Electrocardiography
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
10 likes•957 views
This document provides an overview of electrocardiography (ECG) analysis. It discusses the electrical conduction system of the heart, including the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, and Purkinje fibers. It explains the three phases of the ECG wave - polarization, depolarization, and repolarization. Key aspects of interpreting ECG strips such as the P, QRS, and T waves are covered. Common cardiac rhythms like sinus rhythm, sinus bradycardia, sinus tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and ventricular fibrillation are also summarized.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Basics of ecg

This document provides an overview of electrocardiography (ECG) basics for technicians. It discusses the heart's conduction system and how ECGs work to record electrical activity. The 12 standard ECG leads and their placements are described. Key aspects of normal ECG waveforms and intervals like P waves, QRS complex, T waves, and QT interval are explained. Common abnormalities that can cause changes in axis or abnormal complexes are also summarized. The document concludes with tips on interpreting ECGs and the important aspects to include in an ECG report.
Interpretation of common ecg abnormalities

This document provides an overview of how to interpret common ECG abnormalities through 3 sentences or less summaries:
1) It outlines how to measure rate, rhythm, intervals, complexes, and waves on an ECG and identifies what is considered normal.
2) Key abnormal rhythms, rates, intervals, and waves are defined along with their potential causes, such as sinus bradycardia, atrial fibrillation, various heart blocks, ventricular tachycardia, ST segment changes, T wave inversions, bundle branch blocks, and more.
3) Methods for localizing myocardial infarctions and abnormalities seen in conditions like hyperkalemia and hypothermia are also summarized.
ECG Leads in a 12-Lead ECG

The document discusses the 12 leads used in an electrocardiogram (ECG). It explains that the 12 leads can be categorized as either limb leads or precordial leads. The 6 limb leads include 3 bipolar leads (I, II, III) that record electrical activity in the frontal plane, and 3 unipolar augmented leads (aVL, aVR, aVF) derived mathematically from the bipolar leads. The 6 precordial leads are unipolar chest leads that record electrical activity in the horizontal plane. Together, the 12 leads provide a multi-dimensional view of the heart's electrical activity.
Basic electrocardiography and Beyond

This document provides an overview of basic electrocardiography and introduces more advanced concepts. It covers topics such as cardiac anatomy, depolarization and repolarization, the placement of electrodes, the 12-lead ECG system, and vectorcardiography. The document aims to explain electrocardiography fundamentals and relationships between bipolar and unipolar limb leads, as well as discuss additional leads and their clinical significance. It concludes by emphasizing the importance of understanding electrocardiography principles.
Anesthesia Ventilator

This PPT includes,
basics of ventilator
and all the required details about Installation,servicing and maintenance of a Anaesthesia Ventilator.
Defibrillation & cardioversion by DJ

Dr. Dharmendra Joshi provides an overview of defibrillation and cardioversion. Some key points include:
- Defibrillation involves delivering unsynchronized energy during any cardiac cycle phase to terminate arrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation. Cardioversion delivers synchronized energy to large QRS complexes.
- Biphasic waveforms are now preferred over monophasic as they provide effective defibrillation at lower energies, reducing risk of injury.
- Safety is paramount, with operators announcing charges and discharges to avoid contact with patient or equipment. Complications can include arrhythmias, burns, embolism and myocardial necrosis. Troubleshooting focuses on proper equipment connection and settings.
Patient different position under anesthesia

Patient positioning is a joint responsibility of the surgeon and anesthesiologist to balance surgical needs and risks to the patient. Key factors to consider include the procedure, patient characteristics, and physiological impacts of different positions. Common positions include supine, lateral, lithotomy and prone, each with benefits and risks requiring precautions like padding pressure points. The team must plan positioning prior to surgery based on these considerations.
Ecg 1

The ECG is a recording of the heart's electrical activity during each heartbeat. It detects this activity through electrodes placed on the skin. The ECG provides information about heart rate and rhythm, the size and position of the chambers, any damage to the heart, and the effects of medications. Key components of the ECG include the P wave, which represents atrial depolarization; the PR interval; the QRS complex, which represents ventricular depolarization; and the QT interval. The ECG is analyzed using 12 standard leads that detect the heart's electrical activity from different angles.
Recommended
Basics of ecg

This document provides an overview of electrocardiography (ECG) basics for technicians. It discusses the heart's conduction system and how ECGs work to record electrical activity. The 12 standard ECG leads and their placements are described. Key aspects of normal ECG waveforms and intervals like P waves, QRS complex, T waves, and QT interval are explained. Common abnormalities that can cause changes in axis or abnormal complexes are also summarized. The document concludes with tips on interpreting ECGs and the important aspects to include in an ECG report.
Interpretation of common ecg abnormalities

This document provides an overview of how to interpret common ECG abnormalities through 3 sentences or less summaries:
1) It outlines how to measure rate, rhythm, intervals, complexes, and waves on an ECG and identifies what is considered normal.
2) Key abnormal rhythms, rates, intervals, and waves are defined along with their potential causes, such as sinus bradycardia, atrial fibrillation, various heart blocks, ventricular tachycardia, ST segment changes, T wave inversions, bundle branch blocks, and more.
3) Methods for localizing myocardial infarctions and abnormalities seen in conditions like hyperkalemia and hypothermia are also summarized.
ECG Leads in a 12-Lead ECG

The document discusses the 12 leads used in an electrocardiogram (ECG). It explains that the 12 leads can be categorized as either limb leads or precordial leads. The 6 limb leads include 3 bipolar leads (I, II, III) that record electrical activity in the frontal plane, and 3 unipolar augmented leads (aVL, aVR, aVF) derived mathematically from the bipolar leads. The 6 precordial leads are unipolar chest leads that record electrical activity in the horizontal plane. Together, the 12 leads provide a multi-dimensional view of the heart's electrical activity.
Basic electrocardiography and Beyond

This document provides an overview of basic electrocardiography and introduces more advanced concepts. It covers topics such as cardiac anatomy, depolarization and repolarization, the placement of electrodes, the 12-lead ECG system, and vectorcardiography. The document aims to explain electrocardiography fundamentals and relationships between bipolar and unipolar limb leads, as well as discuss additional leads and their clinical significance. It concludes by emphasizing the importance of understanding electrocardiography principles.
Anesthesia Ventilator

