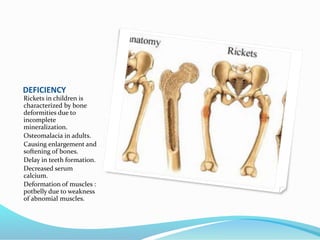
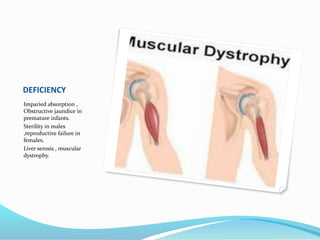
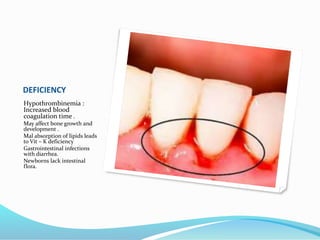
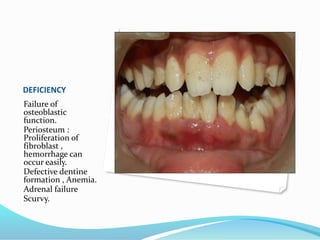
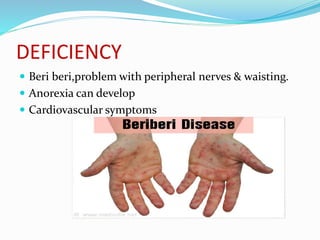
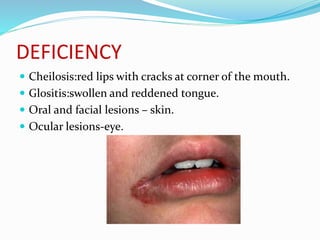
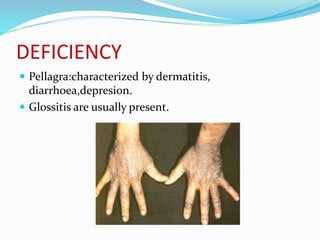
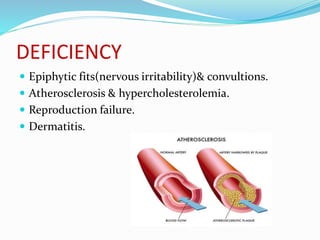
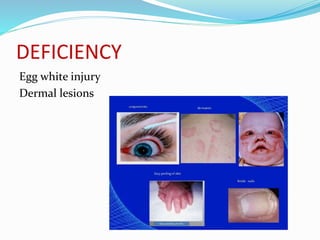
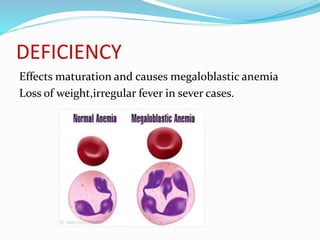
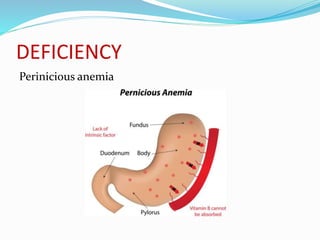
This document summarizes key vitamins and their functions. It discusses both fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) and water-soluble vitamins (C, B-complex). Each vitamin is described in terms of its chemical properties, functions in the body, food sources, and deficiency symptoms. The document provides a comprehensive overview of the essential vitamins needed for human health.