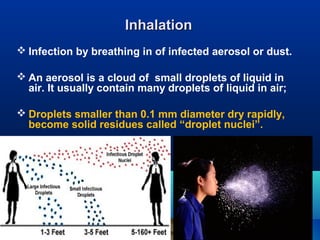
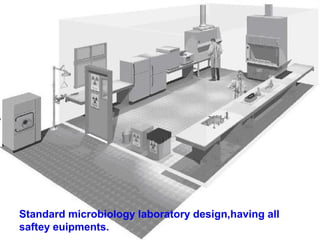
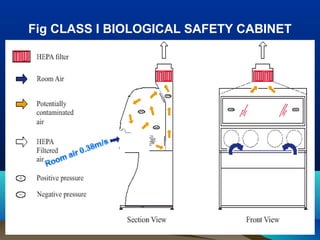
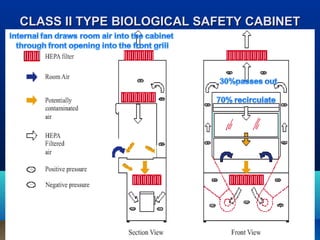
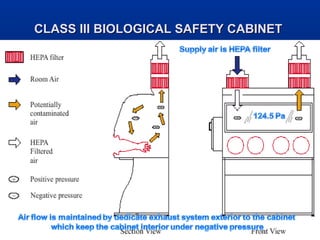
This document discusses laboratory safety, with a focus on microbiology laboratories. It outlines various routes of infection in laboratories, including inoculation, ingestion, and inhalation. Microorganisms are classified into four risk groups based on their hazards. The document also discusses codes of practice, safe laboratory design features, biological safety cabinets, and other safety measures like personal protective equipment and decontamination procedures. Proper laboratory design, facilities, and biosafety management are essential for safety.