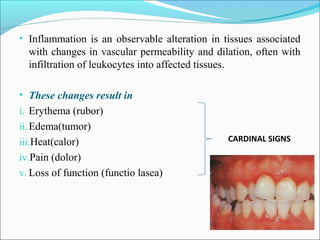
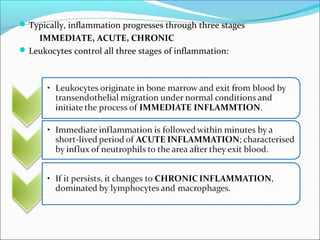
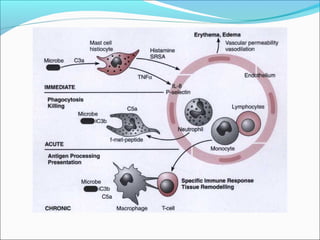
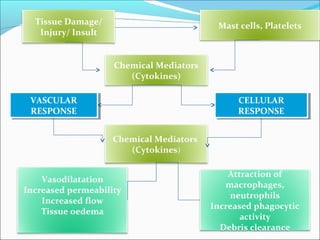
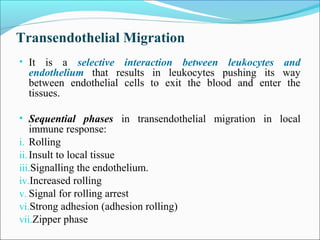
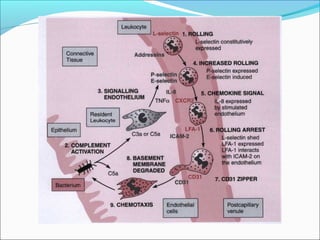
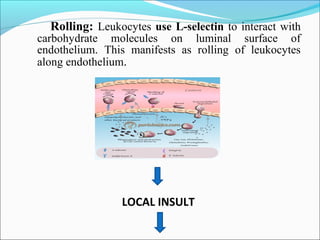
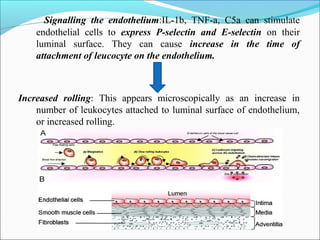
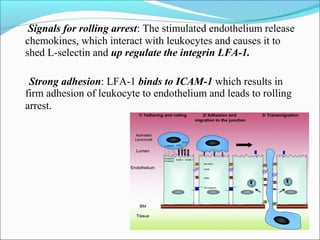
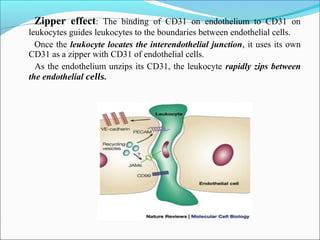
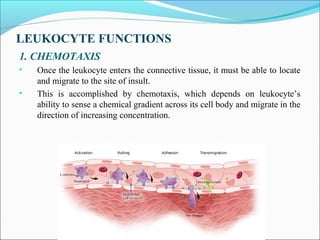
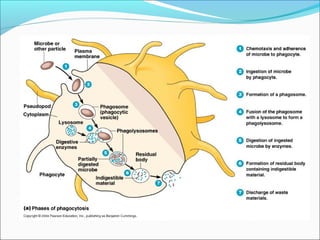
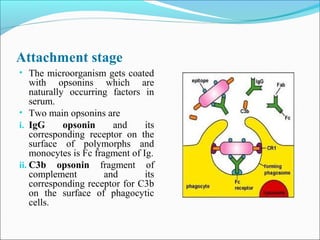
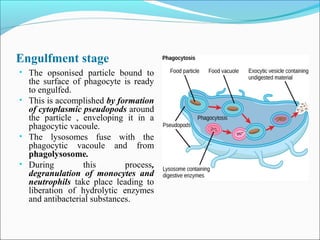
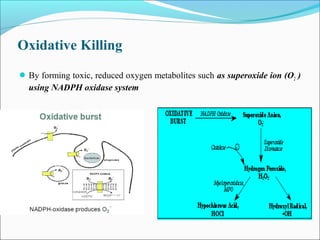
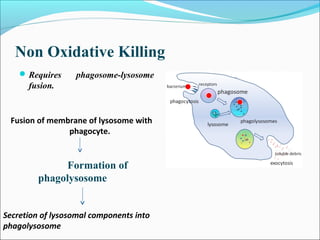
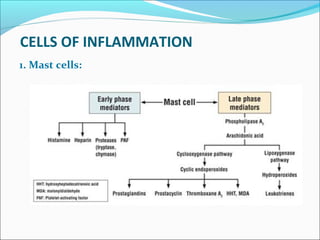
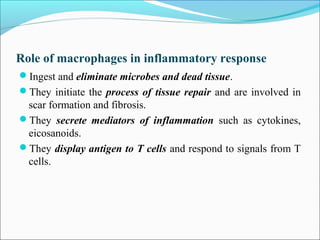
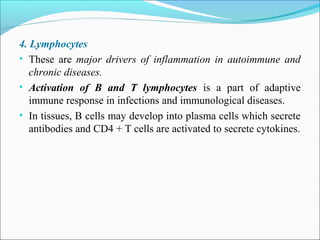
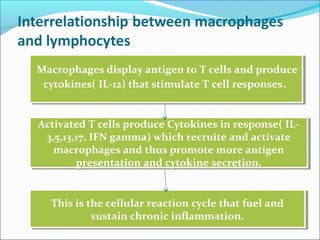
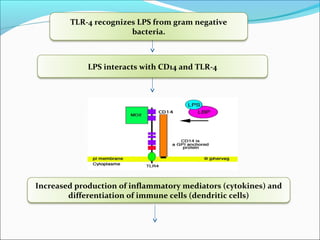
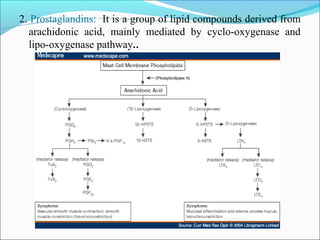
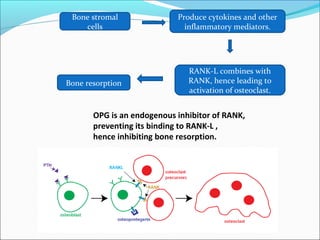
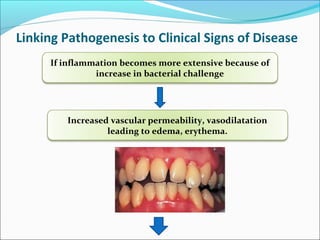
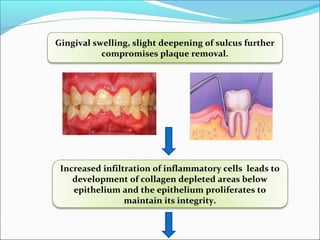
