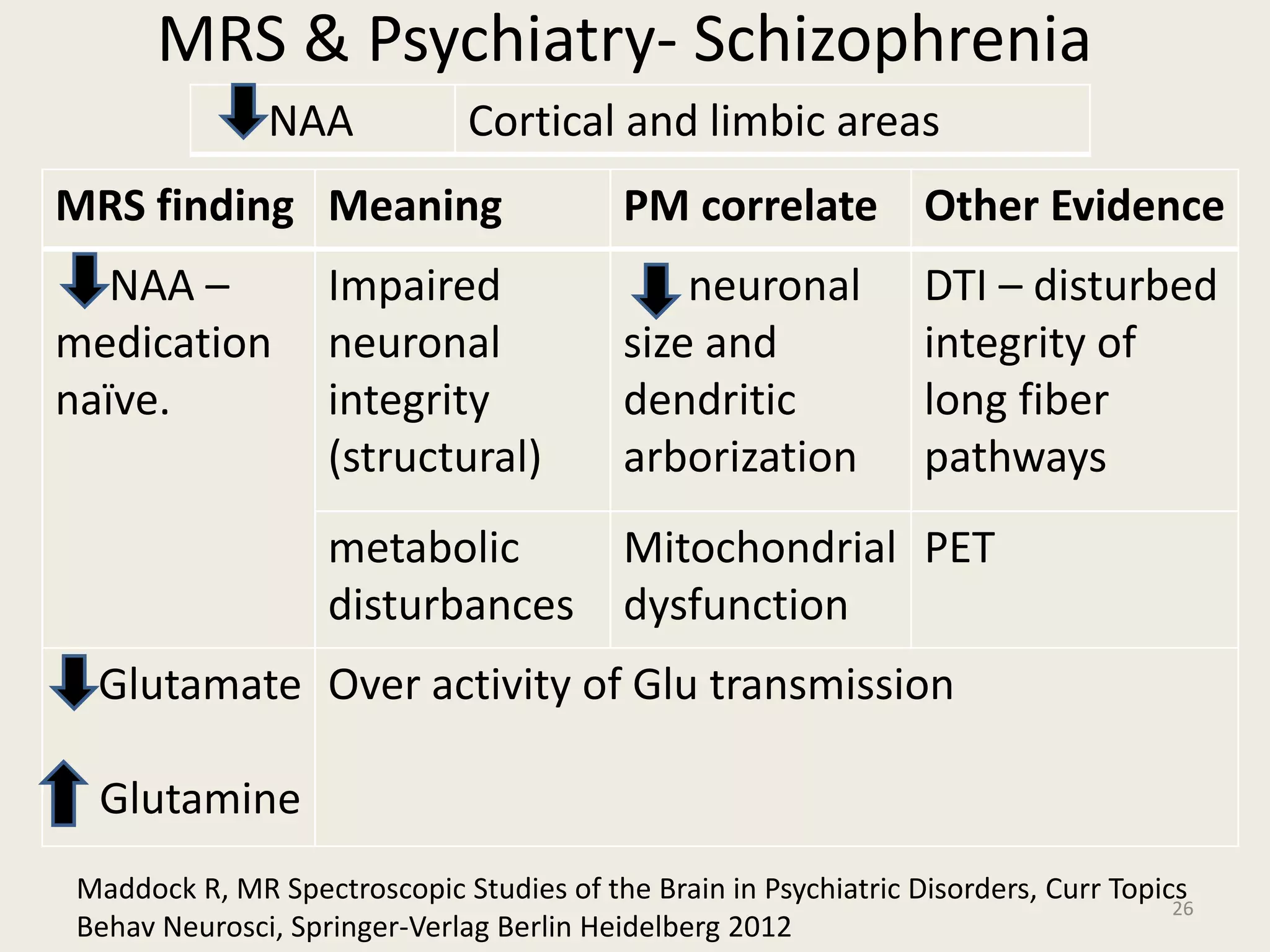
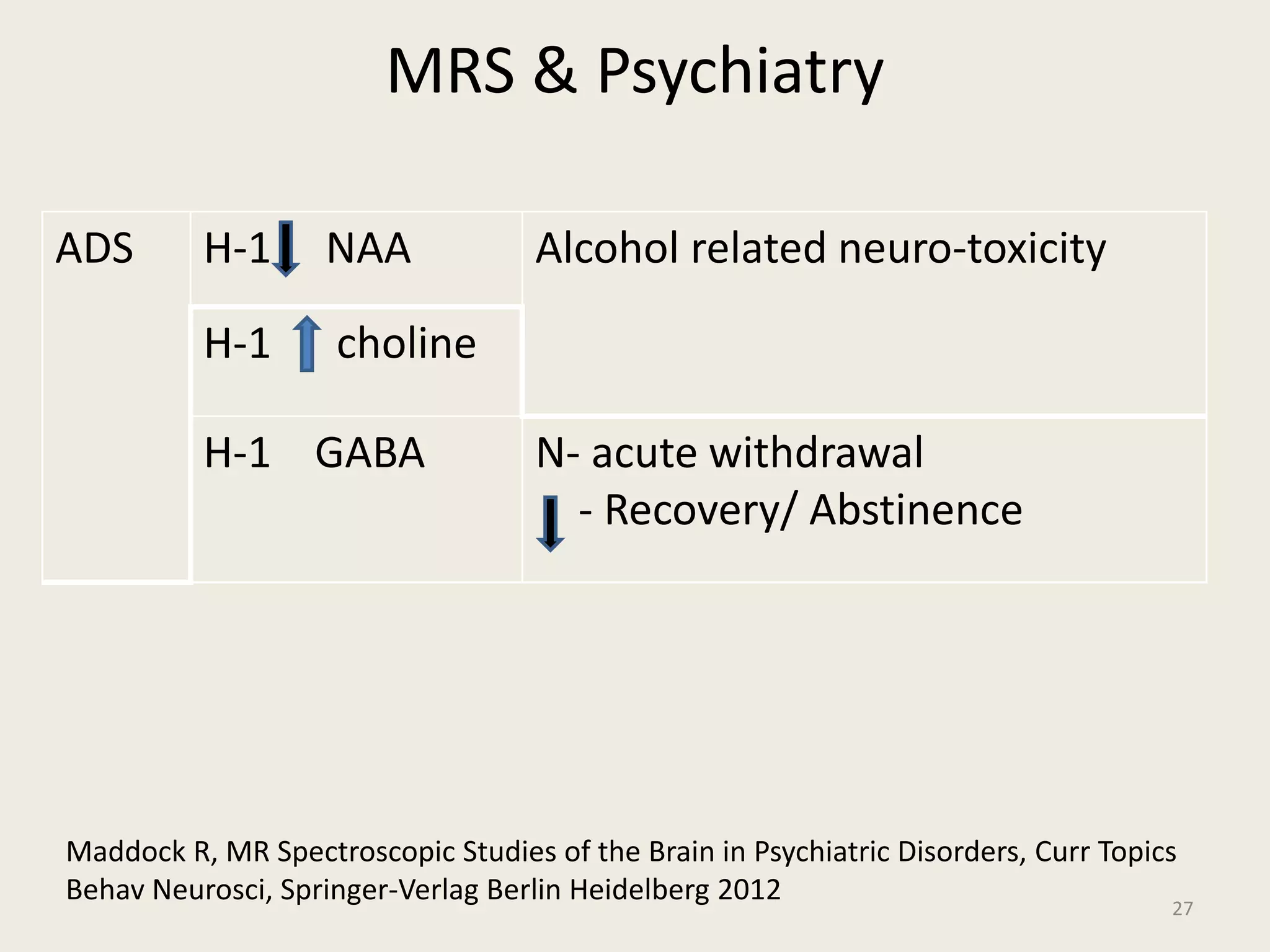
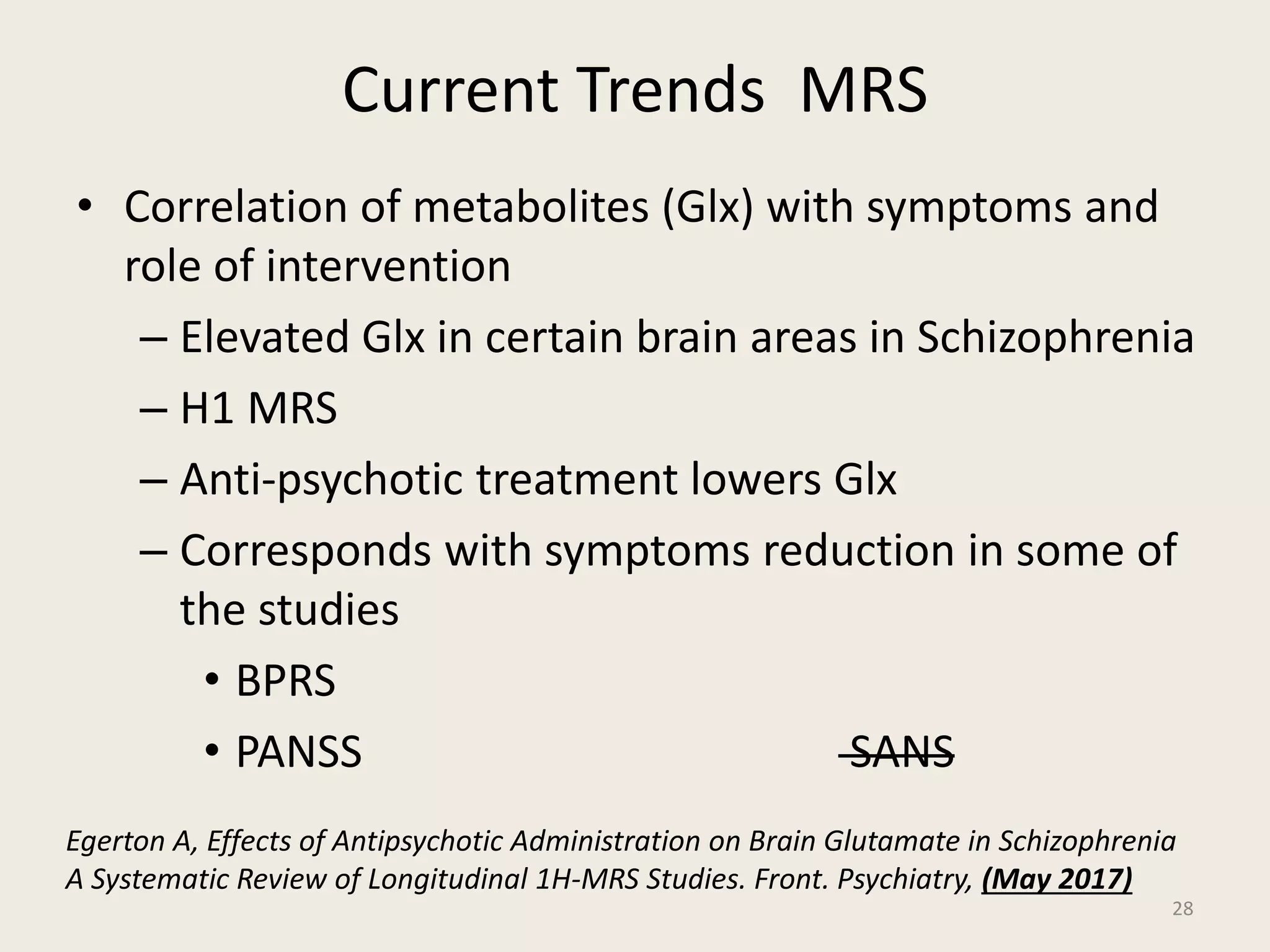
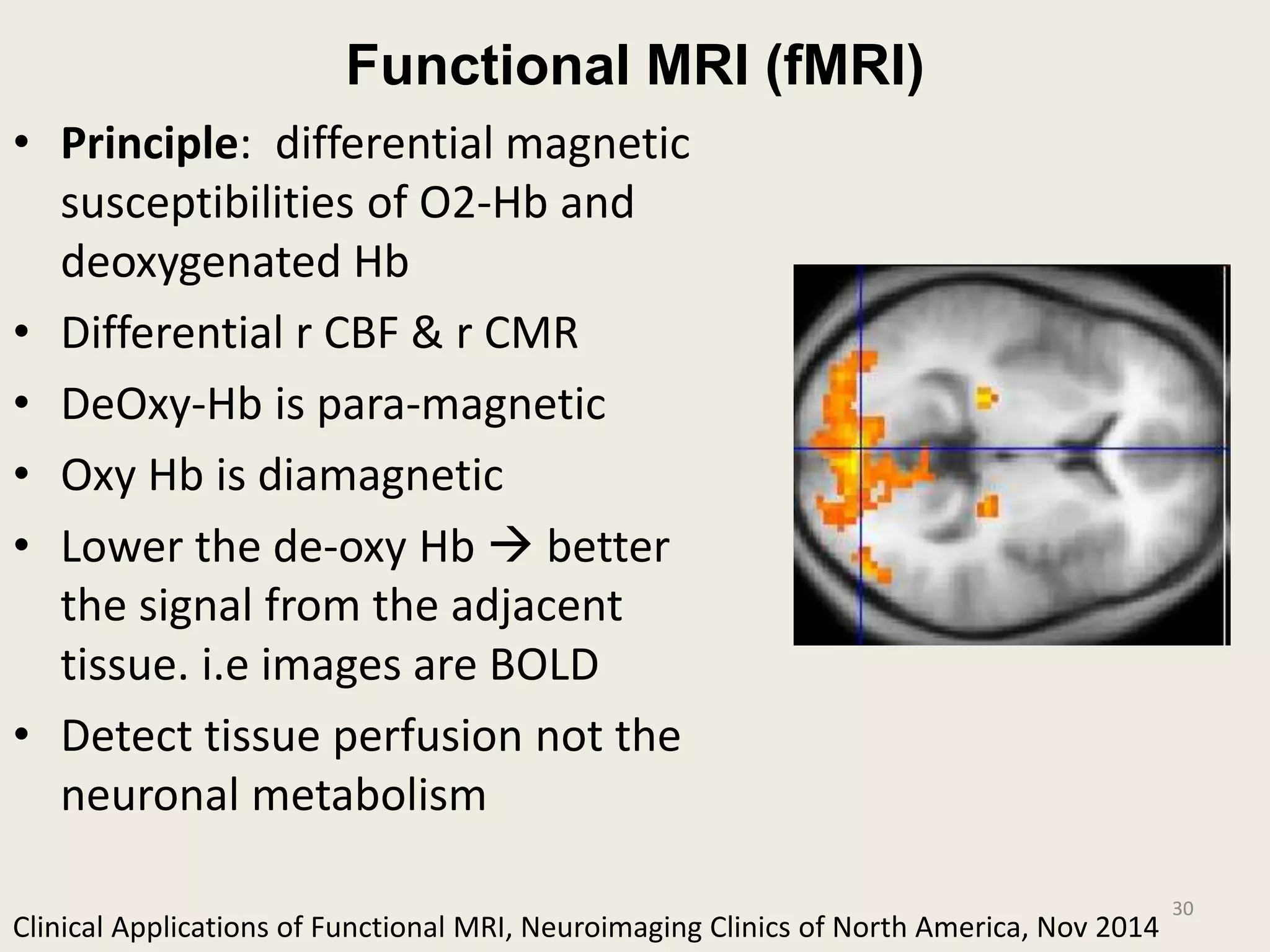
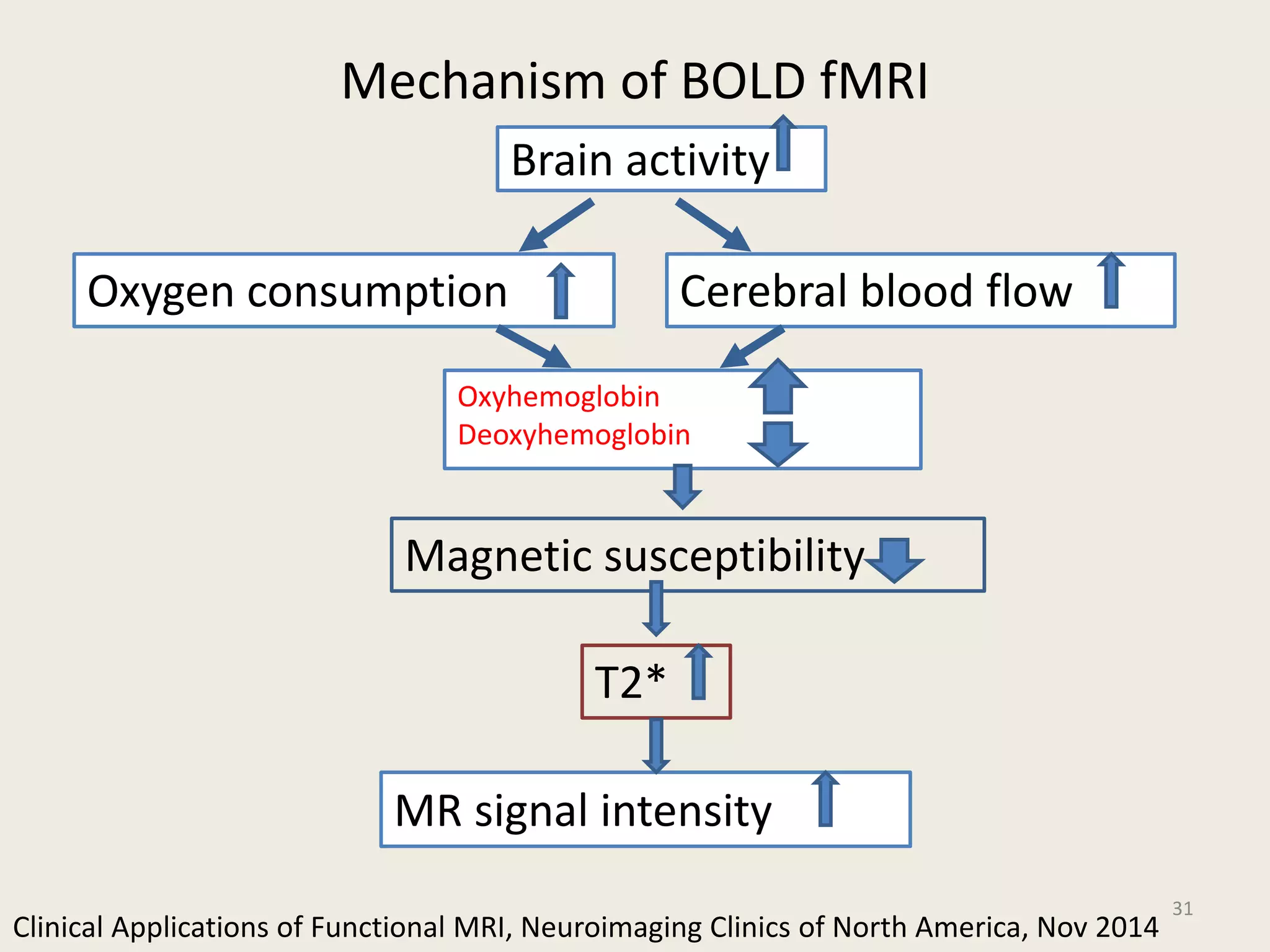