This PPT includes,
basics of ventilator
and all the required details about Installation,servicing and maintenance of a Anaesthesia Ventilator.
Defibrillation & cardioversion by DJ

Dr. Dharmendra Joshi provides an overview of defibrillation and cardioversion. Some key points include:
- Defibrillation involves delivering unsynchronized energy during any cardiac cycle phase to terminate arrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation. Cardioversion delivers synchronized energy to large QRS complexes.
- Biphasic waveforms are now preferred over monophasic as they provide effective defibrillation at lower energies, reducing risk of injury.
- Safety is paramount, with operators announcing charges and discharges to avoid contact with patient or equipment. Complications can include arrhythmias, burns, embolism and myocardial necrosis. Troubleshooting focuses on proper equipment connection and settings.
Patient different position under anesthesia

Patient positioning is a joint responsibility of the surgeon and anesthesiologist to balance surgical needs and risks to the patient. Key factors to consider include the procedure, patient characteristics, and physiological impacts of different positions. Common positions include supine, lateral, lithotomy and prone, each with benefits and risks requiring precautions like padding pressure points. The team must plan positioning prior to surgery based on these considerations.
Ecg 1

The ECG is a recording of the heart's electrical activity during each heartbeat. It detects this activity through electrodes placed on the skin. The ECG provides information about heart rate and rhythm, the size and position of the chambers, any damage to the heart, and the effects of medications. Key components of the ECG include the P wave, which represents atrial depolarization; the PR interval; the QRS complex, which represents ventricular depolarization; and the QT interval. The ECG is analyzed using 12 standard leads that detect the heart's electrical activity from different angles.
Pre anaesthetic assessment and preoperative fasting guidelines

The document outlines the key steps and objectives of pre-anaesthetic consultation:
- Evaluate the patient's medical condition and optimise any risk factors.
- Determine the anaesthetic technique and perioperative care plan.
- Obtain informed consent from the patient after discussing anaesthesia and the procedure.
- The assessment may involve medical history, physical exam, and targeted lab/imaging tests to evaluate risk.
- The goals are to ensure patient safety and provide preoperative counselling and risk assessment.
Cardiac risk stratification

The document discusses various methods of assessing cardiac risk for patients undergoing surgery. It describes several cardiac risk indices, including the Goldman Multifactorial Cardiac Risk Index, Eagle's Cardiac Risk Index, Detsky's Cardiac Risk Index, and the Revised Cardiac Risk Index. It also discusses the American College of Cardiology Cardiac Risk Classification and factors that can affect cardiac risk, such as coronary artery disease, diabetes, hypertension, and the type of surgery. The document provides guidelines for stratifying cardiac risk based on the invasiveness and risk level of the surgical procedure. It further discusses ways to minimize risk, such as through the use of beta blockers, lipid-lowering agents, and a2-adre
Basics of ECG

The document provides information about electrocardiograms (ECGs):
1) It defines an ECG as the physical translation of the electrical phenomena created in the heart muscles and produced as a graph by an ECG machine.
2) It describes how ECGs can be used to identify arrhythmias, ischemia, chamber hypertrophy, and other cardiac conditions.
3) It explains the basics of heart anatomy including the four chambers and valves, and how the electrical conduction system generates and transmits electrical impulses to trigger contractions.
Basics of ECG.ppt dr.k.subramanyam

This document provides an overview of electrocardiography (ECG), including how an ECG works, the basics of recording an ECG, ECG leads, normal ECG waveforms and intervals, interpreting an ECG, common abnormalities, and how to report an ECG. It discusses topics such as the cardiac conduction system, Einthoven's triangle, the 12-lead ECG, determining heart rate and axis, normal sinus rhythm, P waves, QRS complex, ST segment, T waves, and the QT interval.
Monitoring in ICU

Blood pressure monitoring
NIBP
IBP
Central venous pressure monitoring
Pulmonary artery pressure monitoring
Mixed venous oxygen monitoring
Cardiac output
12 lead electrocardiogram

learn how to obtain an ECG, anyone can do it:
This presentation aims to show the clinical process of obtaining an ECG and features some tips and suggestions to troubleshoot and improve the quality of the tracing.
Please note that you're welcome to use any slides as long as you reference my post when you do so to maintain the integrity of authorship
If interested in detailed answers, please email: aamirdash@yahoo.com
Thanks, Ahmad
ECG

An electrocardiogram (ECG) records the electrical activity of the heart. It detects depolarization and repolarization of the myocardium through electrodes attached to the skin. The normal conduction pathway in the heart involves electrical signals traveling from the sinoatrial node through the atria and atrioventricular node before reaching the ventricles. An ECG provides 12 leads that together give multiple views of the heart's electrical activity. Key waves include the P wave, QRS complex, ST segment, and T wave. Nurses must ensure proper ECG procedure and monitor for any abnormalities.
Golden rules of anesthesia

anesthesia is a vast area for study . to make it simple for paramedics some important rules of anesthesia are explained in the most simplest way. rules of anesthesia can very as per the type of anesthesia.
Defibrillater

A defibrillator is a device that delivers an electric shock to the heart to stop ventricular fibrillation or atrial fibrillation, which are abnormal heart rhythms. Ventricular fibrillation occurs when the heart's lower chambers quiver instead of pumping blood, which can be fatal if not treated within minutes by delivering a shock via a defibrillator to reset the heart's rhythm. Defibrillators can be external or internal, and use electric shocks of varying voltages and durations depending on the type and location of use to convert the heart rhythm back to normal.
Ecg

- The document describes the basics of electrocardiography including normal impulse conduction in the heart, the components of a normal ECG waveform, lead placements, and common abnormalities.
- It explains that a normal ECG involves conduction through the sinoatrial node, AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches and Purkinje fibers. The waveform includes the P wave, QRS complex and T wave representing atrial and ventricular depolarization and repolarization.
- Placement of the 12 leads is described including the 6 limb leads forming Einthoven's triangle and 6 precordial chest leads. Commonly assessed intervals like PR and QT are also defined. Abnormalities in acute MI, electrolyte disorders and arr
Cardiac contractility

