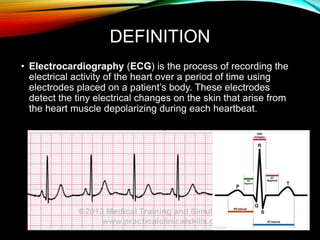
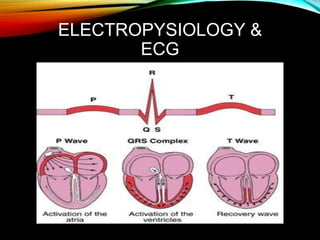
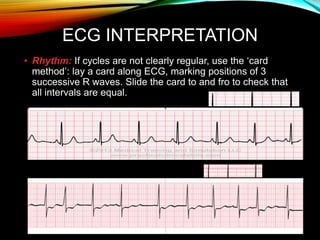
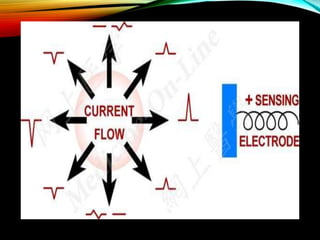
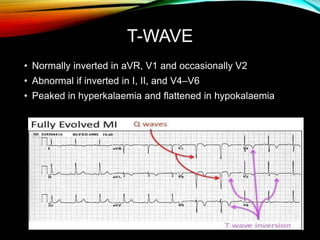
- An ECG records the electrical activity of the heart over time using electrodes placed on the skin. It detects tiny electrical changes arising from the heart muscle contracting during each heartbeat.
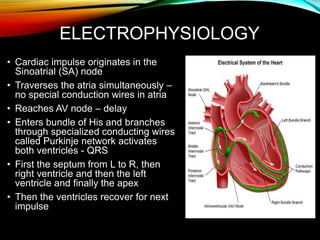
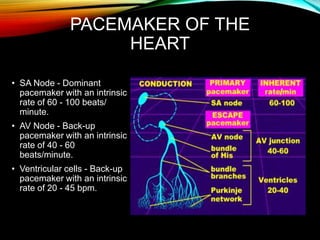
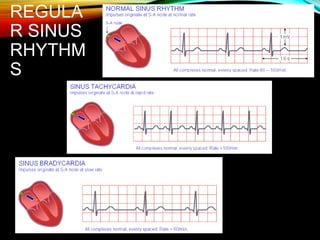
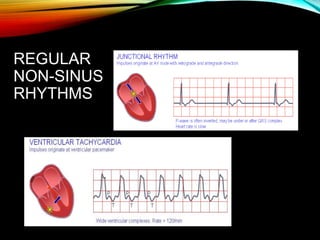
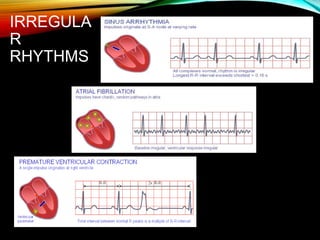
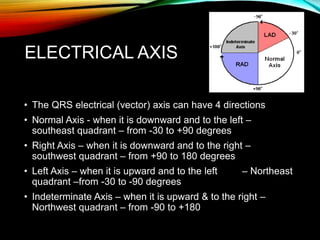
- The cardiac impulse originates in the sinoatrial node and travels through the atria and ventricles via specialized conduction pathways before the ventricles contract.
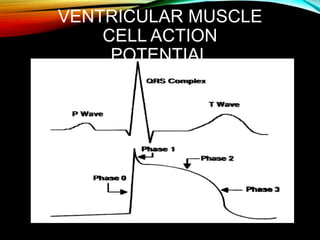
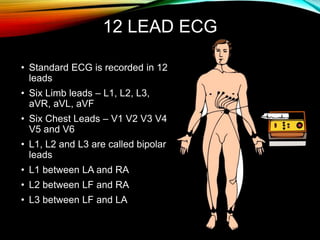
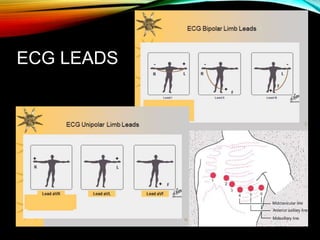
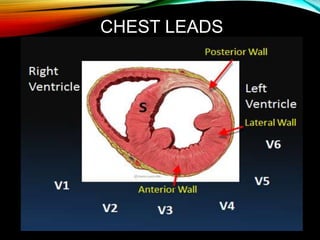
