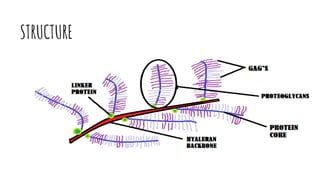
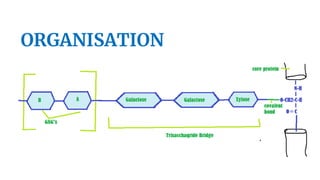
Proteoglycans are proteins covalently bonded to glycosaminoglycans and play crucial roles in the extracellular matrix, determined by the type of glycosaminoglycans involved. Different types of proteoglycans vary by tissue and cell type, with key examples including aggrecan, syndecan, serglycin, lumican, and neurocan, each with specific functions. Their structure and composition, including core proteins and glycosaminoglycan chains, are vital for their physiological roles, such as impact absorption in cartilage and cell signaling.