The document discusses cardiac electrophysiology and contractility. It describes the pacemaker potential and automaticity of the sinoatrial node, which allows it to initiate action potentials without external stimulation at a rate of 100 beats per minute. It also discusses the conduction of action potentials through the heart via the atrioventricular node, bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers. Contraction is triggered by increases in intracellular calcium levels. The cardiac action potential is longer than in skeletal muscle, lasting 200-300 milliseconds, which allows time for relaxation between contractions.
ELECTROCARDIOGRAM BASIC

This document provides an overview of electrocardiography (ECG/EKG). It discusses cardiac anatomy, the origin and spread of the cardiac impulse, electrophysiology of the heart, and the recording and interpretation of the ECG. Key points covered include the waves of the normal ECG (P, QRS, T), intervals (PR, QT), cardiac conduction system, 12-lead ECG system, axis determination, and common abnormalities. The overall goal is to describe the basics of ECG including its recording and clinical applications.
Transcutaneous pacing

Transcutaneous pacing is a temporary means of stimulating the heart electrically from the outside of the chest to treat bradycardia and heart block. It delivers pulses through pads placed on the chest to pace the heart until the underlying cause is resolved or a permanent pacing strategy can be applied. The goals are to keep the patient stable hemodynamically. Settings adjusted include pacemaker rate and output level, and mode (asynchronous fixed rate or synchronous demand). The procedure involves applying pads and monitoring for electrical and mechanical capture as output is increased until the heart rate is stabilized.
Defibrillator (ppt)

The document discusses defibrillation, which uses electric shocks to stop abnormal heart rhythms and allow a normal rhythm to resume. It defines defibrillation and describes the history and mechanisms involved. The types of defibrillators are explained, including automated external defibrillators. Precautions for defibrillation and troubleshooting defibrillators are also reviewed.
Pulseoximeter and Plethysmography by Pandian M

Plethysmography is a technique that measures changes in volume in different areas of the body using blood pressure cuffs or other sensors attached to a machine called a plethysmograph. It is effective at detecting changes caused by blood flow and can help doctors determine if a patient has blood clots or calculate lung volume. The document describes the procedures for limb and lung plethysmography tests and how they are interpreted to assess conditions like blood clots or respiratory issues. Common uses of plethysmography are listed in clinical settings like operating rooms and ICUs.
Breathing System

An anesthesia circuit connects the anesthesia machine to the patient to deliver anesthetic gases and remove carbon dioxide. Various circuit designs exist, including open, semi-open, semi-closed, and closed systems. The ideal circuit is reliable, safe, and easy to use while imposing minimal resistance and dead space. The circle system allows for rebreathing of gases using low fresh gas flows and includes unidirectional valves, tubing, a Y-piece, reservoir bag, and carbon dioxide absorber. Soda lime is commonly used for carbon dioxide absorption but its interaction with anesthetic agents can produce toxic compounds.
BASICS OF ECG

The ECG is an essential tool for health professionals in making a diagnosis of abnormal heart rhythms when one is suspected. It is a routine investigation in people who complain of symptoms such as chest pain as well as breathlessness. The findings of the ECG can also have an effect on treatment of certain conditions, for example it is helpful in deciding some aspects of treatment in people who have suffered from a heart attack.
Uses of Ultrasound in Anesthesiology

Apart from regional blocks, there are numerous avenues where ultrasound has been utilized by Anesthesiologists.
The coronary circulation

The coronary circulation refers to the blood vessels that supply and drain the heart. The heart receives its blood supply from two coronary arteries - the left and right coronary arteries. The left coronary artery supplies the left side of the heart including parts of the left atrium and ventricle. It branches into the anterior interventricular artery and circumflex artery. The right coronary artery supplies the right side of the heart and parts of the left side. It has branches like the right marginal artery and posterior interventricular artery. Deoxygenated blood from the heart drains into the coronary sinus and other cardiac veins before emptying into the right atrium.
ECG, step by step approach (Updated)

crème de la crème basics to understand electrocardiographic analysis in an easy & simple way with some specifications to its use in Emergency medicine/clinical toxicology practice.
Structure and function of heart by Shashank Bandre Class 10 CBSE 

In this slide you will get information about the structure and mechanism of heart ................ :) :) Hope it will help you....... :)
electrocardiography

This document provides an overview of electrocardiography (ECG), including the conduction system of the heart, types of ECG monitoring, basics of ECG interpretation including key waves and intervals, methods for determining heart rate, cardiac rhythm determination, normal ECG patterns, common arrhythmias, and electrode placement for 12-lead ECGs. The objectives are to review heart electrical conduction, describe ECG monitoring and interpretation, identify normal and abnormal ECG patterns, and understand factors such as rate, rhythm, P waves, and intervals that are used to interpret ECGs.
More Related Content
What's hot
Pre anaesthetic assessment and preoperative fasting guidelines

The document outlines the key steps and objectives of pre-anaesthetic consultation:
- Evaluate the patient's medical condition and optimise any risk factors.
- Determine the anaesthetic technique and perioperative care plan.
- Obtain informed consent from the patient after discussing anaesthesia and the procedure.
- The assessment may involve medical history, physical exam, and targeted lab/imaging tests to evaluate risk.
- The goals are to ensure patient safety and provide preoperative counselling and risk assessment.
Cardiac risk stratification

The document discusses various methods of assessing cardiac risk for patients undergoing surgery. It describes several cardiac risk indices, including the Goldman Multifactorial Cardiac Risk Index, Eagle's Cardiac Risk Index, Detsky's Cardiac Risk Index, and the Revised Cardiac Risk Index. It also discusses the American College of Cardiology Cardiac Risk Classification and factors that can affect cardiac risk, such as coronary artery disease, diabetes, hypertension, and the type of surgery. The document provides guidelines for stratifying cardiac risk based on the invasiveness and risk level of the surgical procedure. It further discusses ways to minimize risk, such as through the use of beta blockers, lipid-lowering agents, and a2-adre
Basics of ECG