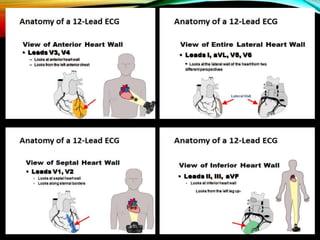
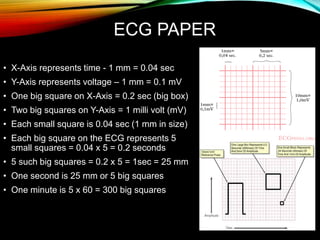
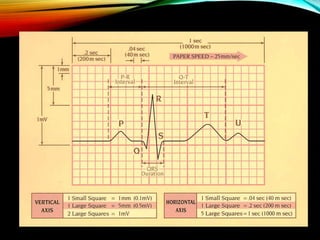
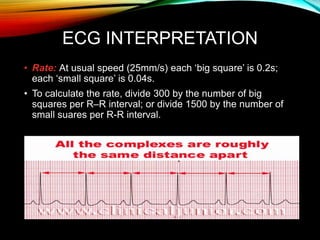
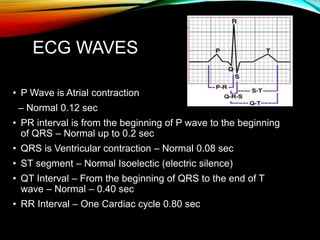
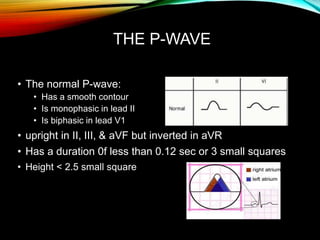
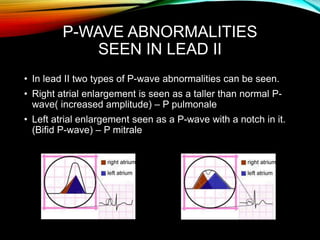
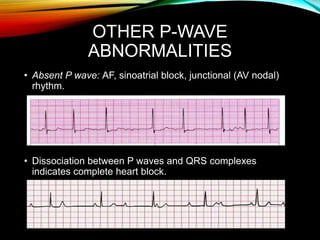
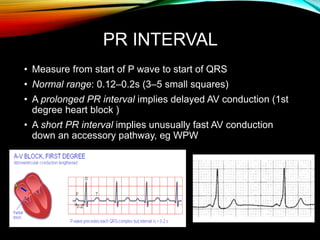
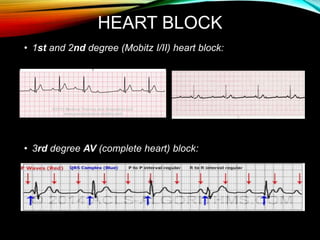
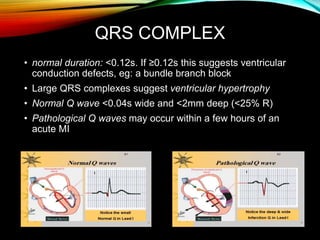
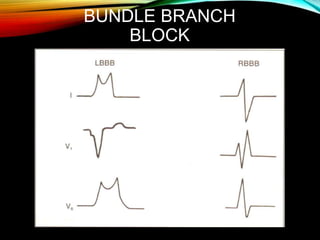
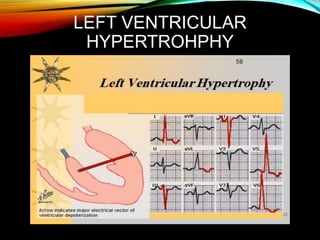
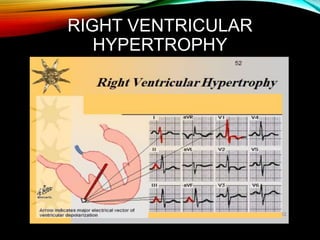
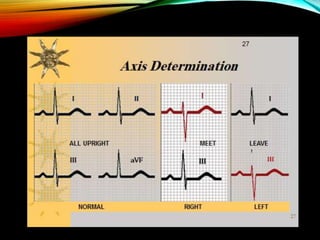
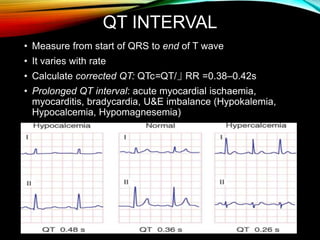
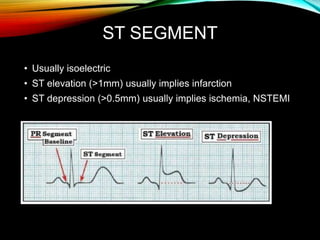
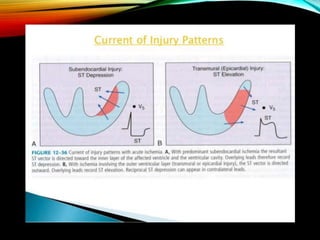
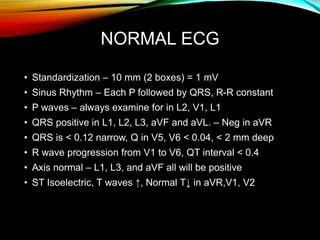
- A standard 12-lead ECG provides multiple views of the heart to analyze the rate and rhythm of the heart as well as measure key intervals like the PR interval, QRS duration, and QT interval to identify any abnormalities.