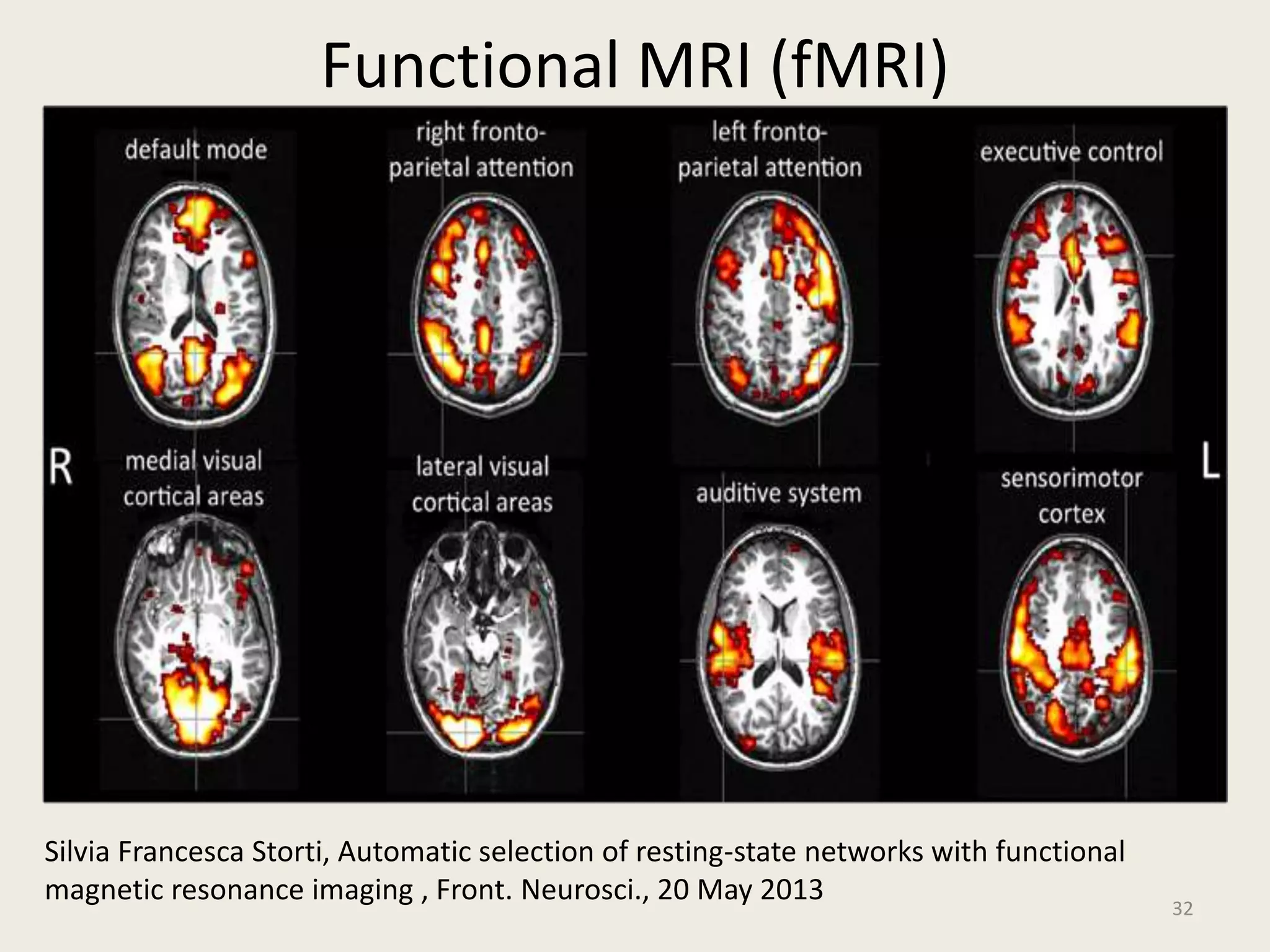
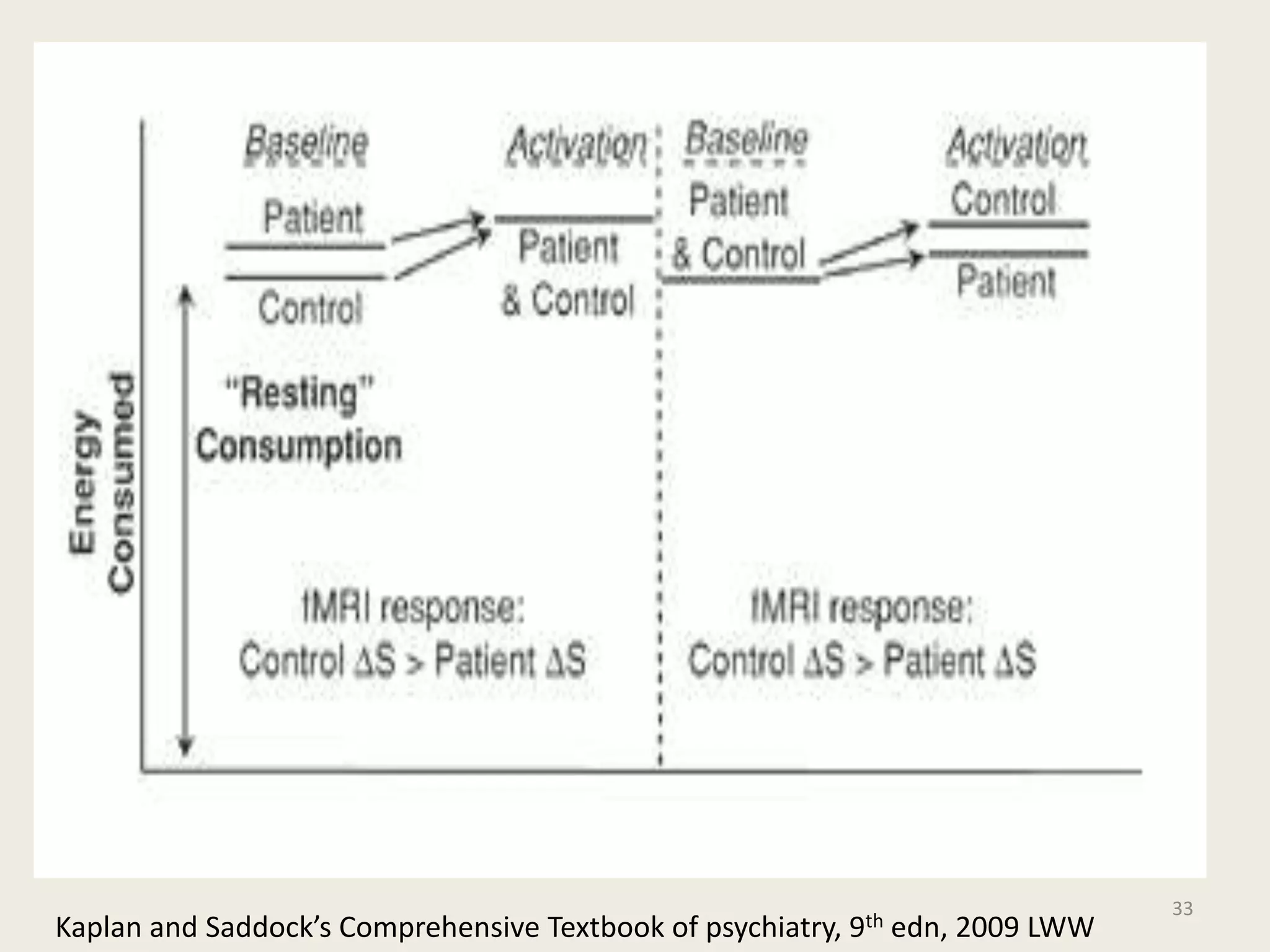
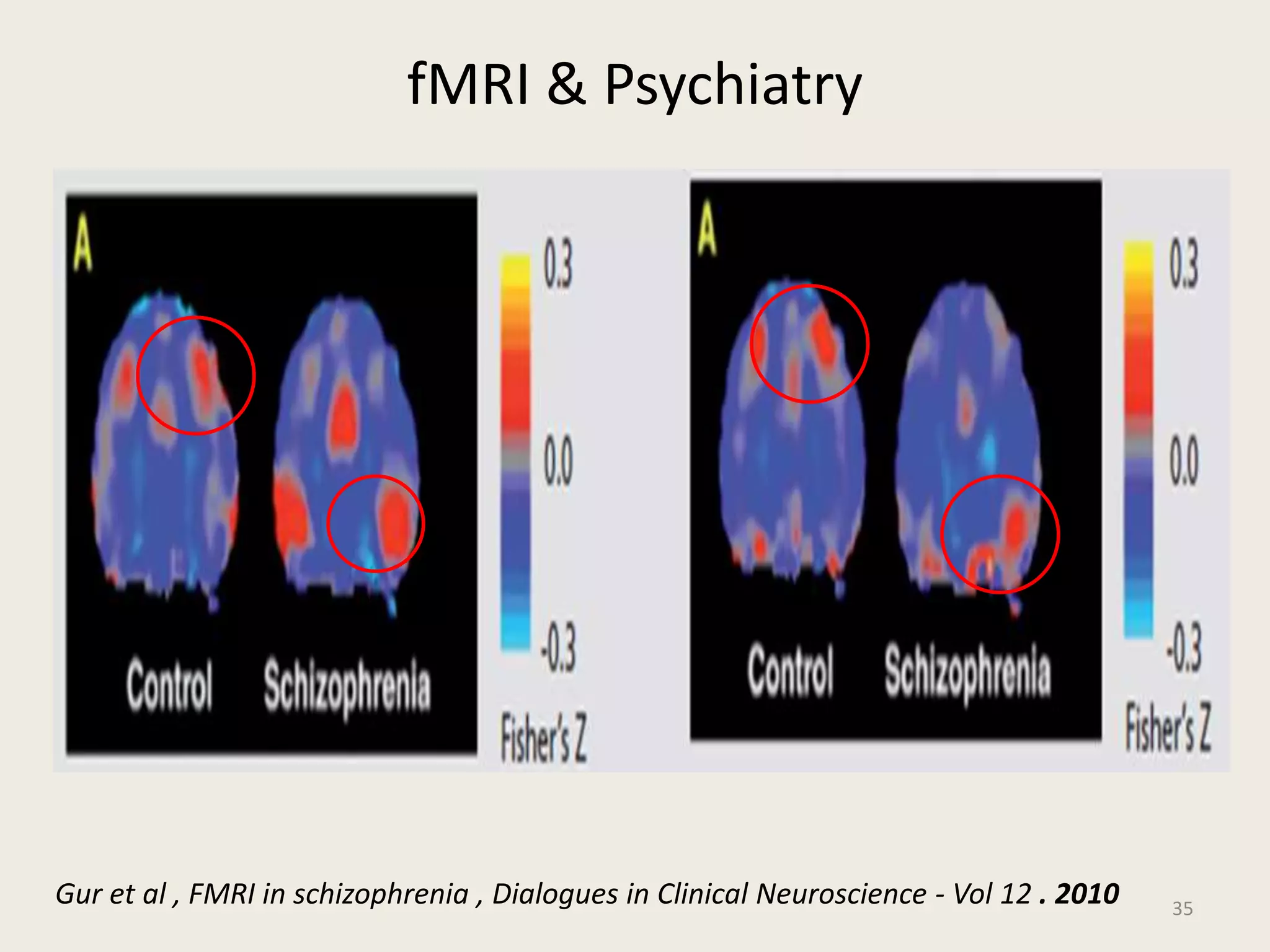
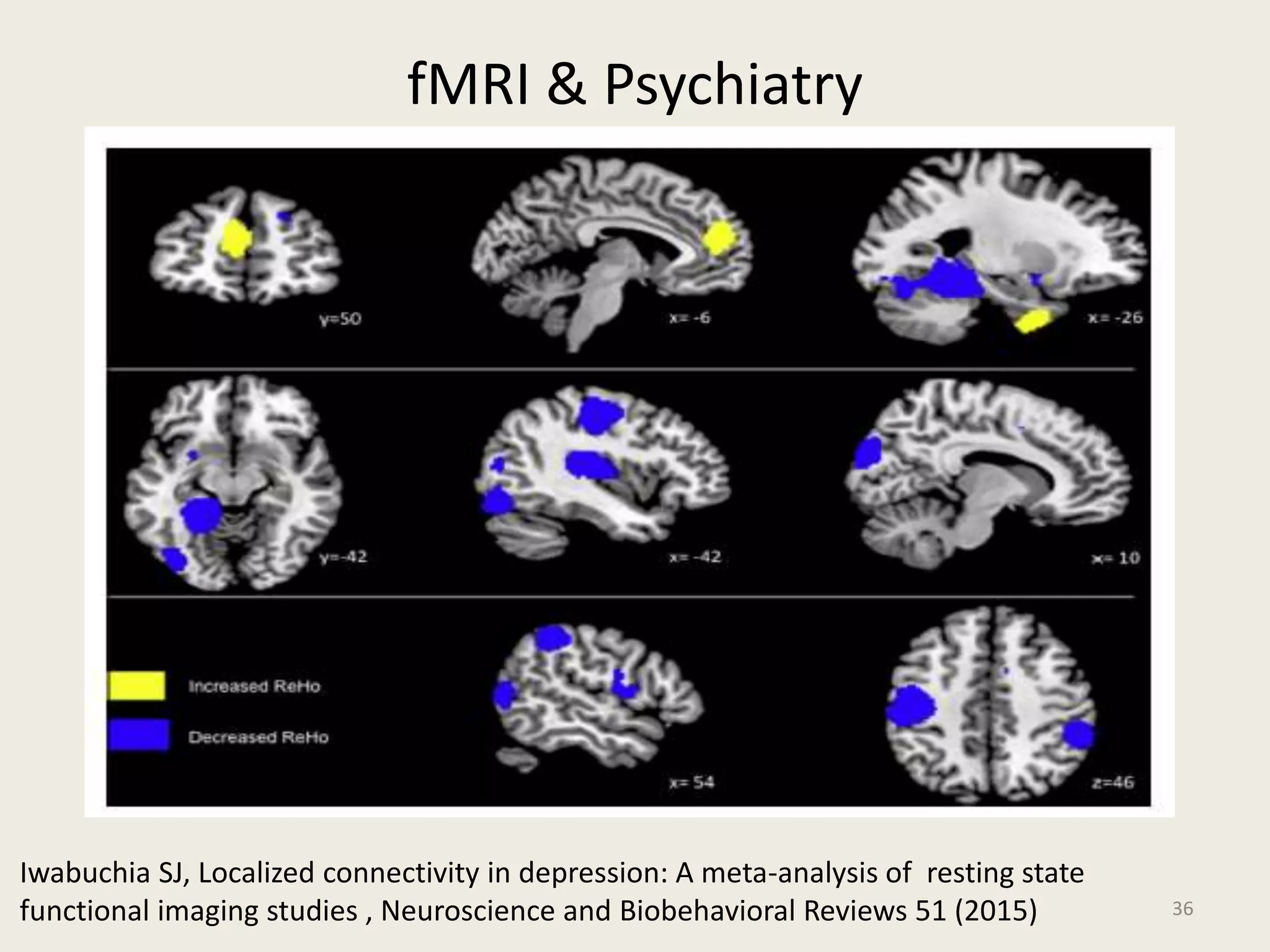
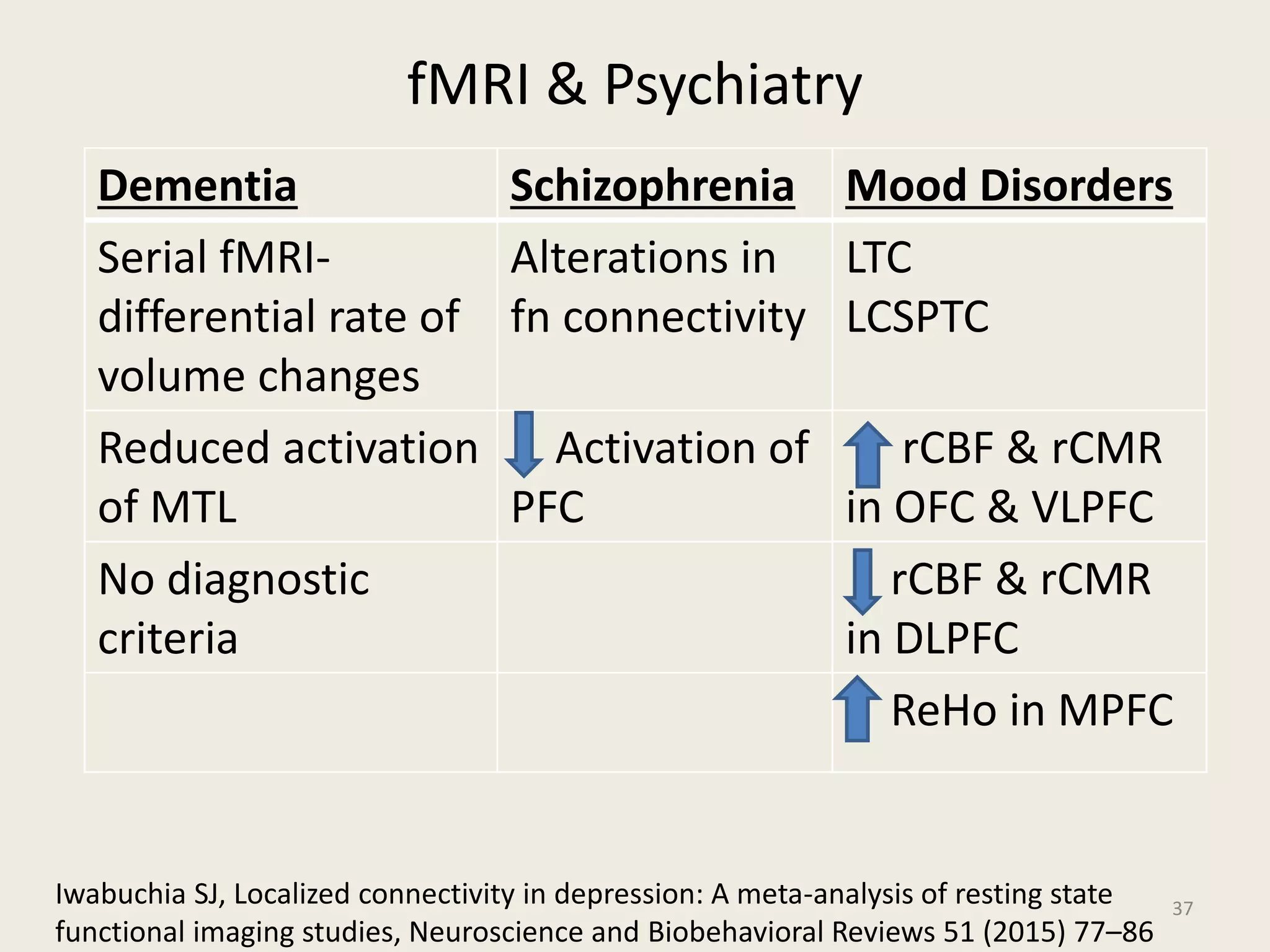