The document provides information about electrocardiograms (ECGs):
1) It defines an ECG as the physical translation of the electrical phenomena created in the heart muscles and produced as a graph by an ECG machine.
2) It describes how ECGs can be used to identify arrhythmias, ischemia, chamber hypertrophy, and other cardiac conditions.
3) It explains the basics of heart anatomy including the four chambers and valves, and how the electrical conduction system generates and transmits electrical impulses to trigger contractions.
Basics of ECG.ppt dr.k.subramanyam

This document provides an overview of electrocardiography (ECG), including how an ECG works, the basics of recording an ECG, ECG leads, normal ECG waveforms and intervals, interpreting an ECG, common abnormalities, and how to report an ECG. It discusses topics such as the cardiac conduction system, Einthoven's triangle, the 12-lead ECG, determining heart rate and axis, normal sinus rhythm, P waves, QRS complex, ST segment, T waves, and the QT interval.
Monitoring in ICU

Blood pressure monitoring
NIBP
IBP
Central venous pressure monitoring
Pulmonary artery pressure monitoring
Mixed venous oxygen monitoring
Cardiac output
12 lead electrocardiogram

learn how to obtain an ECG, anyone can do it:
This presentation aims to show the clinical process of obtaining an ECG and features some tips and suggestions to troubleshoot and improve the quality of the tracing.
Please note that you're welcome to use any slides as long as you reference my post when you do so to maintain the integrity of authorship
If interested in detailed answers, please email: aamirdash@yahoo.com
Thanks, Ahmad
ECG

An electrocardiogram (ECG) records the electrical activity of the heart. It detects depolarization and repolarization of the myocardium through electrodes attached to the skin. The normal conduction pathway in the heart involves electrical signals traveling from the sinoatrial node through the atria and atrioventricular node before reaching the ventricles. An ECG provides 12 leads that together give multiple views of the heart's electrical activity. Key waves include the P wave, QRS complex, ST segment, and T wave. Nurses must ensure proper ECG procedure and monitor for any abnormalities.
Golden rules of anesthesia

anesthesia is a vast area for study . to make it simple for paramedics some important rules of anesthesia are explained in the most simplest way. rules of anesthesia can very as per the type of anesthesia.
Defibrillater

A defibrillator is a device that delivers an electric shock to the heart to stop ventricular fibrillation or atrial fibrillation, which are abnormal heart rhythms. Ventricular fibrillation occurs when the heart's lower chambers quiver instead of pumping blood, which can be fatal if not treated within minutes by delivering a shock via a defibrillator to reset the heart's rhythm. Defibrillators can be external or internal, and use electric shocks of varying voltages and durations depending on the type and location of use to convert the heart rhythm back to normal.
Ecg

- The document describes the basics of electrocardiography including normal impulse conduction in the heart, the components of a normal ECG waveform, lead placements, and common abnormalities.
- It explains that a normal ECG involves conduction through the sinoatrial node, AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches and Purkinje fibers. The waveform includes the P wave, QRS complex and T wave representing atrial and ventricular depolarization and repolarization.
- Placement of the 12 leads is described including the 6 limb leads forming Einthoven's triangle and 6 precordial chest leads. Commonly assessed intervals like PR and QT are also defined. Abnormalities in acute MI, electrolyte disorders and arr
Cardiac contractility

The document discusses cardiac electrophysiology and contractility. It describes the pacemaker potential and automaticity of the sinoatrial node, which allows it to initiate action potentials without external stimulation at a rate of 100 beats per minute. It also discusses the conduction of action potentials through the heart via the atrioventricular node, bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers. Contraction is triggered by increases in intracellular calcium levels. The cardiac action potential is longer than in skeletal muscle, lasting 200-300 milliseconds, which allows time for relaxation between contractions.
ELECTROCARDIOGRAM BASIC

This document provides an overview of electrocardiography (ECG/EKG). It discusses cardiac anatomy, the origin and spread of the cardiac impulse, electrophysiology of the heart, and the recording and interpretation of the ECG. Key points covered include the waves of the normal ECG (P, QRS, T), intervals (PR, QT), cardiac conduction system, 12-lead ECG system, axis determination, and common abnormalities. The overall goal is to describe the basics of ECG including its recording and clinical applications.
Transcutaneous pacing

Transcutaneous pacing is a temporary means of stimulating the heart electrically from the outside of the chest to treat bradycardia and heart block. It delivers pulses through pads placed on the chest to pace the heart until the underlying cause is resolved or a permanent pacing strategy can be applied. The goals are to keep the patient stable hemodynamically. Settings adjusted include pacemaker rate and output level, and mode (asynchronous fixed rate or synchronous demand). The procedure involves applying pads and monitoring for electrical and mechanical capture as output is increased until the heart rate is stabilized.
Defibrillator (ppt)

The document discusses defibrillation, which uses electric shocks to stop abnormal heart rhythms and allow a normal rhythm to resume. It defines defibrillation and describes the history and mechanisms involved. The types of defibrillators are explained, including automated external defibrillators. Precautions for defibrillation and troubleshooting defibrillators are also reviewed.
Pulseoximeter and Plethysmography by Pandian M

Plethysmography is a technique that measures changes in volume in different areas of the body using blood pressure cuffs or other sensors attached to a machine called a plethysmograph. It is effective at detecting changes caused by blood flow and can help doctors determine if a patient has blood clots or calculate lung volume. The document describes the procedures for limb and lung plethysmography tests and how they are interpreted to assess conditions like blood clots or respiratory issues. Common uses of plethysmography are listed in clinical settings like operating rooms and ICUs.
Breathing System

An anesthesia circuit connects the anesthesia machine to the patient to deliver anesthetic gases and remove carbon dioxide. Various circuit designs exist, including open, semi-open, semi-closed, and closed systems. The ideal circuit is reliable, safe, and easy to use while imposing minimal resistance and dead space. The circle system allows for rebreathing of gases using low fresh gas flows and includes unidirectional valves, tubing, a Y-piece, reservoir bag, and carbon dioxide absorber. Soda lime is commonly used for carbon dioxide absorption but its interaction with anesthetic agents can produce toxic compounds.
BASICS OF ECG

The ECG is an essential tool for health professionals in making a diagnosis of abnormal heart rhythms when one is suspected. It is a routine investigation in people who complain of symptoms such as chest pain as well as breathlessness. The findings of the ECG can also have an effect on treatment of certain conditions, for example it is helpful in deciding some aspects of treatment in people who have suffered from a heart attack.
Uses of Ultrasound in Anesthesiology

