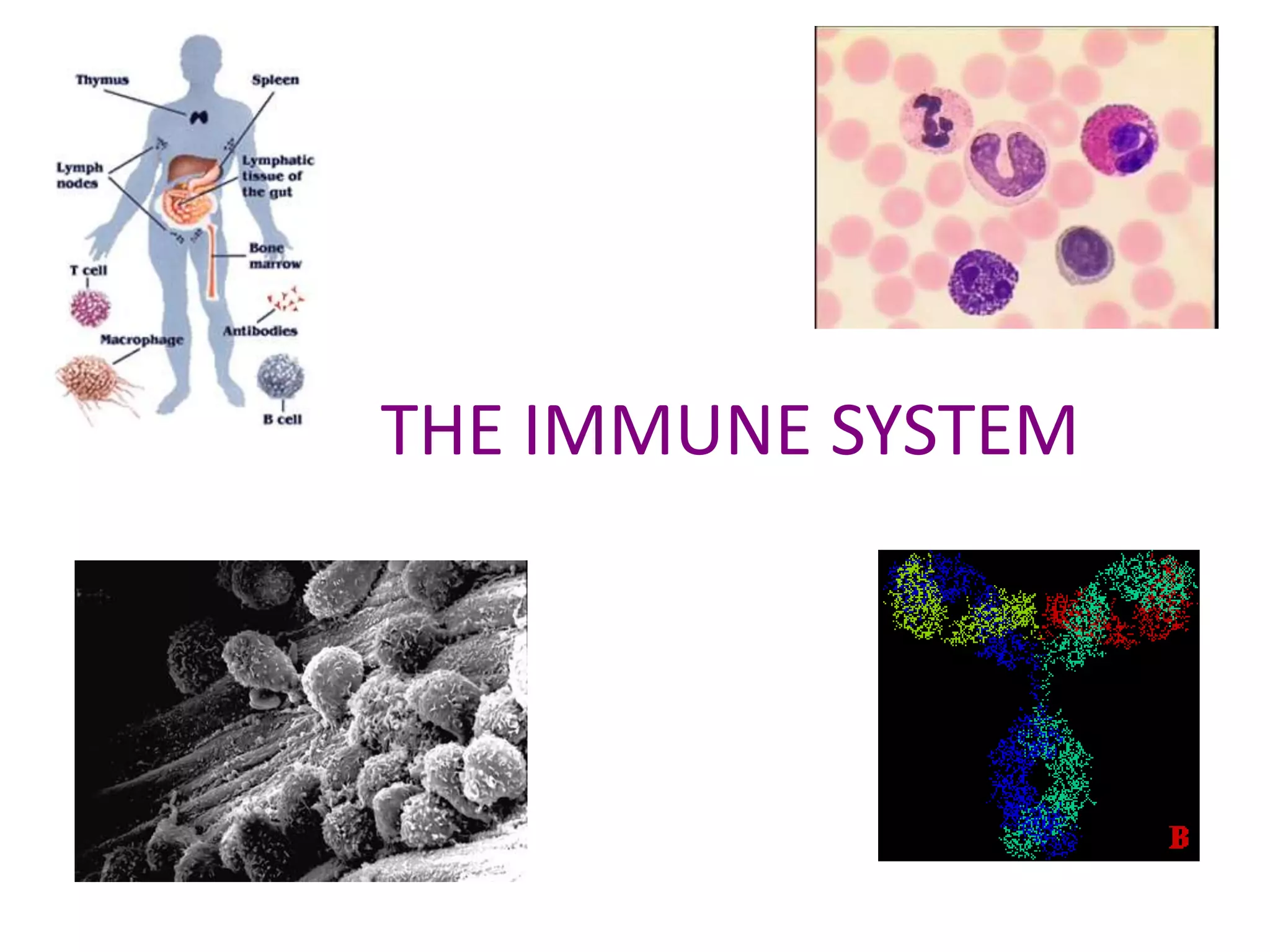
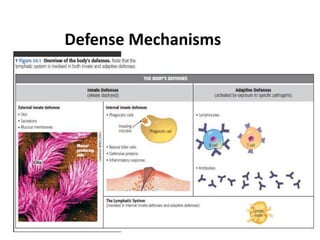
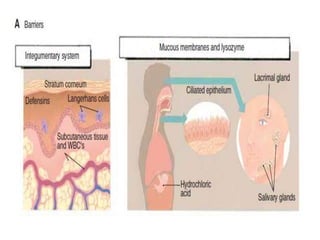
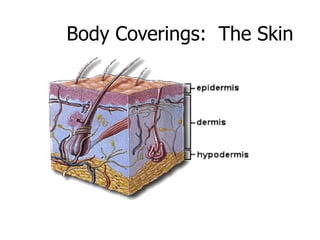
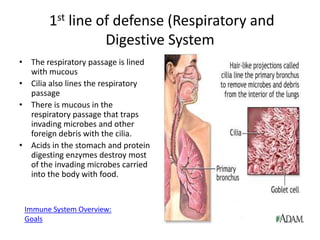
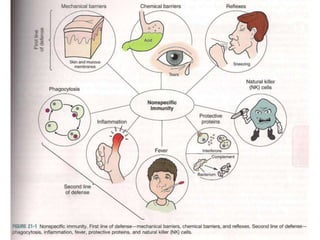
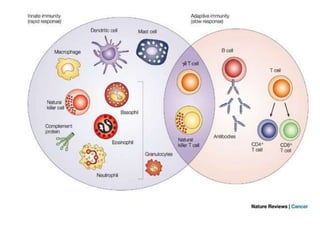
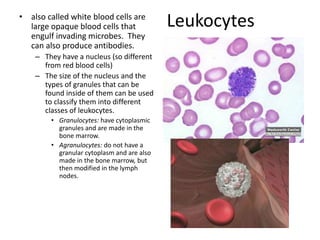
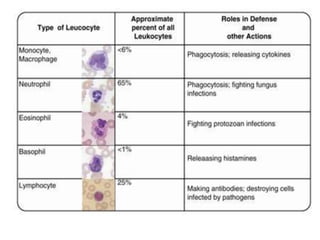
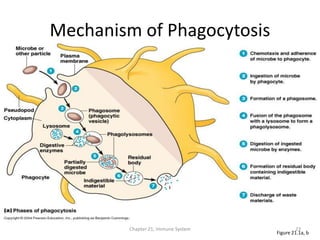
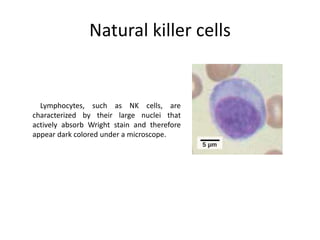
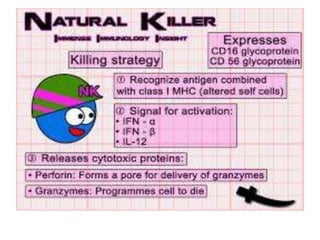
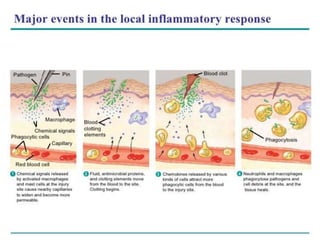
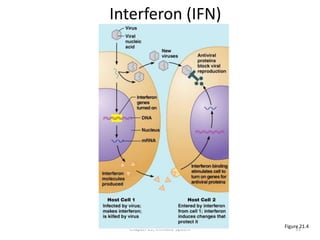
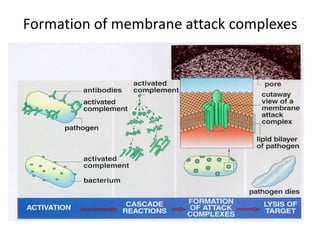
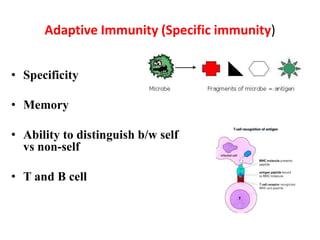
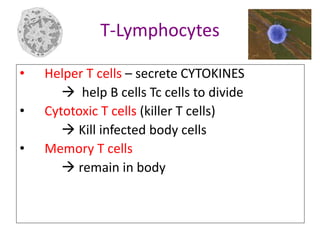