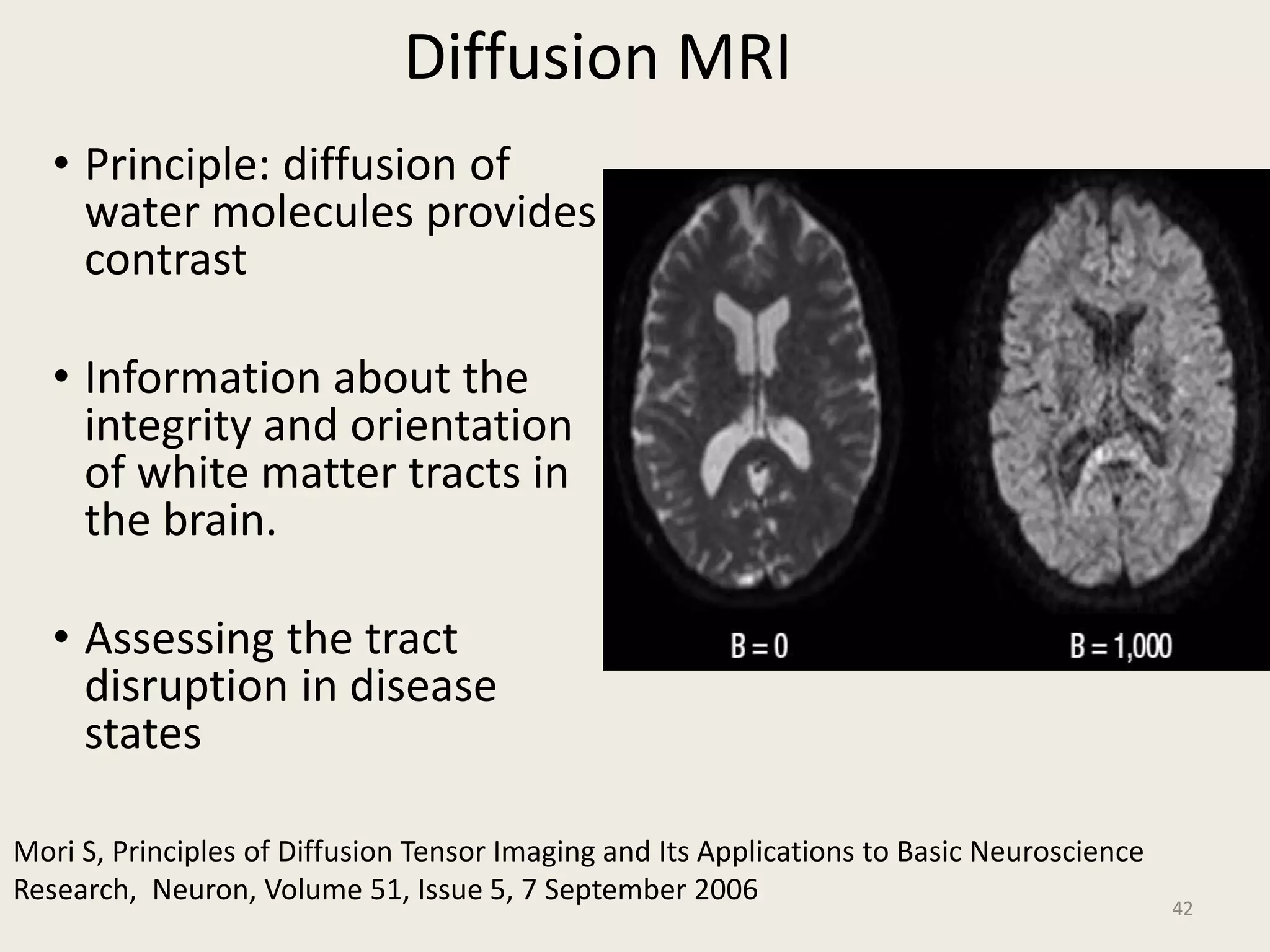
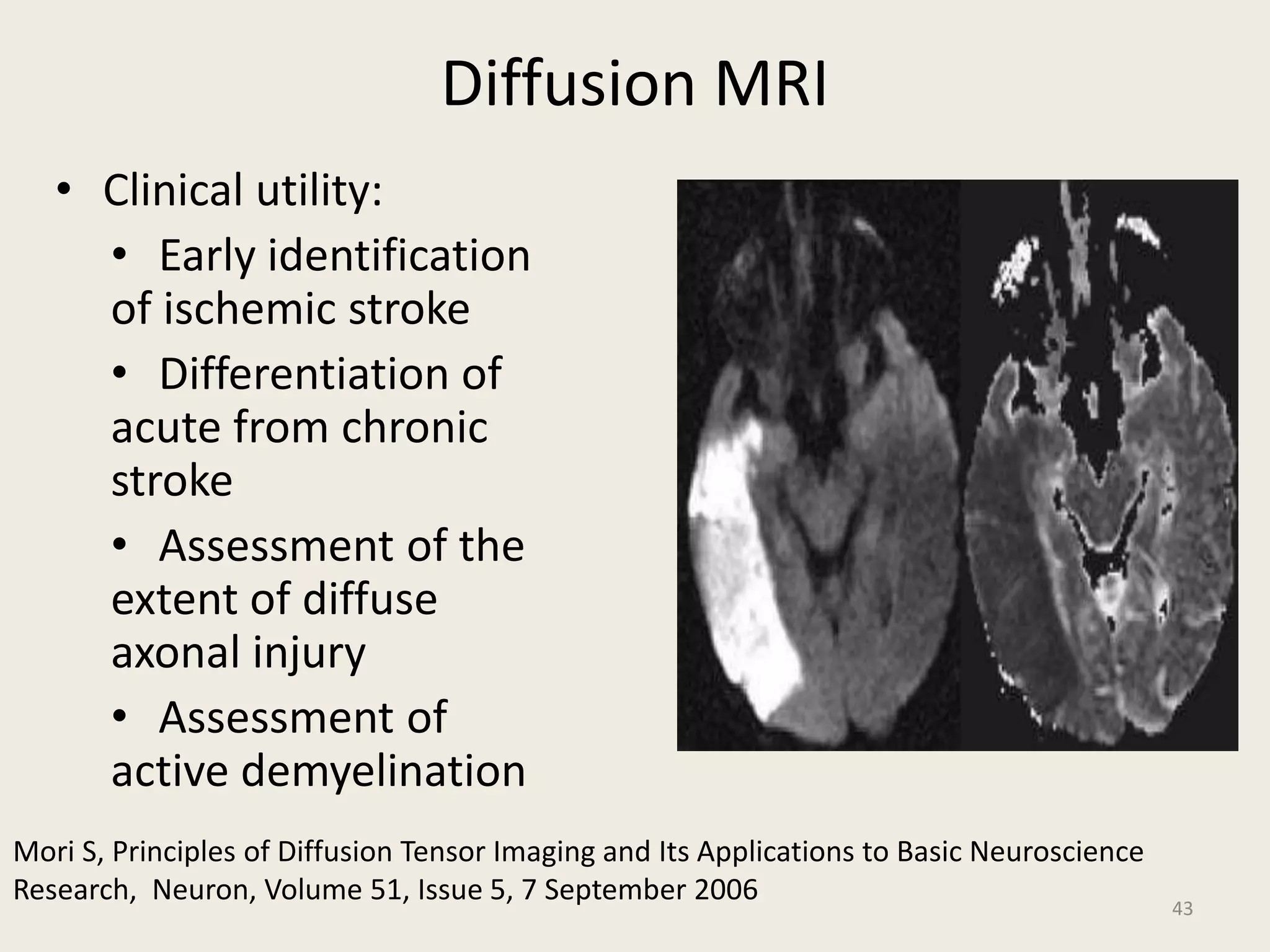
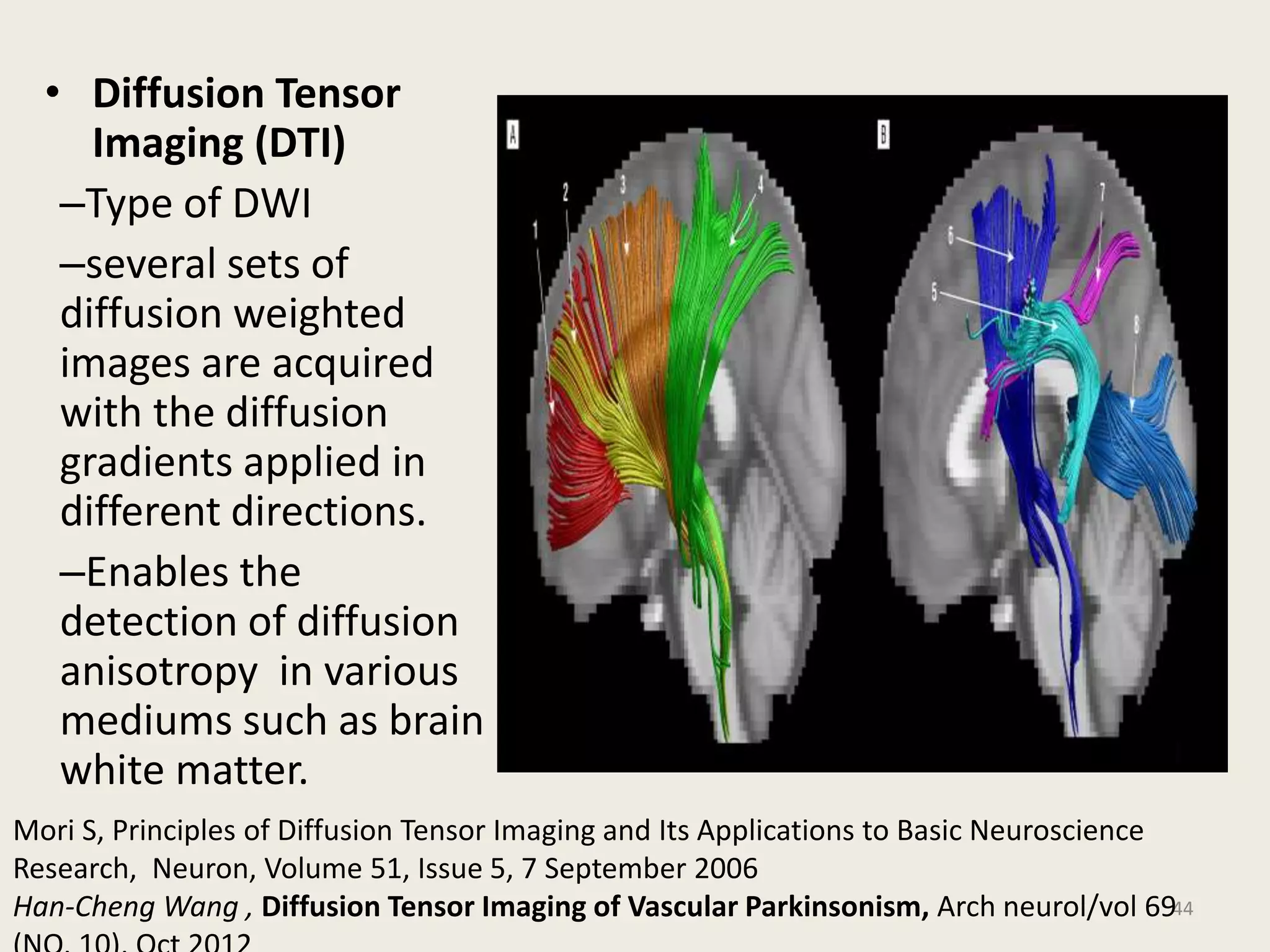
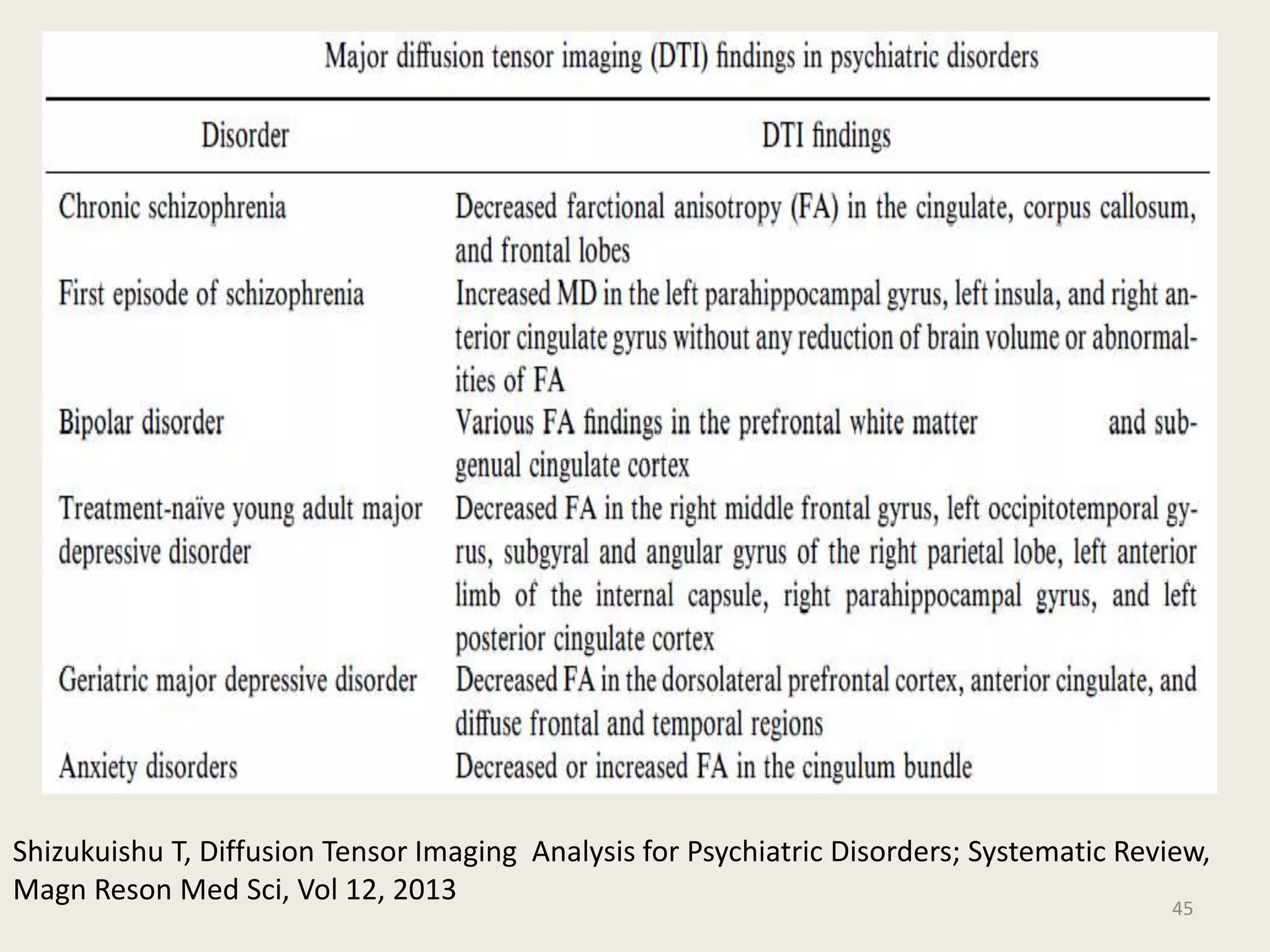