Apart from regional blocks, there are numerous avenues where ultrasound has been utilized by Anesthesiologists.
The coronary circulation

The coronary circulation refers to the blood vessels that supply and drain the heart. The heart receives its blood supply from two coronary arteries - the left and right coronary arteries. The left coronary artery supplies the left side of the heart including parts of the left atrium and ventricle. It branches into the anterior interventricular artery and circumflex artery. The right coronary artery supplies the right side of the heart and parts of the left side. It has branches like the right marginal artery and posterior interventricular artery. Deoxygenated blood from the heart drains into the coronary sinus and other cardiac veins before emptying into the right atrium.
ECG, step by step approach (Updated)

crème de la crème basics to understand electrocardiographic analysis in an easy & simple way with some specifications to its use in Emergency medicine/clinical toxicology practice.
What's hot (20)
Pre anaesthetic assessment and preoperative fasting guidelines

Pre anaesthetic assessment and preoperative fasting guidelines
Viewers also liked
Structure and function of heart by Shashank Bandre Class 10 CBSE 

In this slide you will get information about the structure and mechanism of heart ................ :) :) Hope it will help you....... :)
electrocardiography

This document provides an overview of electrocardiography (ECG), including the conduction system of the heart, types of ECG monitoring, basics of ECG interpretation including key waves and intervals, methods for determining heart rate, cardiac rhythm determination, normal ECG patterns, common arrhythmias, and electrode placement for 12-lead ECGs. The objectives are to review heart electrical conduction, describe ECG monitoring and interpretation, identify normal and abnormal ECG patterns, and understand factors such as rate, rhythm, P waves, and intervals that are used to interpret ECGs.
Circulation and exercise

The circulatory system adapts to exercise in both short-term and long-term ways. In the short-term, the heart rate increases to pump more blood, delivering more oxygen to working muscles. The lungs also work harder to remove carbon dioxide and replenish oxygen. Long-term, regular exercise causes the heart to grow stronger, increasing stroke volume and lowering resting heart rate. It also enhances blood flow and oxygen delivery through increased capillaries and blood volume.
Introduction to Electrocardiography

This presentation covers few basic things about ECG, especially for UG Medical students like ECG leads, normal ECG waves, axis of ECG and how to look for common ECG misplacements.
Respiratory system and gaseous exchange

The respiratory system allows for gas exchange through a series of steps: 1) Ventilation - the movement of air into and out of the lungs through inspiration and expiration. 2) External respiration - the diffusion of oxygen from the alveoli into the blood and carbon dioxide from the blood into the alveoli. 3) Internal respiration - the diffusion of oxygen from the blood into the tissue cells and carbon dioxide from the tissue cells into the blood. This process is controlled by the respiratory center in the brain and allows for cellular respiration to occur.
Exercise physiology 7 

The cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together to deliver oxygen to muscles and remove carbon dioxide during exercise. The cardiovascular system increases heart rate, stroke volume, and cardiac output to boost blood flow and oxygen delivery. The respiratory system increases ventilation through deeper breaths to ensure adequate gas exchange. These physiological responses are critical for meeting the increased demands of physical activity.
L3 conduction system of the heart

The conduction system of the heart consists of specialized cardiac muscle fibers that generate and conduct electrical impulses through the heart to coordinate the cardiac cycle. The key components are the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers. The sinoatrial node initiates the heartbeat and stimulates the atria to contract. The impulse then travels to the atrioventricular node and through the bundle of His to stimulate simultaneous contraction of the ventricles. The autonomic nervous system also regulates heart rate in response to physiological demands on the body.
The heart conduction system

The document contains information about labeling the parts of the heart and the cardiac output. It defines cardiac output as the amount of blood pumped by the heart per minute, which is calculated by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume. It then provides an example calculation of a person's cardiac output. The document also describes the conduction system of the heart, noting that the sinoatrial node acts as the pacemaker and the atrioventricular node relays electrical impulses to allow for coordinated contraction of the atria and ventricles.
Gas exchange

1) Cells need oxygen for cellular respiration and must remove carbon dioxide as it is a waste product.
2) Gases diffuse across the plasma membrane along concentration gradients. Efficient gas exchange requires a moist, thin membrane with a large surface area.
3) Multi-cellular organisms have specialized structures like lungs and gills to increase surface area and link to transport systems to supply all cells.
Conduction of the heart

The conduction system of the heart comprises the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, atrioventricular bundle, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers. The sinoatrial node initiates heartbeats and determines heart rate by firing electrical impulses that spread through the atria. The atrioventricular node is located near the atrioventricular valve and delays electrical signals to the ventricles to ensure the atria fully contract before the ventricles. The atrioventricular bundle then divides into right and left bundle branches to conduct impulses to the Purkinje fibers and throughout the ventricles.
NURSING PROCEDURE OBTAIN 12 LEAD ECG

An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) records the electrical activity of the heart. A 12-lead ECG uses electrodes placed on the wrists, ankles, and chest to assess the heart from 12 different views. It is a valuable diagnostic tool that displays the heart's electrical activity as waveforms. The procedure involves preparing the ECG machine, attaching electrodes to the patient's limbs and chest in specific positions, recording the 12 leads automatically, and removing the electrodes after.
Human Heart and its function

The circulatory system is made up of the heart and blood vessels. The heart is a muscular organ about the size of a fist located slightly left of the breastbone. It pumps blood through blood vessels including arteries, veins, and capillaries. The heart has four chambers - two upper chambers called atria that receive blood and two lower chambers called ventricles that pump blood out of the heart. It contracts in a cardiac cycle where the atria and ventricles contract simultaneously to circulate blood throughout the body.
Conduction system of heart

This document provides an overview of the conduction system of the heart. It begins with the development of the primitive cardiac tube and differentiation of heart structures. It then describes the specialized conduction tissues including the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers. It discusses impulse conduction through the heart and characteristics of cardiac conduction cells. Finally, it covers conduction defects, implications for congenital heart anomalies like ASD and VSD, and considerations for cardiac surgery.
Blood supply of heart (1)

