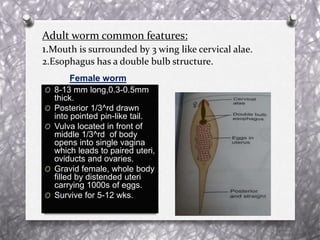
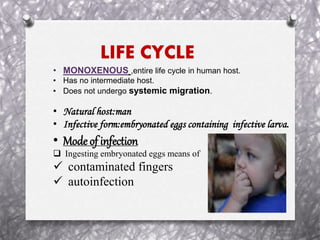
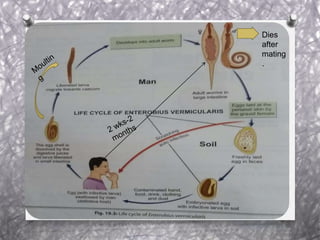
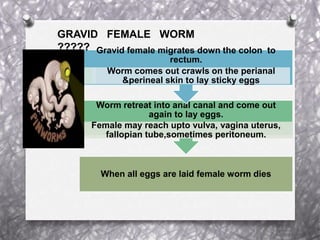
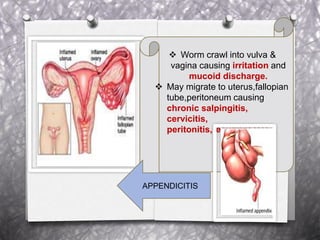
Pinworm, or Enterobius vermicularis, is a common parasitic worm that infects the human large intestine. The adult female worm lives in the caecum and colon and lays thousands of eggs per night around the anal area. The eggs are infectious within 6 hours of being laid and can remain viable for up to 2 weeks in moist conditions. People become infected by ingesting the eggs, often through hand-to-mouth contact. The life cycle is direct with no intermediate host. Pinworm infection is most common in children and can cause symptoms like anal itching and sleep disturbance.