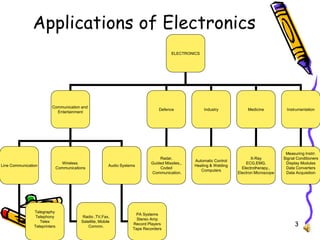
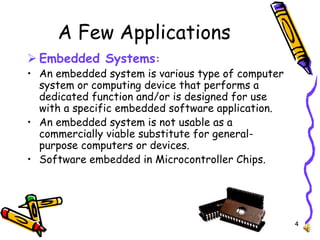
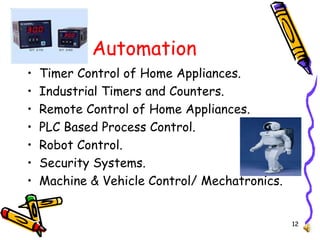
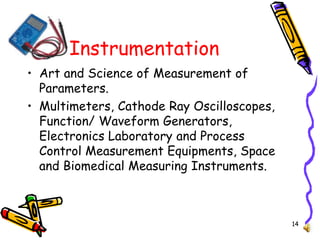
El documento detalla las tendencias y aplicaciones de la electrónica, abarcando desde la mecánica de electrones y dispositivos electrónicos hasta sistemas de comunicación, automatización y medicina. Destaca tecnologías como RFID, comunicaciones móviles y satelitales, así como la importancia de la electrónica en industrias como la defensa y el entretenimiento. Se presentan ejemplos específicos y se menciona el uso de sistemas embebidos en diversas aplicaciones.