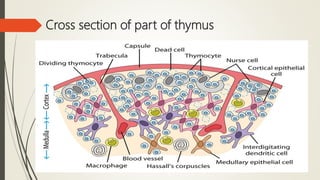
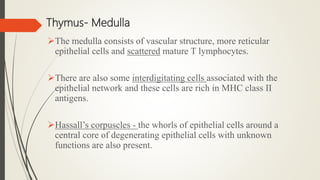
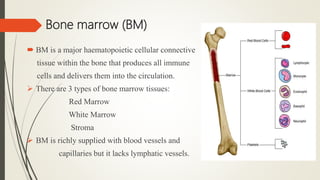
The document discusses lymphoid organs, which facilitate the production and maturation of lymphocytes, categorizing them into primary (thymus and bone marrow) and secondary (spleen and lymph nodes) types. The thymus is a crucial primary organ for T cell maturation, while the bone marrow serves both as a primary site for B cell development and a secondary lymphoid organ for antibody synthesis. Key functions of these organs include T cell education, immune response management, and the production of immune cells and antibodies.