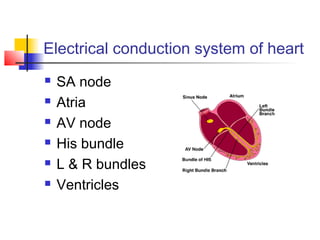
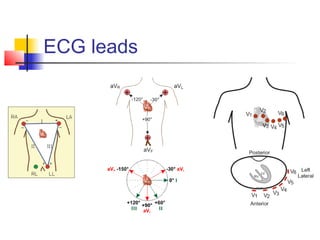
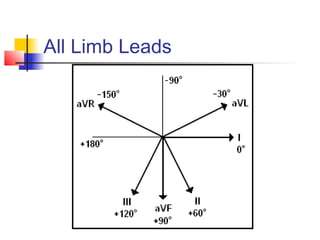
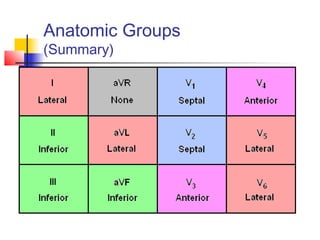
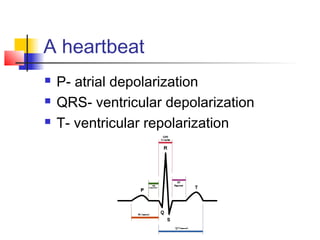
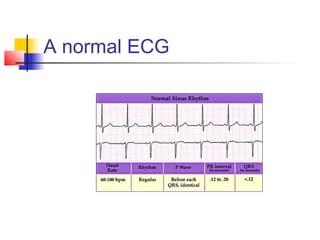
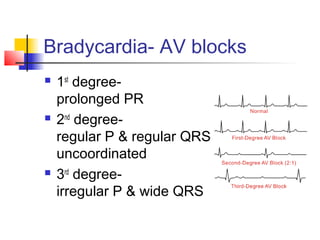
The document discusses the basics of electrocardiography including the electrical conduction system of the heart, the placement of ECG leads, components of the ECG waveform, and how to interpret key aspects of the ECG such as heart rate, rhythm, intervals, and complexes. It also summarizes the most common arrhythmias like bradycardia, atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and ventricular tachycardia, as well as their typical treatments with medications, cardioversion, ablation, or pacemaker implantation.