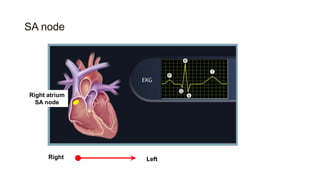
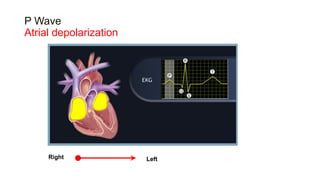
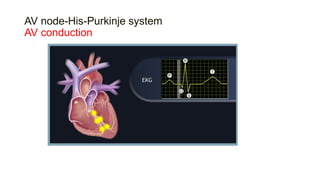
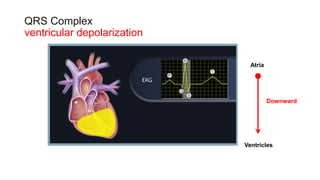
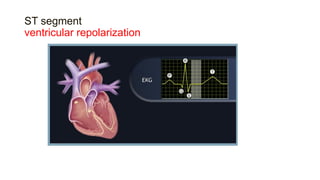
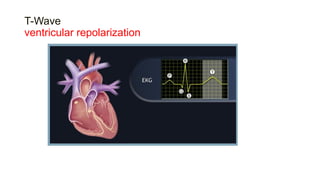
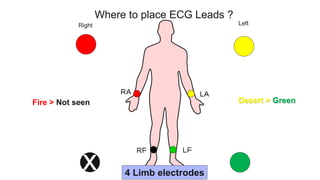
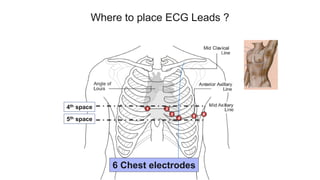
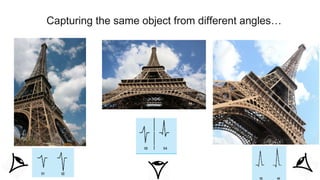
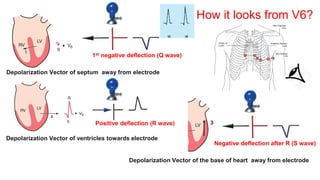
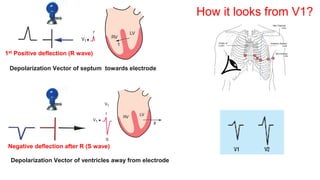
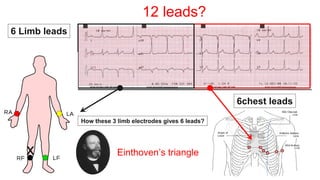
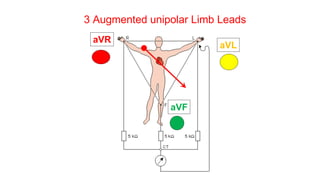
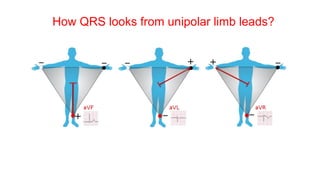
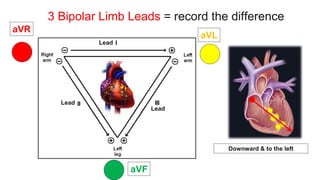
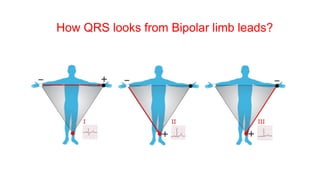
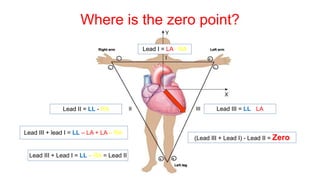
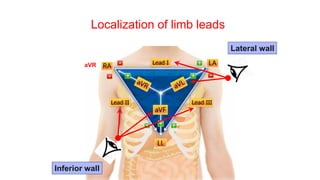
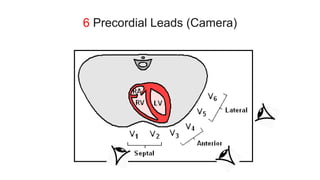
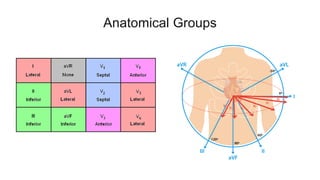
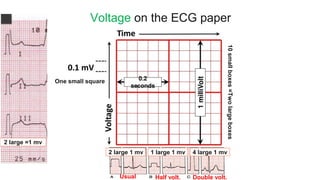
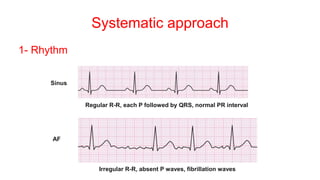