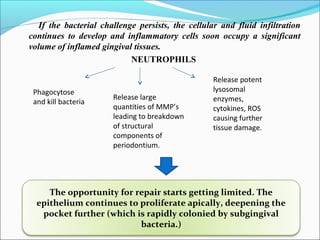
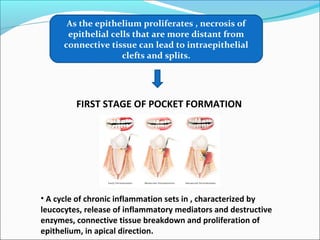
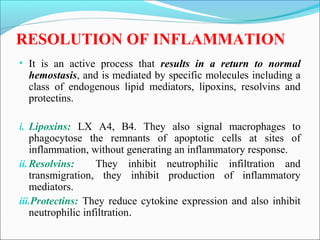
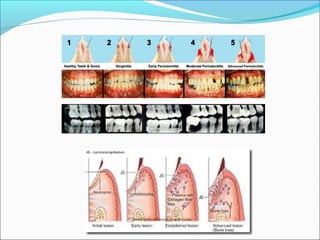
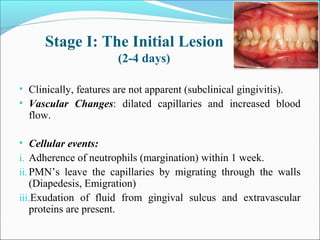
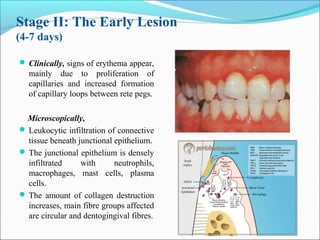
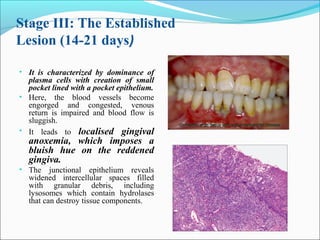
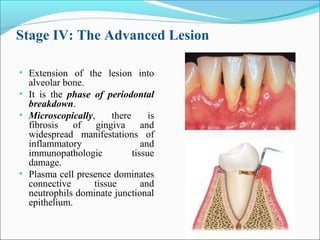
This document summarizes inflammation and its role in periodontal disease. It defines inflammation and describes the cardinal signs. It outlines the process of transendothelial migration of leukocytes and their functions, including chemotaxis and phagocytosis. It discusses the cells involved in inflammation and the inflammatory responses that occur in the periodontium. It then links the pathogenesis of periodontal disease to the clinical signs seen, involving the destruction of connective tissue attachment and bone loss due to an imbalance between pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators. Resolution of inflammation is also briefly mentioned.