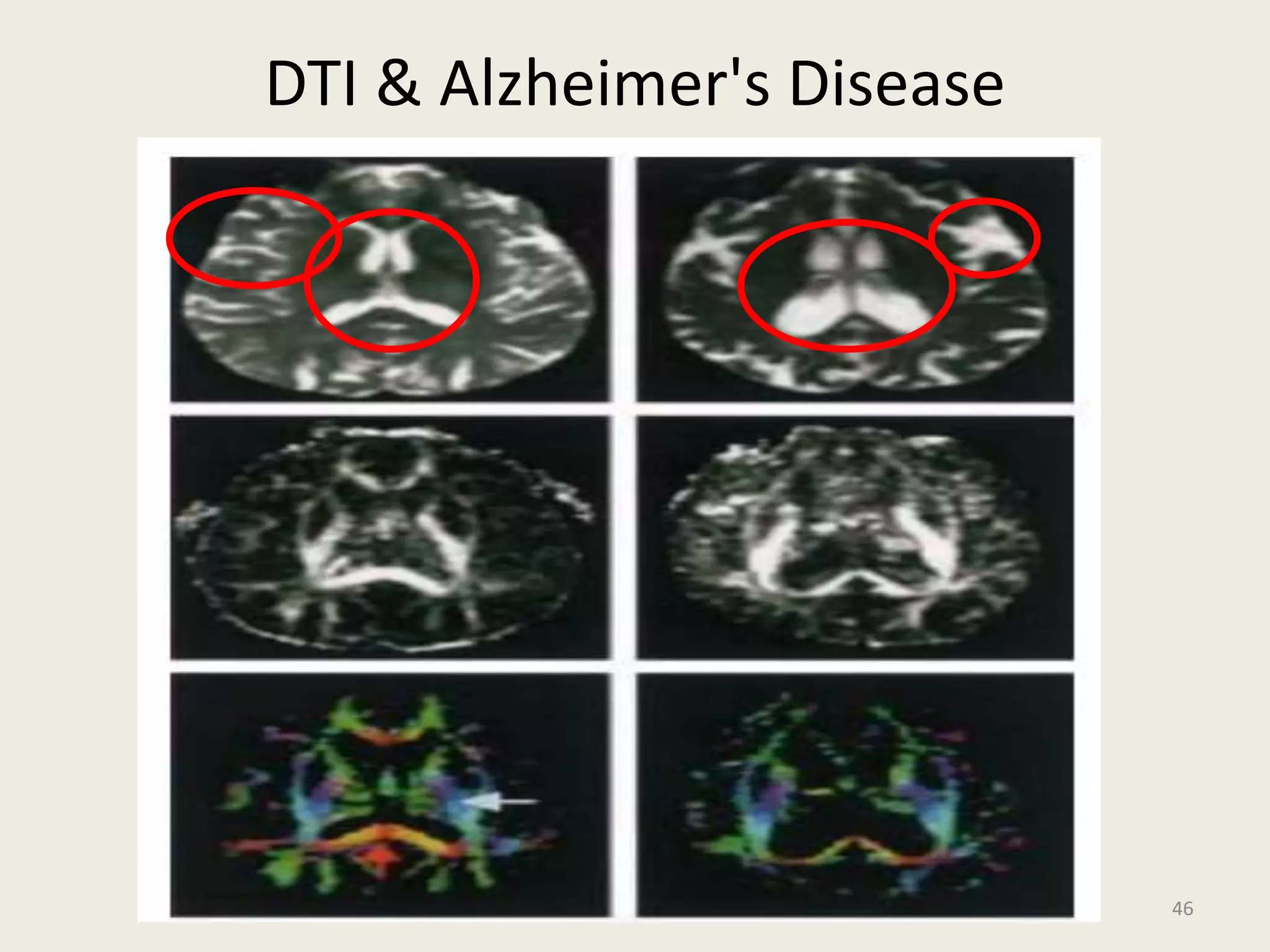
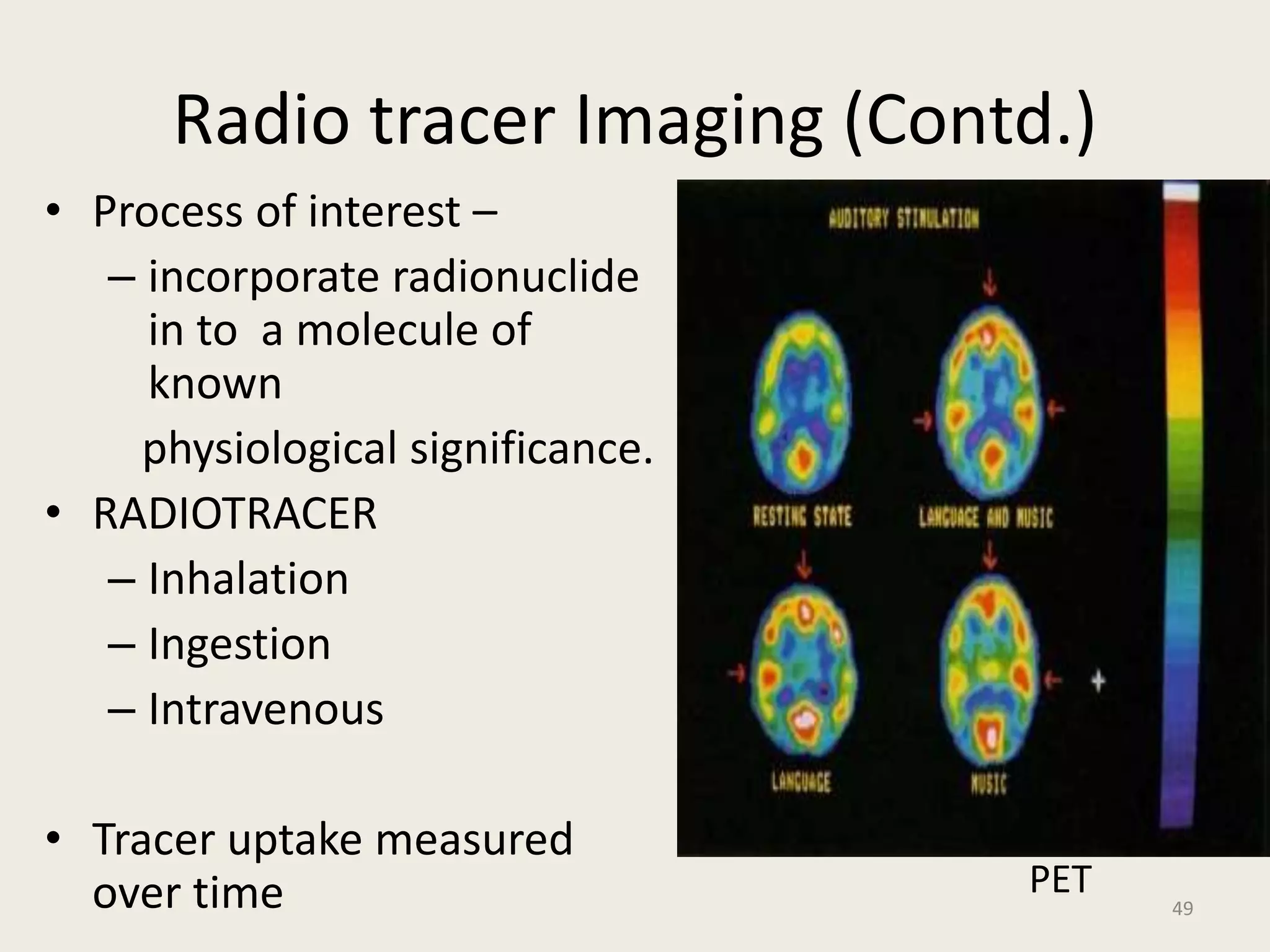
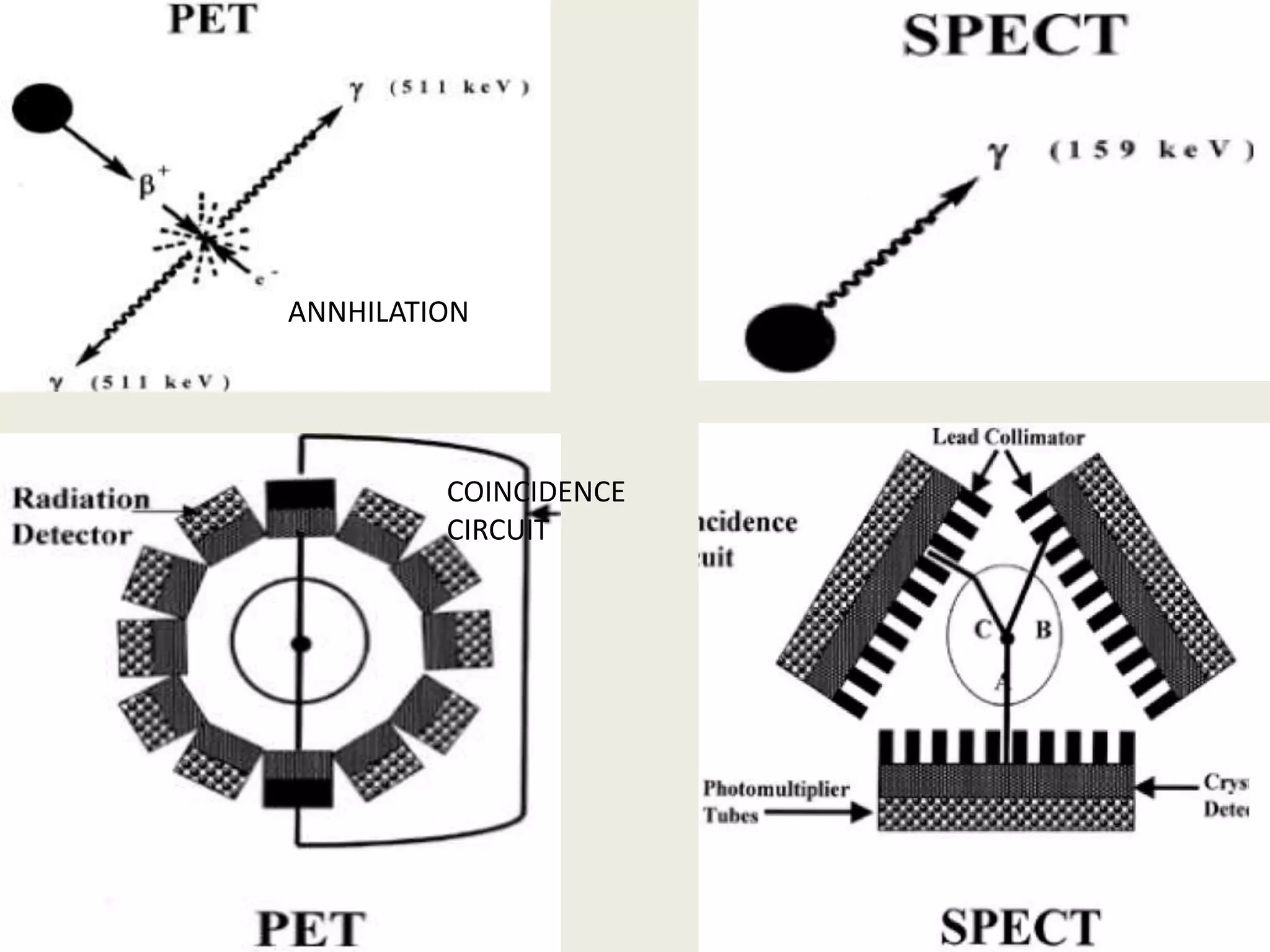
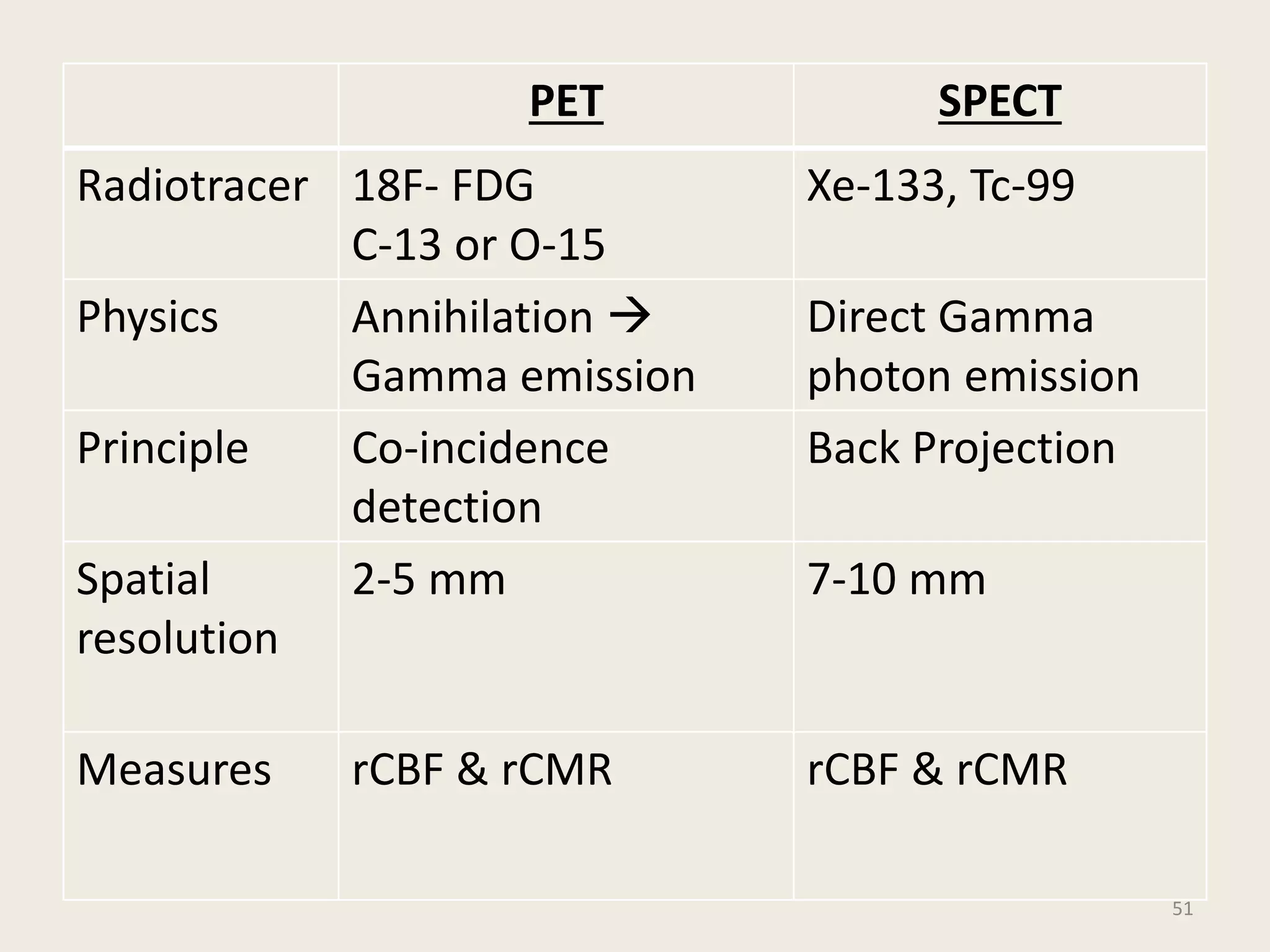
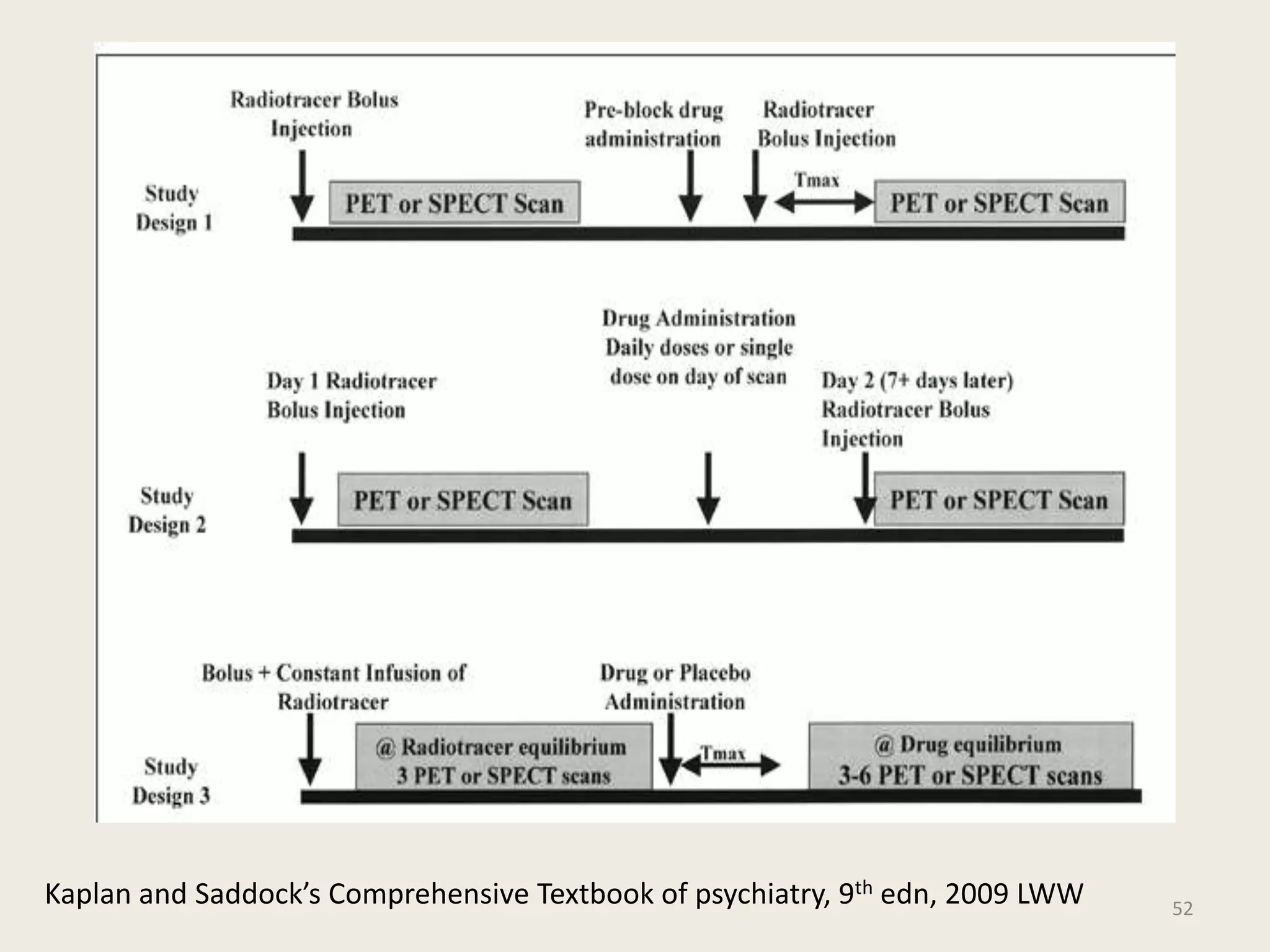