The document describes the blood supply and conduction system of the heart. It discusses the right and left coronary arteries, which are the main arteries that supply blood to the heart. It details the branches and territories supplied by each artery. It also describes the conduction system of the heart, including the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers. It provides an overview of how electrical impulses are conducted through the heart to trigger contractions.
Blood clotting

Blood clotting is a process called coagulation where blood changes from a liquid to a solid gel-like state. It occurs through a cascade of biochemical reactions involving multiple clotting factors. Initially fibrinogen is converted to fibrin, which forms a mesh that entangles blood cells. Then the clot undergoes further changes to strengthen it. Precise regulation of coagulation prevents clotting inside healthy blood vessels but allows it to occur when vessels are damaged.
Conduction System of the Heart

The conduction system of the heart is initiated by the sinoatrial node, which acts as the dominant pacemaker. It is located in the junction of the right atrium and superior vena cava and is innervated by the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. Conduction then proceeds through the atrioventricular node, which slows conduction to allow for ventricular filling, and the bundle of His divides into left and right bundle branches to stimulate the ventricles.
Heart Structure and Function

The document describes the structure and function of the heart. It explains that deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium via the vena cava and is then pumped to the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery. Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the left atrium via the pulmonary veins. The left atrium then pumps the blood to the left ventricle, which pumps it out to the body through the aorta. Valves prevent backflow of blood throughout the heart.
Shortcut to ECG

Salient features of the book are -
- The book provides a shortcut to understand and remember certain specific formulae and points you require to interpret the 12-lead ECG.
- Treatment protocols (in green boxes) for most of the important conditions are also included.
- View sample ECGs as you read along the topics.
- The content is explained in a very simple language to provide good conceptions, written from a student’s point of view.
- People can gain their belief in the book after going through sample ECGs which would be available at www.themedicalpost.net/ecg
- The book competes with the other books available in the market in simplicity, summaries, treatment protocols, live diagrams and regularly updated sample ECGs on the website.
6 response of the cardiovascular system to exercise

The cardiovascular system responds to exercise in several ways:
1. The heart rate and stroke volume increase to elevate cardiac output and deliver more oxygen to working muscles.
2. Blood is redistributed to working muscles, increasing blood flow.
3. Blood pressure rises to maintain blood flow during increased demand.
Regular aerobic exercise improves cardiorespiratory endurance and maximum oxygen consumption, lowering risk of diseases like hypertension and coronary heart disease. The DASH diet also helps lower blood pressure through increased potassium and calcium intake.
Viewers also liked (20)
Structure and function of heart by Shashank Bandre Class 10 CBSE 

Structure and function of heart by Shashank Bandre Class 10 CBSE
6 response of the cardiovascular system to exercise

6 response of the cardiovascular system to exercise
Similar to Electrocardiography
ECG complete lecture notes along with interpretation

The document discusses the electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), which records the electrical activity of the heart. It describes the cardiac cycle, including the electrical and mechanical events that occur with each heartbeat. Specifically, it discusses the phases of atrial systole and ventricular systole, as well as the mechanical events of ventricular filling, isovolumetric contraction, ventricular ejection, and isovolumetric relaxation. It also explains how electrical changes in heart tissue cause mechanical changes like muscle contraction.
1electrophysiology-110623133004-phpapp02.pdf

This document provides an overview of basic cardiac electrophysiology concepts including:
- The four primary characteristics of cardiac cells: automaticity, excitability, conductivity, and contractility.
- The phases of the cardiac action potential: polarization, depolarization, repolarization.
- Key components of the EKG complex including the P wave, QRS complex, ST segment, and T wave.
- The cardiac conduction system including the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers.
- Methods for calculating heart rate from the rhythm strip including the 6-second rule and rule of 300s.
ECG complete lecture presentation, ECG waveform and leads placement

The document discusses the cardiac cycle and electrocardiography (ECG). It describes:
1. The cardiac cycle has four phases - ventricular filling, isovolumetric contraction, ventricular ejection, and isovolumetric relaxation.
2. An ECG records the electrical activity of the heart to detect abnormalities. It uses limb and precordial leads in a 12-lead system.
3. Key aspects of the ECG that are evaluated include rate, rhythm, intervals, waves, and ST segment changes which can indicate issues like myocardial ischemia.
Ecg basics & cardicac physiology

The document provides information on ECG basics and heart physiology. It discusses the structure of cardiac muscle and how the heart maintains pumping. Key points include the syncytial nature of cardiac muscle, differences in resting membrane potential and action potential compared to skeletal muscle, and the heart's ability for auto-rhythmicity. Factors affecting the cardiac action potential include potassium, calcium, and sodium concentrations as well as temperature. Excitation-contraction coupling and the duration of atrial and ventricular contraction are also covered. The document then discusses the cardiac cycle, heart sounds, regulation of pumping via the Frank-Starling mechanism and autonomic innervation, and the effects of autonomic stimulation. Special topics include the conductive system
Electrocardiography (ecg)

This document provides an overview of electrocardiography (ECG) and myocardial infarctions (MIs). It discusses the basics of ECG formation, electrode placement, lead types, normal ECG components and intervals. It describes how to interpret rate, rhythm, axis, waves and intervals. Abnormal findings indicating MIs such as ST elevation and pathological Q waves are also outlined. The document concludes with descriptions of STEMI and NSTEMI treatment including thrombolytics, angioplasty and medical management.
Ecg

The document summarizes the mechanical and electrical events of the cardiac cycle. It describes:
1) The cardiac cycle involves electrical, pressure, and volume changes between heartbeats including systole when the myocardium contracts and diastole when it relaxes.
2) There are four mechanical events in a cardiac cycle: ventricular filling, isovolumetric contraction, ventricular ejection, and isovolumetric relaxation.
3) An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) records the electrical activity and can detect abnormalities in heart rhythm or conduction.
ECG.ppt

M.sc part. 1 seme 2 . This is topic are biochemistry
ECG are electro cardio graph this full from of ECG
And this topic related a heart function in human body
12 Lead Basics

