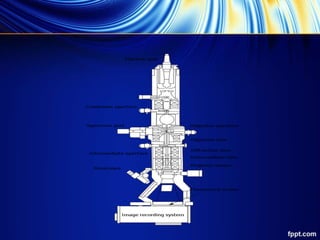
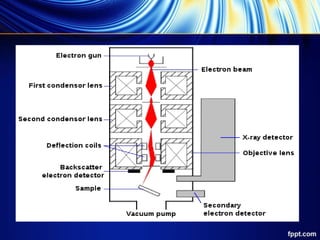
An electron microscope uses accelerated electrons for illumination, providing higher resolving power than light microscopes, and is capable of analyzing objects smaller than 0.2 micrometers. Types of electron microscopes include transmission electron microscopes (TEM) and scanning electron microscopes (SEM), each with specific applications in materials science, biology, and nanotechnology. TEM offers high resolution and magnification but has limitations in sample preparation and throughput, while SEM provides detailed surface images but may struggle with detecting lighter elements.