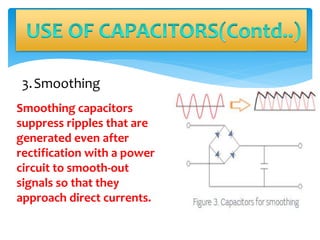
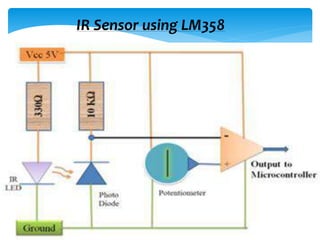
This document provides information on various electronic components including resistors, capacitors, inductors, connectors, LEDs, IR modules, op-amps, and motor driver ICs. Resistors oppose current flow and have a potential drop. Capacitors store charge and are used for coupling, decoupling, and smoothing circuits. Inductors store energy in magnetic fields. The LM358 op-amp can be used as a comparator to convert analog sensor signals to digital outputs. The H-bridge and L293D motor driver ICs enable controlling motor direction and speed. An IR sensor module uses an IR LED transmitter and photodiode receiver with the LM358 to detect objects based on reflected infrared light.