The 12-lead ECG provides important information about the heart's electrical activity. It begins with atrial depolarization seen as the P wave, followed by ventricular depolarization in the QRS complex. The ST segment and T wave represent ventricular repolarization. Each of the 12 leads views the heart from a different angle, with the standard limb leads in the frontal plane and the chest leads in the horizontal plane. Together they allow clinicians to determine the heart's rate, rhythm, and axis.
Ecg part i

Electrocardiography: is the recording of the electrical impulses that are generated in the heart. These impulses initiate the contraction of cardiac muscles.
Antiarrhythmic drugs class Bidya.pdf

Cardiac arrhythmias are irregularities in the heart's rhythm that can be caused by issues with impulse formation, conduction, or both. Common arrhythmias include atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, ectopic beats, and various types of atrioventricular block. Antiarrhythmic drugs are used for management but can paradoxically cause arrhythmias, so careful monitoring is needed. Non-pharmacological treatments include cardioversion, ablation, and implantable defibrillators.
Heart

The document summarizes key aspects of heart physiology:
- The heart pumps blood through two circuits and uses valves to ensure one-way blood flow.
- Cardiac muscle cells contract as a unit due to intercalated disks and gap junctions.
- The heart's conduction system uses specialized pacemaker cells and Purkinje fibers to coordinate contractions.
- An electrocardiogram tracks the heart's electrical activity during a cardiac cycle of atrial and ventricular filling/contraction.
Heart

The document discusses cardiac muscle and the cardiac cycle. It provides details on:
- Cardiac muscle histology and action potential, including ion channels involved
- The cardiac cycle and components such as atrial systole, ventricular ejection, and filling phases
- How the cardiac cycle is coordinated by the conduction system and regulated by the autonomic nervous system
- Key concepts like the Frank-Starling law of the heart and factors affecting cardiac performance
Basic ECG notes

This document provides an overview of electrocardiography (ECG) and how to interpret ECG strips in the context of toxicology. It begins by defining the objectives of learning ECG and its importance in toxicology. It then describes the basic components of an ECG including the waves, intervals, complexes, leads, and normal values. The document explains how to assess heart rate and rhythm on an ECG strip. Finally, it demonstrates some common ECG changes that can occur due to toxic exposures, such as sinus tachycardia, sinus bradycardia, and heart block.
Term paper on ecg and cardiac arrhythmias

The document provides information on ECGs and cardiac arrhythmias. It begins with an introduction to ECGs and what they measure. It then discusses the history of ECGs, the anatomy and conduction system of the heart, common indications for ECGs, how ECGs are arranged and interpreted, and definitions of heart rate and rhythm. The majority of the document categorizes and describes different types of cardiac arrhythmias like sinus tachycardia, sinus bradycardia, premature atrial contractions, atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, junctional rhythm, junctional tachycardia, premature junctional contractions, and supraventricular tachycardia. For each type it discusses causes
Term paper on ECG and cardiac arrhythmias

The document provides information about ECGs and cardiac arrhythmias. It discusses the history and development of ECGs, the anatomy and conduction system of the heart, common arrhythmias like sinus tachycardia and sinus bradycardia, and how to diagnose and manage various types of cardiac arrhythmias using ECGs. The document contains diagrams of ECG readings and the heart to illustrate different arrhythmias and the heart's structure and function.
Electrocardiogram(ecg)

The electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) measures and records the electrical activity of the heart. It was developed in 1893 by Willem Einthoven, who received the Nobel Prize for his work. An ECG works by detecting the tiny electrical changes on the skin that occur with each heartbeat. It shows the heart's rate and rhythm, as well as any damage to heart muscle. A standard 12-lead ECG provides multiple views of the heart and can help diagnose conditions like heart attacks.
Cardiac Electrophysiology

This document provides a high-level overview of cardiac electrophysiology and EKG interpretation. It discusses the different types of cardiac cells, the cardiac action potential, and the phases of the cardiac cycle. It describes how electrical signals travel through the heart via specialized conduction pathways, and explains common EKG complexes and intervals like the P wave, QRS complex, and ST segment. Key concepts covered include the roles of the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, and Purkinje fibers in cardiac conduction.
BASIC CADIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY.ppt

This document provides an overview of basic cardiovascular physiology. It discusses the electrical and mechanical properties of the heart, including cardiac action potentials, refractory periods, the generation and propagation of cardiac impulses, and the effects of ions on cardiac function. It also summarizes the cardiac cycle and its phases, heart sounds, pressure changes during the cycle, and the coordinated control of the heart through the autonomic nervous system.
05 ecg 2011

1. The document discusses the electrocardiogram (ECG) and the electrical signals that control heart activity.
2. It explains that the sinoatrial node initiates an electrical impulse that travels to the atrioventricular node and then to the ventricles via the bundle branches.
3. This causes the muscles of the heart to contract and the valves to open and close, pumping blood through the heart and into the lungs and body.
Heart physiology, blood physiology

The document provides background information on cardiovascular physiology. It discusses how the heart pumps blood through the body via the cardiac cycle of contraction and relaxation. An electrocardiogram (ECG) records the electrical activity of the heart during this cycle. Key aspects of the ECG include the P, QRS, and T waves and intervals like P-R that correspond to different phases of the cardiac cycle. Contraction of the heart chambers (systole) pumps blood into the arteries, while relaxation (diastole) allows the chambers to refill. The opening and closing of heart valves during the cycle produces characteristic sounds. Regular exercise can increase stroke volume and reduce the heart rate increase needed during exertion. The document outlines experiments to
Similar to Electrocardiography (20)
ECG complete lecture notes along with interpretation

ECG complete lecture notes along with interpretation
ECG complete lecture presentation, ECG waveform and leads placement

