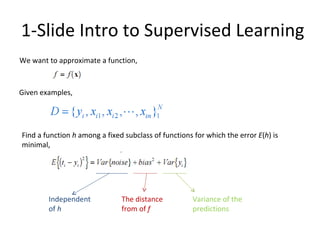
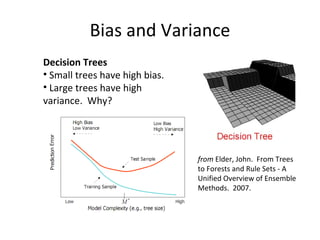
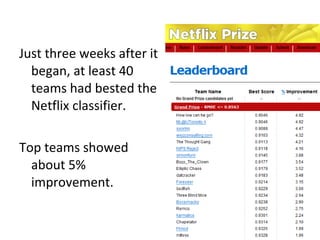
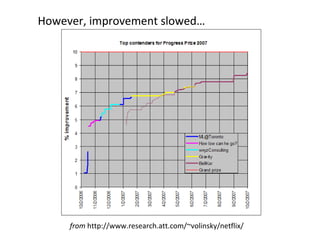
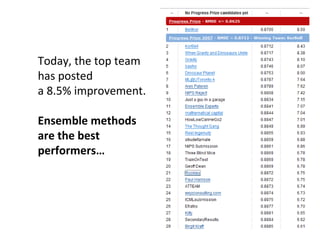
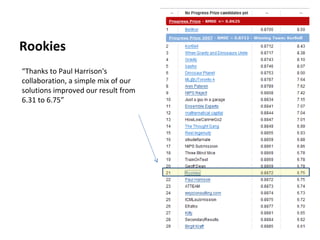
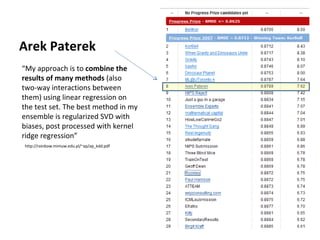
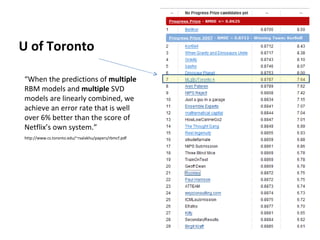
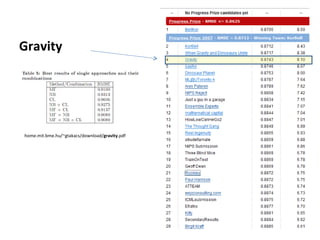
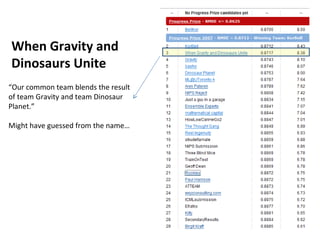
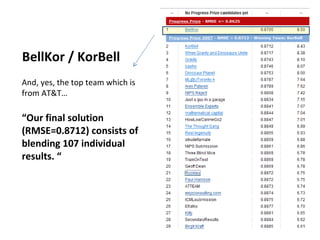
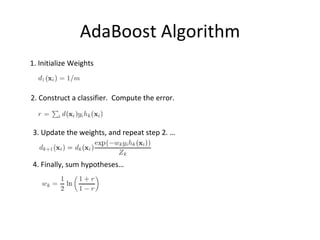
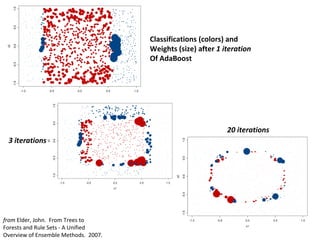
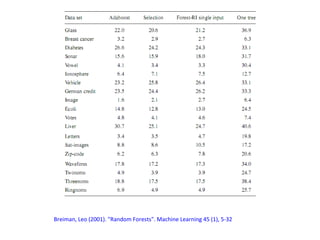
Ensemble learning methods were very successful in the Netflix Prize competition to improve movie recommendations. These methods combine the predictions from multiple models to obtain better accuracy than single models. Popular ensemble techniques included bagging, boosting, and random forests. The winning teams in the Netflix Prize all used ensemble methods that blended the predictions of dozens or hundreds of individual models.