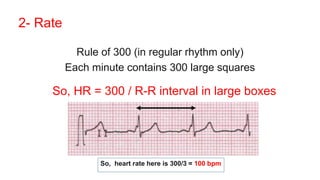
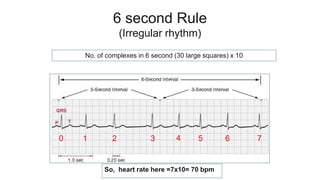
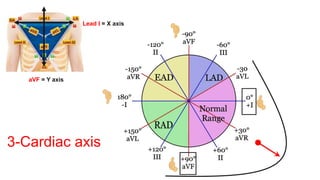
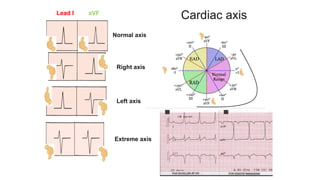
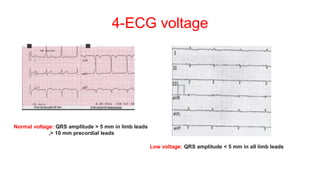
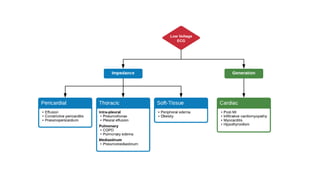
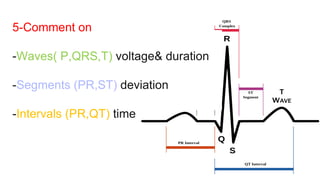
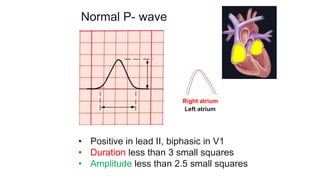
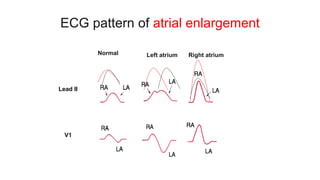
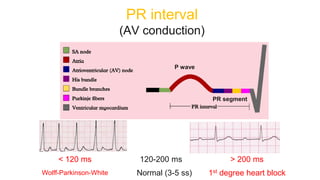
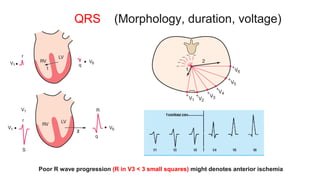
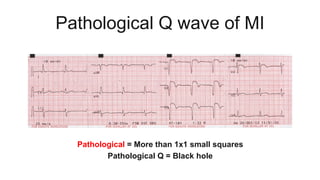
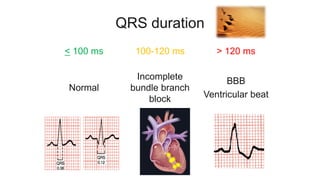
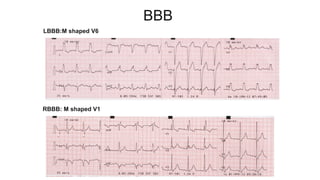
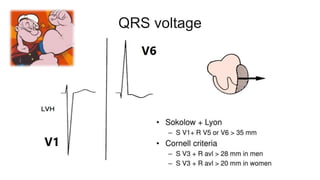
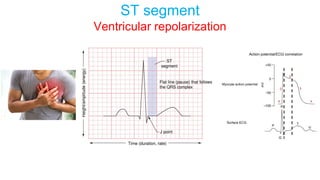
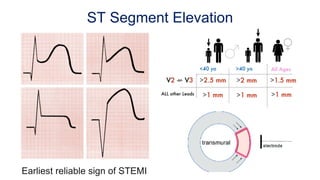
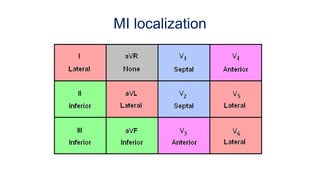
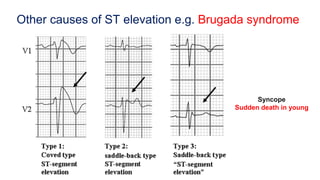
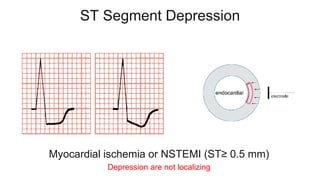
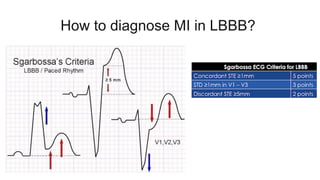
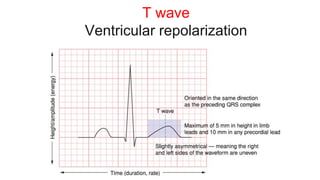
