Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


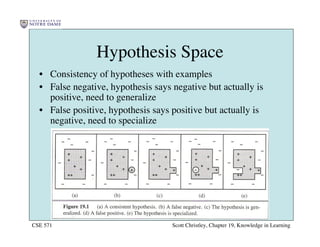



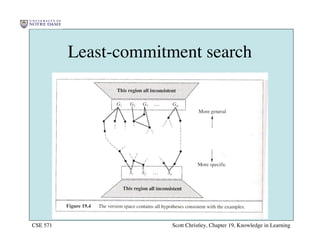


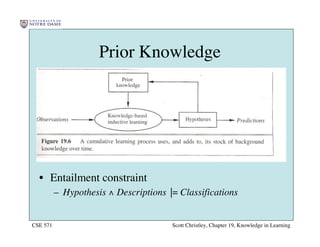
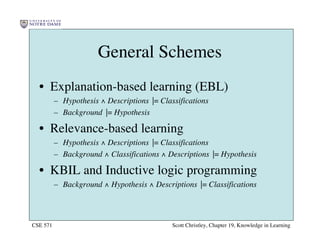

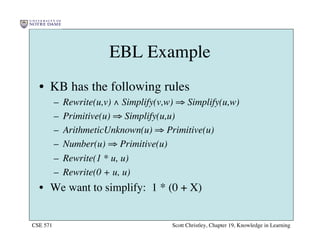
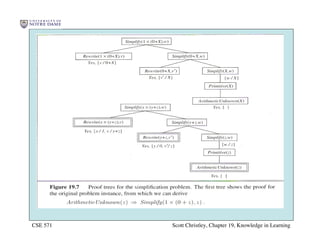
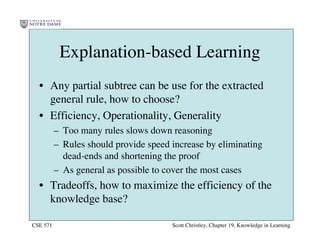
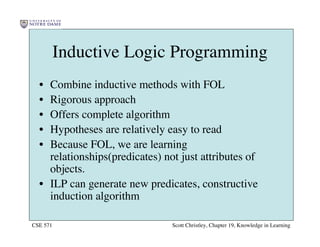
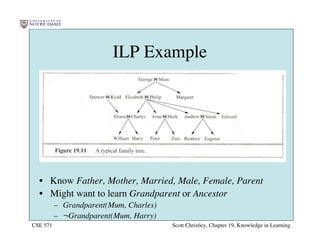


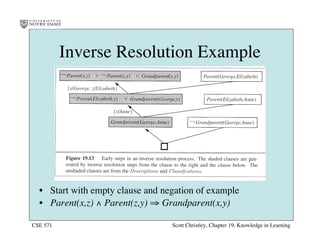


This chapter discusses different approaches for incorporating prior knowledge into machine learning algorithms. It describes decision trees/lists that represent knowledge as facts and learning first-order logic sentences that represent objects and relations. It also discusses constructing hypothesis spaces, inductive learning approaches, and search strategies like least-commitment search. Explanation-based learning and inductive logic programming are presented as ways to leverage background knowledge to more efficiently learn from examples. Inverse resolution is discussed as a way to perform inductive logic programming by running proofs backward.





















