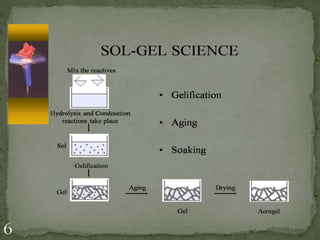
This document provides information about the sol-gel method process, which consists of several steps: 1) formation of a sol through hydrolysis and condensation reactions, 2) gel formation through further condensation and polycondensation, 3) drying to produce aerogels or xerogels, 4) calcination to remove organic species and densify the gel, and 5) heat treatment to shape the material. The sol-gel method allows production of monosized nanoparticles and synthesis of glasses and ceramics at lower temperatures but controlling particle growth and agglomeration can be challenging.