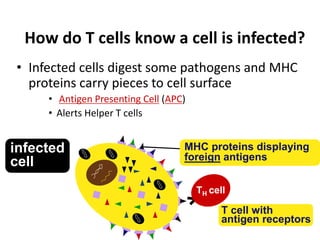
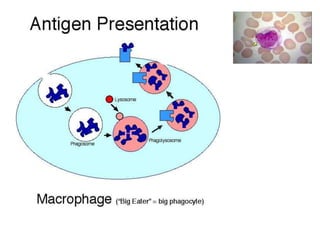
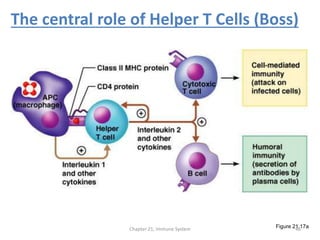
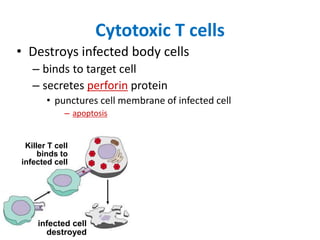
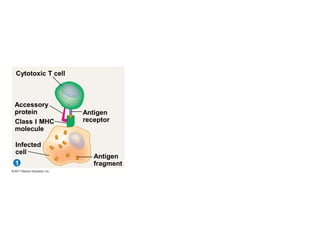
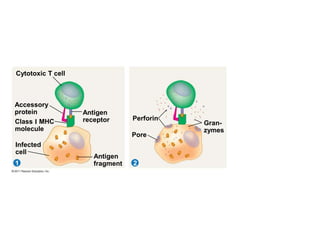
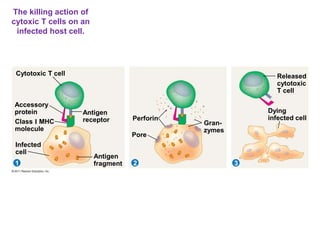
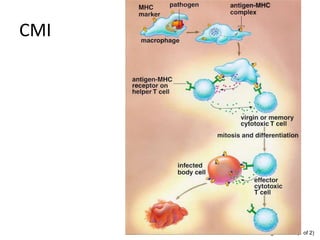
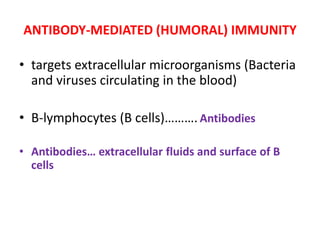
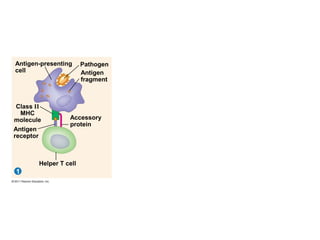
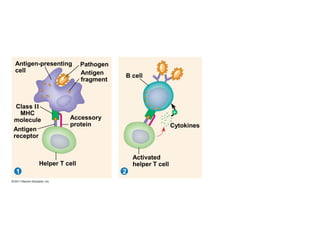
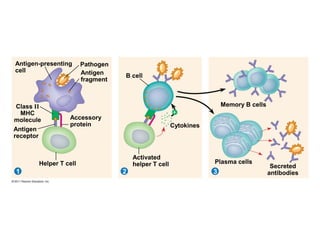
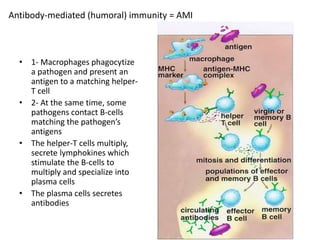
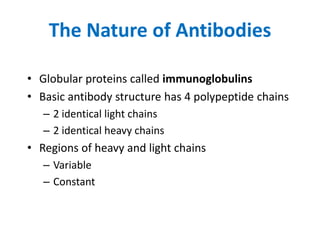
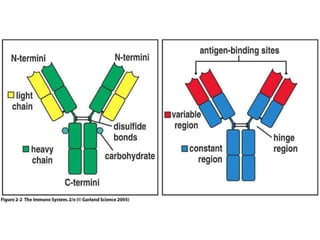
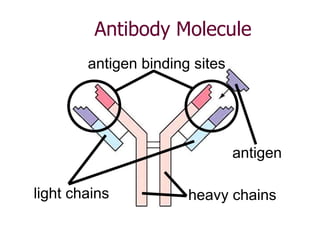
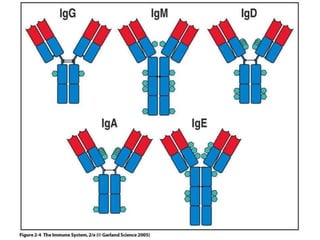
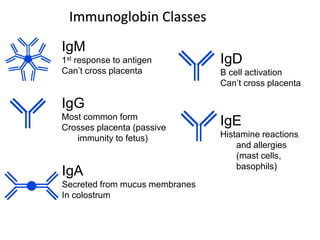
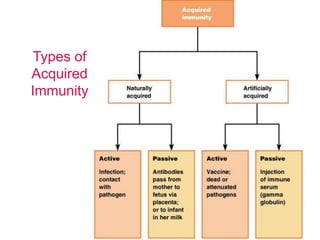
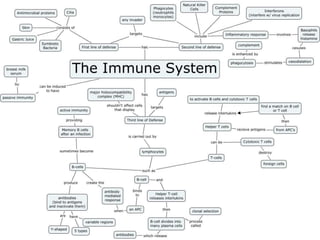
The immune system has two main lines of defense - innate (non-specific) and adaptive (specific). The innate system provides immediate protection and involves physical and chemical barriers like skin and stomach acid. If pathogens breach these barriers, the second line uses phagocytes, natural killer cells, and inflammation to attack invaders. The adaptive system has a delayed but stronger response that involves lymphocytes. It distinguishes self from non-self and has immunological memory, providing lifelong protection against reinfection.