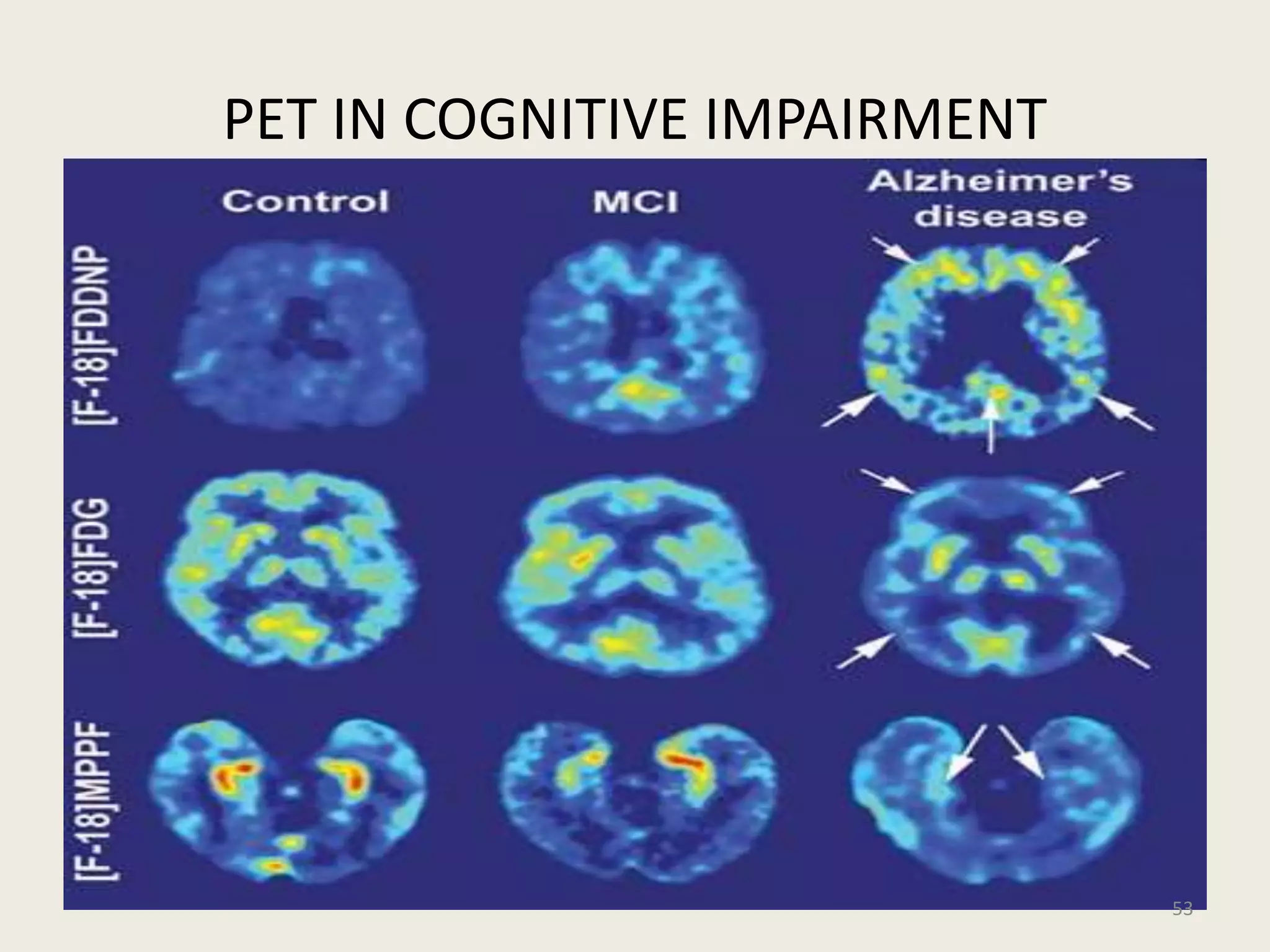
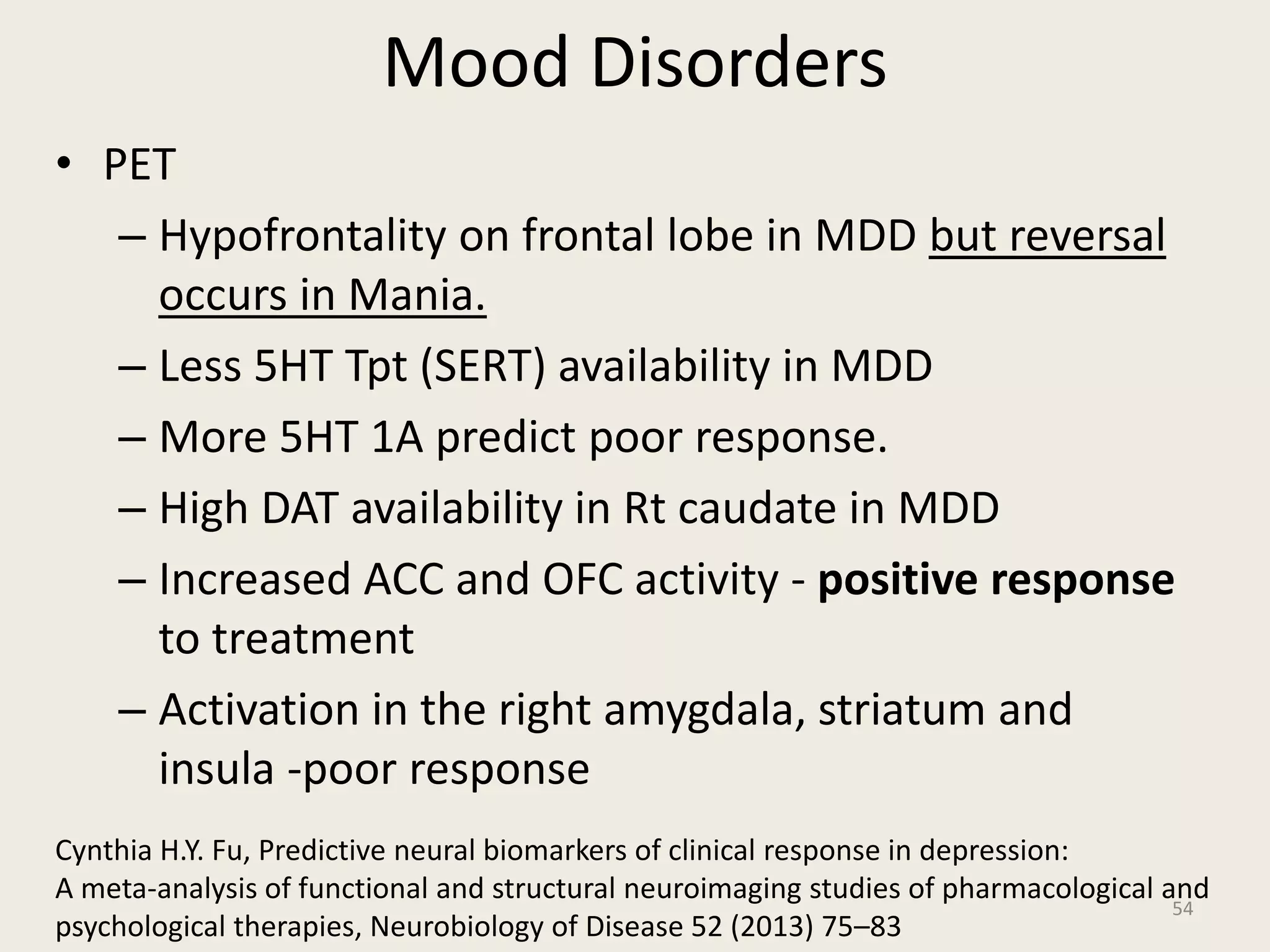
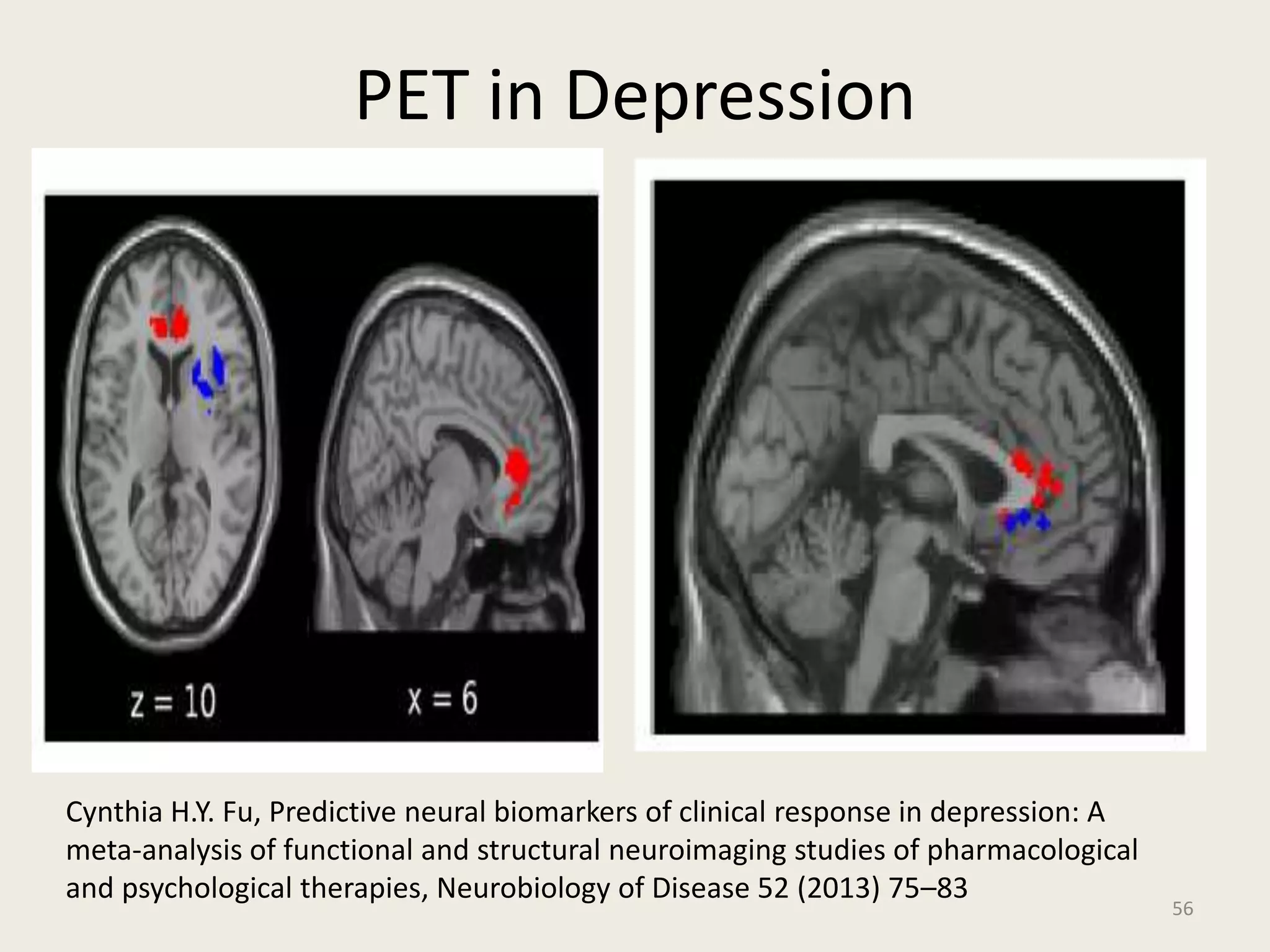
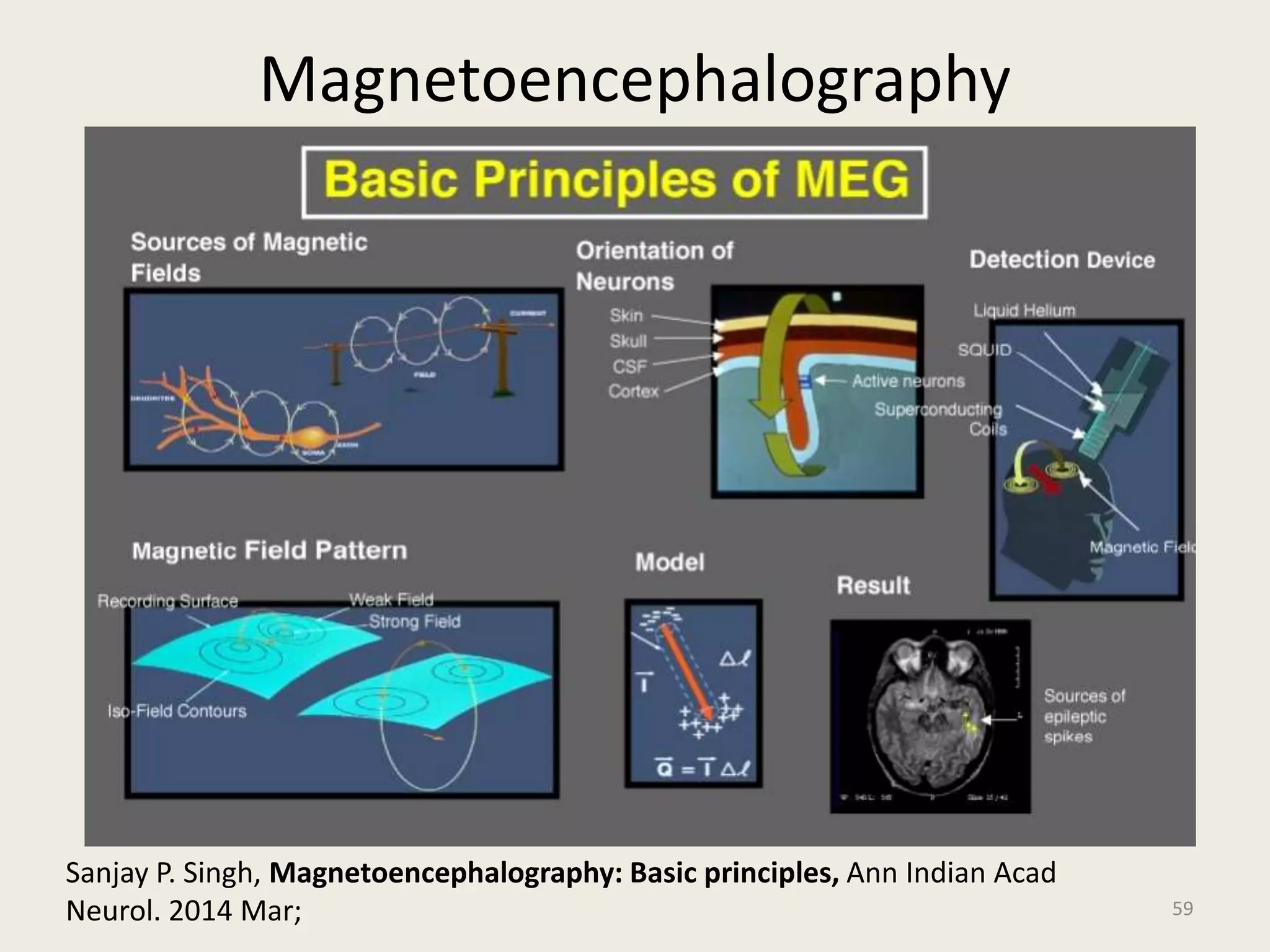
The document provides an overview of functional neuroimaging techniques used in psychiatry, including their principles, applications, and future trends. It discusses various imaging modalities such as MRI, fMRI, MRS, PET, SPECT, and diffusion tensor imaging. It describes how these techniques are used to study structural and functional correlates of psychiatric disorders and examine areas of the brain involved in conditions like schizophrenia, depression, addiction, and dementia. The document also outlines how neuroimaging is enhancing our understanding of psychopathology and treatment responses in these illnesses.