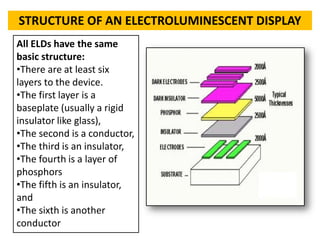
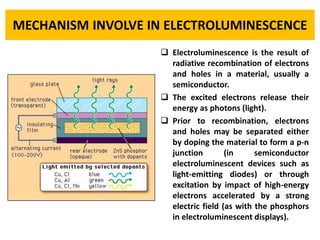
This document discusses electroluminescence and electroluminescent displays. It begins by defining electroluminescence as the emission of light from a material in response to electricity. There are two mechanisms for electroluminescence - intrinsic and charge injection. It then covers electroluminescent materials and devices, describing common inorganic and organic materials used, as well as the basic structure and functioning of electroluminescent displays and their advantages over other display technologies. It concludes by discussing the history and applications of electroluminescent displays.



![ELECTROLUMINESCENT MATERIALS
•There may be either organic or inorganic electroluminescent materials. The active materials are generally semiconductors of wide enough bandwidth to allow exit of the light.
•The most typical inorganic thin-film EL (TFEL) is ZnS:Mnwith yellow- orange emission. Examples of the range of EL material include:
Powdered zinc sulfide doped with copper (producing greenish light) or silver (producing bright blue light)
Thin-film zinc sulfide doped with manganese (producing orange-red color)
Naturally blue diamond, which includes a trace of boron that acts as a dopant.
Semiconductors containing Group III and Group V elements, such as indium phosphide(InP), gallium arsenide (GaAs), and gallium nitride (GaN).
Certain organic semiconductors, such as [Ru(bpy)3]2+(PF6-)2, where bpyis 2,2'-bipyridine.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electroluminesecnce-140911000941-phpapp02/85/Electroluminesecnce-6-320.jpg)