ECG complete lecture presentation, ECG waveform and leads placement
Electrocardiography
- 2. Electrical conduction system of the heart ECG Phases: polarization, depolarization, repolarization Electrode Placement Interpreting ECG strips & waves Cardiac Rhythms Rhythm Quiz Agenda
- 3. Most important aspect heart’s anatomy & physiology to master in ECG analysis Composed of myocardial tissue ECG supplies information how well conduction system of the heart is functioning Neurons serve conduction function for the rest of the body Myocardial tissue has 2 advantages over nerve tissue Electrical Conduction System
- 4. Sinoatrial node, “pacemaker” of the heart Small concentration of myocardial tissue Initiates impulses that depolarize the rest of the heart Located in upper portion of the right atrium Electrical impulse that triggers each heartbeat Spreads through the atria Muscle tissue to contract in a coordinated manner Inherent rate of 60-100 beats per minute SA Node
- 5. Atrioventricular node Large bundle of myocardial tissue Internodal tracts connect SA node to AV node 2 pathways: beat & alpha Delays impulses from SA node to allowing atria to complete their contraction and empty completely Atrial kick Prevents extra beats from being conducted Distal portion of AV node is the bundle of His that splits into two branches: left & right bundle branches AV Node
- 6. Spread across respective ventricles and become purkinje fibers Ventricles contract Electrical signal having passed through both atria and ventricles making them contract = one heart beat AV Node
- 7. Records the electrical activity of the heart Detected by electrodes Electrical activity of myocardial cells result in complex electrical reaction occurring in each fiber of myocardium Millions of fibers of the myocardium react electrically to an impulse creating a wave of energy detected by the ECG ECG pattern: characteristic wave forms produced by electrical activity Painless Three phases of electrochemical activity: polarization, depolarization, and repolarization ECG
- 8. Cells ready to contract SA node ready to initiate impulse Extracellular ions: Na and Ca strong positive electrical charge Intracellular ion: K weak positive electrical charge Difference of strength of electrical charges create a positive charge on outside of the cell membrane & negative charge on the inside Polarization
- 9. “Action phase” Shift in ion concentrations Na ions rush into the cell, followed by slower Ca ions K ions pushed out of the cell creating polarity of cell to become reversed Negative charge along outside of the cell membrane & positive charge inside the cell membrane Shortens fibers producing contractions Contraction increases pressure, pushing blood out of heart chambers “systole” Depolarization
- 10. “Recovery phase” Sodium Potassium pump Pump out Na and Ca and pump in K reestablishing electrical charge along cell membrane Muscle fibers of myocardium are relaxing returning to preconstraction state Relaxation decreasing pressure, heart chambers fill “diastole” Repolarization
- 11. 1) cleanse skin removing: oils, sweat, dirt and hair 2) place electrode sticky side down and begin placing on one corner, avoiding touching sticky side 3) smooth electrode to skin in circular motion and connect monitor wire 5 lead ECG: -white: RA second intercostal space (right side) -brown: chest (middle) -green: RL (right side) -red: LL (left side) -black: LA second intercostal space (left side) Electrode Placement
- 12. Electrode Placement Smoke over fire, snow over grass, brown in the middle
- 13. Interpreting ECG Strips Each small box= 0.04 seconds, 1mm Each large box= 0.20 seconds, 5mm 25mm/second papers
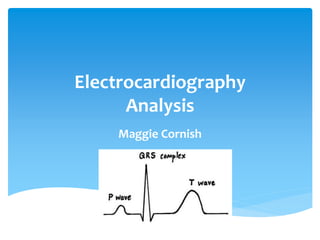
- 14. Atrial depolarization Time for electrical impulse from SA node to spread through the atrial muscle Amplitude: 2-2.5 mm in height Duration: 0.06-0.11 seconds P-R interval: -time takes an impulse to travel from the atria through the AV node, bundle of his, and bundle branches to the Purkinje fibres -beginning of p wave to beginning of QRS complex -duration: 0.12-0.20 seconds P wave & P-R interval
- 15. P-R Interval
- 16. Ventricular depolarization 3 waves: Q,R,S Q wave: beginning, sometimes not present R wave: positive deflection S wave: negative deflection Duration: no longer than 10 seconds QRS Complex
- 17. T wave: repolarization of ventricles S-T segment: end of ventricular depolarization and beginning of ventricular repolarization QT interval: -time necessary for ventricle depolarization & repolarization -beginning of QRS complex to end of T wave T wave, Q-T interval, S-T segment
- 18. Sinus Rhythm • Normal • Electrical stimuli initiated in SA node, conducted through AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers • Depolarization and repolarization of atria and ventricles
- 19. Sinus Bradycardia • HR: <60 bpm • Rhythm unchanged • Normal sinus slowed down • Waves further apart
- 20. Sinus Tachycardia • HR: >100 bpm • Sinus rhythm greater than 100 bpm • Waves closer together
- 21. Atrial Fibrillation • No P wave since SA node isn’t functioning • Atria generates up to 600 stimuli/min • Instead seeing P wave, number of small waves of different sizes “fibrillatory waves” (F waves) • Stimuli not strong enough to depolarize the AV node, rhythm is irregular since number of stimuli being generated in atria • Fast rhythm: 110-140 bpm • QRS normal since abnormality above the ventricles
- 22. Atrial Flutter • Similar to atrial fibrillation • Abnormality of conduction of atria • Flutter waves bombard Av node but more organized and regular fashion • “saw-tooth” pattern
- 23. Ventricular Fibrillation • Life threatening • Chaotic depolarization of ventricles • No clear P waves or QRS complexes
- 24. Myocardial Infarction • Heart attack • 1st hyperacute T wave: taller and pointed • 2nd ST segment elevation: when heart muscle is being injured by lack of blood flow and oxygen
- 33. Normal Sinus
- 35. Atrial flutter
- 38. Ambulance Technician Study. (2006). ECG basics. Retrieved from http://www.ambulancetechnicianstudy.co.uk/ecgbasics.html#.UKu1b4aA8uc Catalano, J.T. (2002). Guide to ECG analysis (2nd ed.).Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Lewis, S.L., Heitkemper, M.M., Dirksen, S.R, O’Brien, P.G., & Bucher, L. (2010). Medical-surgical nursing in canada (2nd ed.) Toronto, ON: Elsevier Canada Perry, P.A. & Potter, A.G. (2009). Canadian fundamentals of nursing (4th ed.) Toronto, ON: Elsevier Canada University of Nottingham School of Nursing. (2012). Beginners guide to normal heart function, sinus rhythm & common arrhythmias. Retrieved from http://www.nottingham.ac.uk/nursing/practice/resources/cardiology/index.php References
Editor's Notes
- Smoke over fire, snow over grass, brown in the middle