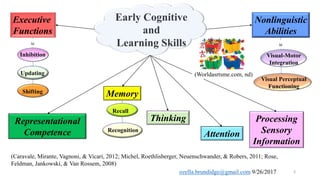
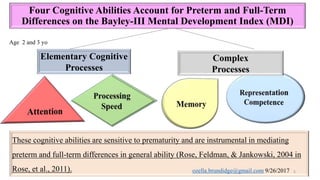
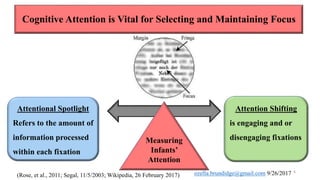
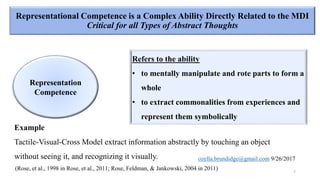
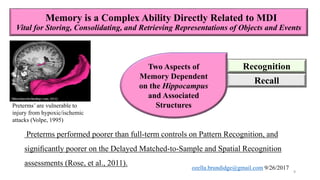
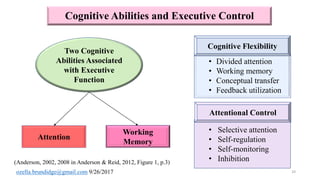
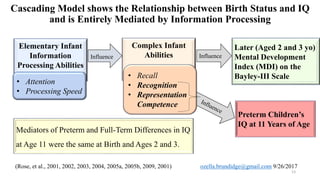
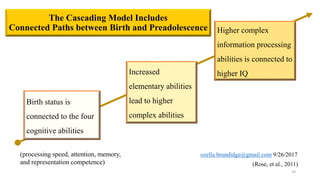
The document discusses early cognitive abilities and their relationship to factors such as birth weight and gestational age, highlighting that lower birth weight and preterm birth are linked to decreased cognitive skills and school readiness. It emphasizes the significance of attention, memory, and executive functions in cognitive development, particularly for children born prematurely. Additionally, the document outlines a cascading model that connects early cognitive abilities to later IQ, illustrating how attention and processing speed influence later cognitive outcomes.





![Cognitive and Neuropsychological Characteristics of Late
Preterm (34-36 GA) Preschoolers Born with Complications
Skills of LPT are
Associated with
Skills LPT are Not
Associated with
Visuospatial
(p=.005) Executive
Function
Visuomotor
(p=.012)
Noun Fluency
[p=.018]
Action-Verb Fluency
[p=.026]
Measured by
• Attention/Working Memory
• Receptive Language
• Expressive Language
• Nonverbal Reasoning
• Manual Coordination/
Dexterity Deficit
(Baron, Erickson, Ahronovich, Coulehan, Baker, & Litman, 2009) 15
ozella.brundidge@gmail.com 9/26/2017](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/earlycognitiveabilitiesrelatedtolearning-170926222816/85/Early-cognitive-abilities-related-to-learning-15-320.jpg)