This document provides an introduction to organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). It describes OLEDs as thin, flexible displays that are self-luminous and more energy efficient than LCD displays. The document discusses the components and manufacturing of OLEDs. It explains that OLEDs work by emitting light through a process called electrophosphorescence when electricity is applied. Different types of OLEDs are described, including passive matrix OLEDs best for small screens, and active matrix OLEDs more suitable for large displays. Advantages of OLEDs over LCDs are highlighted as lower power consumption, higher power efficiency, and less power needed to produce the same brightness.
![OLED
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
Imagine having high definition TV that is 80 inches wide and less than a quarterinch thick, consumes less power than most TVs on the market today and can be rolled up
when you're not using it. What if you could have a "heads up" display in your car? How
about a display monitor built into your clothing? These devices may be possible in the
near future with the help of a technology called organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs).
Figure 1.1: Samsung's prototype 40-inch OLED TV
OLEDs are solid-state devices composed of thin films of organic molecules that
create light with the application of electricity. OLEDs can provide brighter, crisper
displays on electronic devices and use less power than conventional light emitting
diodes (LEDs) or liquid crystal displays (LCDs) used today.[3]
1.1 WHAT IS OLED?
An OLED is a solid state device or electronic device that typically consists of
organic thin films sandwiched between two thin film conductive electrodes. When
electrical current is applied, a bright light is emitted. OLED use a carbon-based designer
molecule that emits light when an electric current passes through it. This is called
electrophosphorescence. Even with the layered system, these systems are thin . usually
less than 500 nm or about 200 times smaller than a human hair.[3]
DEPT OF ECE, CBIT, KOLAR
2014
Page 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oledreport-140301074235-phpapp02/75/OLED-report-2014-1-2048.jpg)
![OLED
When used to produce displays. OLED technology produces self-luminous
displays that do not require backlighting and hence more energy efficient. These
properties result in thin, very compact displays. The displays require very little power, ie,
only 2-10 volts.[6]
OLED technology uses substances that emit red, green, blue or white light.
Without any other source of illumination, OLED materials present bright, clear video
and images that are easy to see at almost any angle. Enhancing organic material
helps to control the brightness and colour of light, i.e, the brightness of an
OLED
is
determined
by
how
much
power
you
supply
to
the
system.
1.2 LITERATURE SURVEY
The first observations of electroluminescence in organic materials were in the early
1950s by A. Bernanose and co-workers at the Nancy-Université, France. They applied
high-voltage alternating current (AC) fields in air to materials such as acridine orange,
either deposited on or dissolved in cellulose or cellophane thin films. The proposed
mechanism was either direct excitation of the dye molecules or excitation of electrons.
In 1960, Martin Pope and co-workers at New York University developed ohmic
dark-injecting electrode contacts to organic crystals. They further described the necessary
energetic requirements (work functions) for hole and electron injecting electrode contacts.
These contacts are the basis of charge injection in all modern OLED devices. Pope's
group also first observed direct current (DC) electroluminescence under vacuum on a
pure single crystal of anthracene and on anthracene crystals doped with tetracene in 1963
using a small area silver electrode at 400V. The proposed mechanism was fieldaccelerated electron excitation of molecular fluorescence.[5]
Pope's group reported in 1965 that in the absence of an external electric field, the
electroluminescence in anthracene crystals is caused by the recombination of a
thermalized electron and hole, and that the conducting level of anthracene is higher in
energy than the exciton energy level. Also in 1965, W. Helfrich and W. G. Schneider of
the National Research Council in Canada produced double injection recombination
electroluminescence for the first time in an anthracene single crystal using hole and
electron injecting electrodes, the forerunner of modern double injection devices. In the
same year, Dow Chemical researchers patented a method of preparing electroluminescent
cells using high voltage (500–1500 V) AC-driven (100–3000 Hz) electrically-insulated
one millimetre thin layers of a melted phosphor consisting of ground anthracene powder,
DEPT OF ECE, CBIT, KOLAR
2014
Page 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oledreport-140301074235-phpapp02/85/OLED-report-2014-2-320.jpg)
![OLED
tetracene, and graphite powder. Their proposed mechanism involved electronic excitation
at the contacts between the graphite particles and the anthracene molecules.[4]
Device performance was limited by the poor electrical conductivity of
contemporary organic materials. This was overcome by the discovery and development of
highly conductive polymers. For more on the history of such materials, see conductive
polymers.[1]
Electroluminescence from polymer films was first observed by Roger Partridge at
the National Physical Laboratory in the United Kingdom. The device consisted of a film
of poly(n- vinylcarbazole) up to 2.2 micrometres thick located between two charge
injecting electrodes. The results of the project were patented in 1975 and published in
1983.
