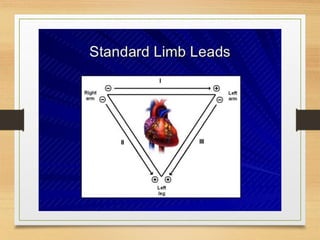
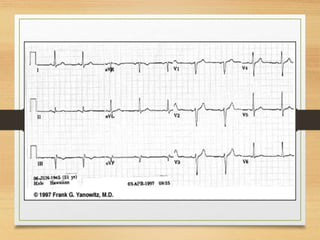
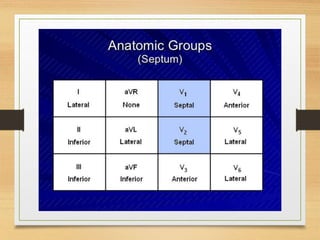
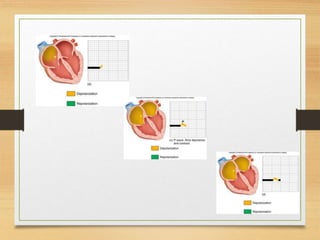
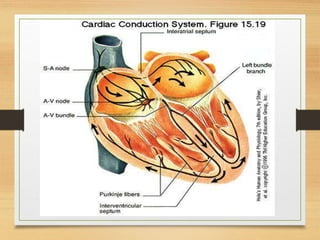
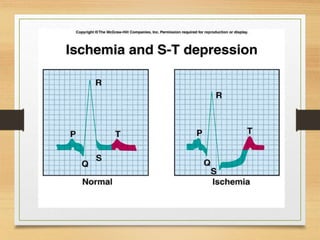
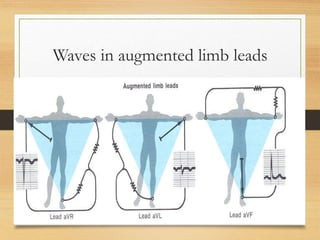
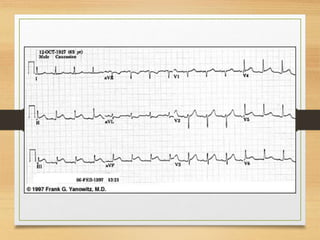
The document discusses electrical activity of the heart as recorded by an electrocardiogram (ECG). It defines key ECG terminology like waves, intervals, complexes and explains what each part of the ECG represents in terms of electrical activity in the heart. Specific waves like P, QRS, T are described in detail along with common abnormalities. Other concepts covered include heart rate calculation methods, cardiac rhythms and axis determination. The document provides a comprehensive overview of interpreting and understanding ECG readings.