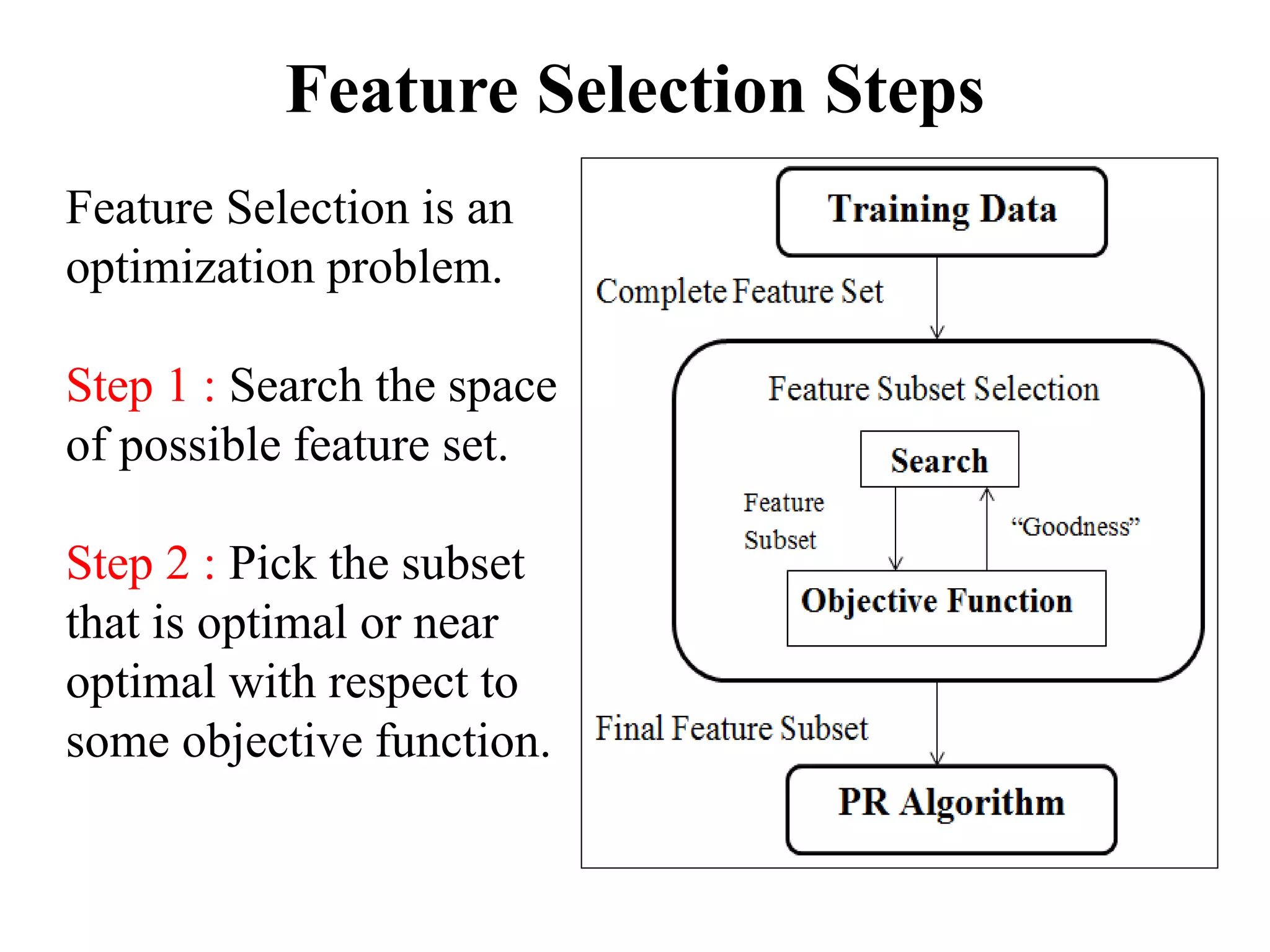
Feature selection is the process of selecting a subset of relevant features for model construction. It reduces complexity and can improve or maintain model accuracy. The curse of dimensionality means that as the number of features increases, the amount of data needed to maintain accuracy also increases exponentially. Feature selection methods include filter methods (statistical tests for correlation), wrapper methods (using the model to select features), and embedded methods (combining filter and wrapper approaches). Common filter methods include linear discriminant analysis, analysis of variance, chi-square tests, and Pearson correlation. Wrapper methods use techniques like forward selection, backward elimination, and recursive feature elimination. Embedded methods dynamically select features based on inferences from previous models.