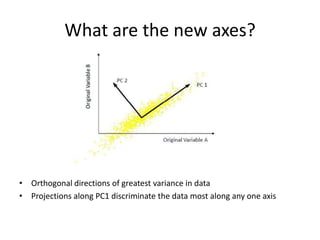
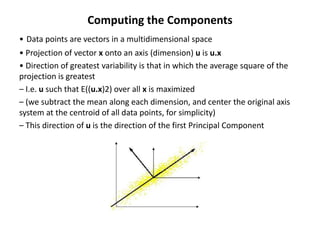
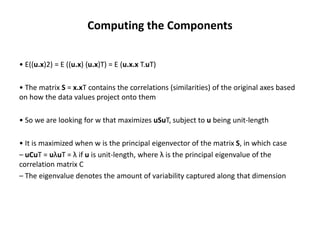
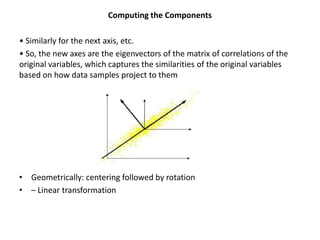
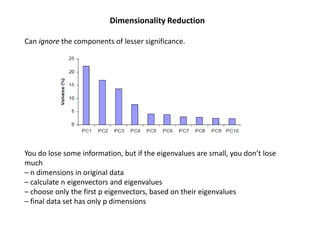
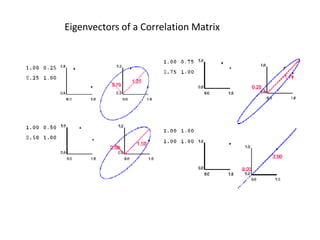
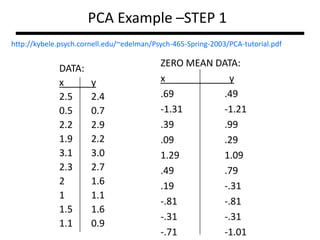
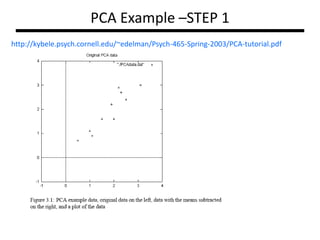
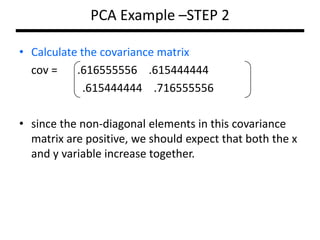
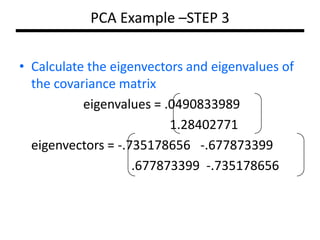
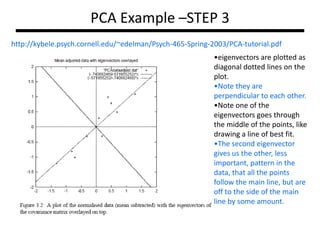
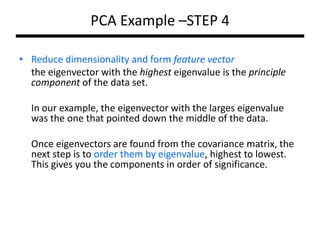
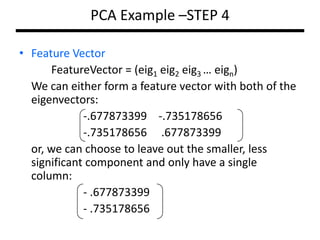
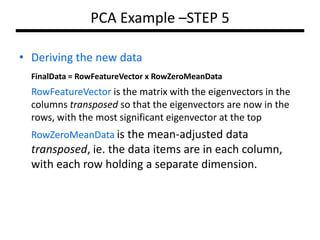
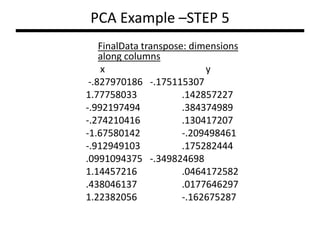
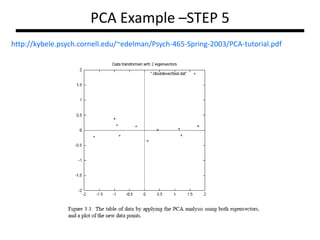
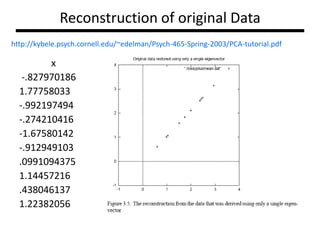
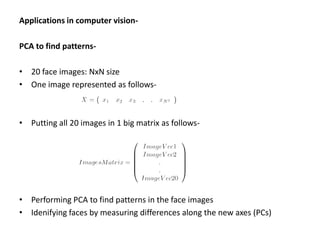
PCA transforms correlated variables into uncorrelated variables called principal components. It finds the directions of maximum variance in high-dimensional data by computing the eigenvectors of the covariance matrix. The first principal component accounts for as much of the variability in the data as possible, and each succeeding component accounts for as much of the remaining variability as possible. Dimensionality reduction is achieved by ignoring components with small eigenvalues, retaining only the most significant components.