The first diode device was reported at Eastman Kodak by Ching W. Tang and
Steven Van Slyke in 1987.This device used a novel two-layer structure with separate hole
transporting and electron transporting layers such that recombination and light emission
occurred in the middle of the organic layer. This resulted in a reduction in operating
voltage and improvements in efficiency and led to the current era of OLED research and
device production.Research into polymer electroluminescence culminated in 1990 with J.
H. Burroughes et al. at the Cavindish laboratory in Cambridge reporting a high efficiency
green light-emitting polymer based device using 100 nm thick films of poly(p-phenylene
vinylene).[2]
DEPT OF ECE, CBIT, KOLAR
2014
Page 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oledreport-140301074235-phpapp02/85/OLED-report-2014-3-320.jpg)














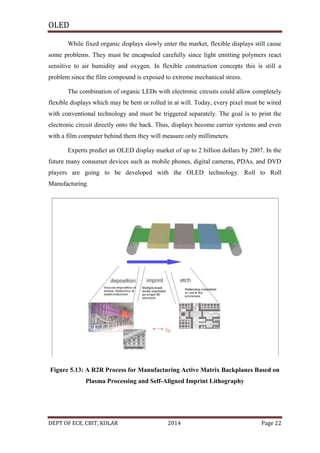





![OLED
BIBILIOGRAPHY
[1]
Delnet online http://www.mdpi.com/109-4300/15/6/2277
[2]
http://www.jgateplus.com/KohnoT, Kuranaga T, Kasai N, Akimoto H,”AMOLED
Display for thin film”, Proceedings of IEEE Transactions on Electron,devices,
Vol-60,No11,Nov 2013,pp-378-396
[3]
S. Yamazaki, J. Koyama, Y. Yamamoto, K. Okamoto,”Overview of OLED
Display Technology.” Proceedings of.SID Symp. Dig. Tech, Vol 183,Nov
2011,pp-15-23
[4]
S. Reineke, F. Lindner, G. Schwartz, N. Seidler, K. Walzer, B.Lussem, K.Leo,
”Better displays with organic display”,Proceedings of Nature,Vol 459,Nov 2009,
pp-234-287
[5]
S.-H. Pieh, M.-S. Kim, C.-J. Sung, J.-D. Seo, H.-S. Choi,C.-W. Han, Y.-H. Tak,
SID,”AMOLED materials and OLED displays”,Proceedings of Symposium
Digest,Vol 40,Dec 2009, pp-903-1888
[6]
M. W. Lee, O. K. Song, Y. M. Koo, Y. H. Lee, H. K.Chung, and S. S. Kim, SID”
Sensitive film in OLED”,Proceedings of Symposium Digest ,Vol 41,Jan 2010, pp1800-1888
[7]
C.-L. Lin, W.-Y. Chang, C.-C. Hung, and C.-D. Tu,”Kodak first OLED camera”,
Proceedings of IEEE Electron devices,Vol 33,Nov 2010,pp-700-900
[8]
C. W. Kim, J. G. Jung, J. B. Choi, D. H. Kim, C. Yi, H.D. Kim, Y. H. Choi, and
J.Im,SID, ”Sony readies OLED”, Proceedings of Symp. Dig. Tech,Vol 11,Dec
2011,pp-862-889
DEPT OF ECE, CBIT, KOLAR
2014
Page 28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oledreport-140301074235-phpapp02/85/OLED-report-2014-28-320.jpg)