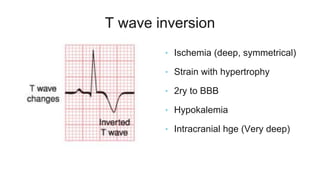
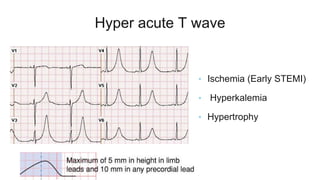
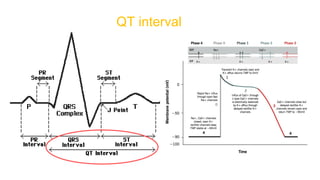
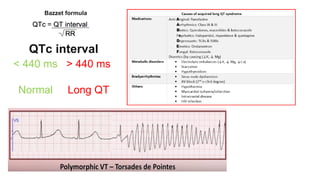
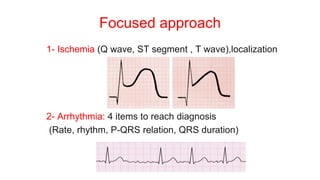
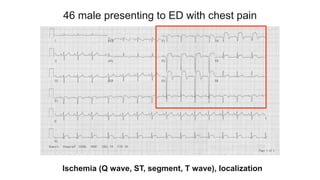
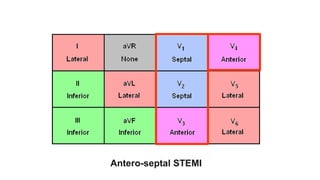
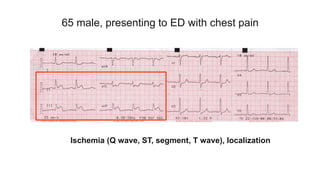
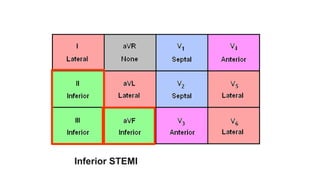
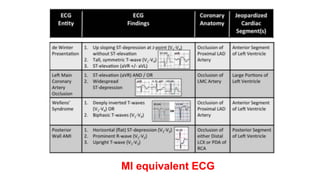
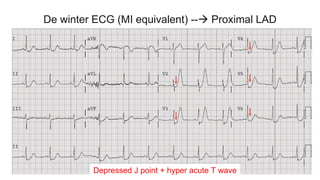
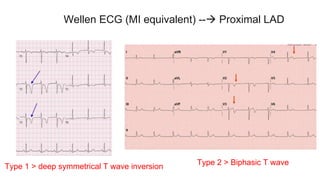
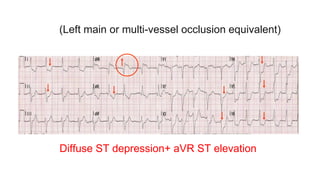
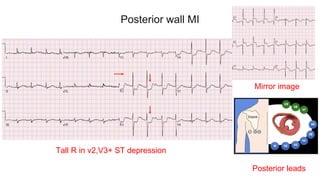
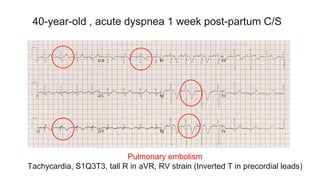
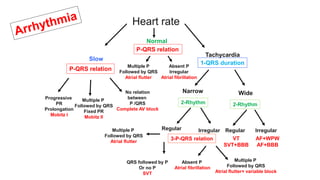
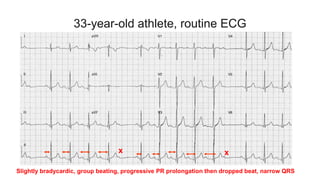
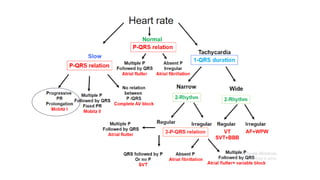
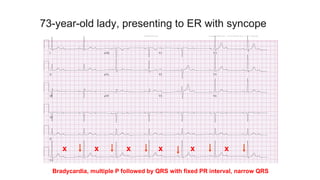
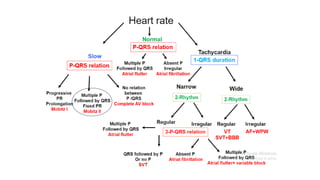
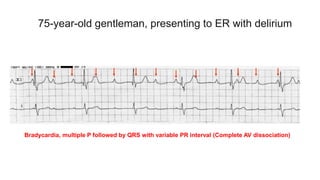
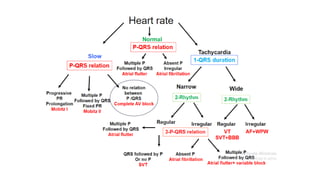
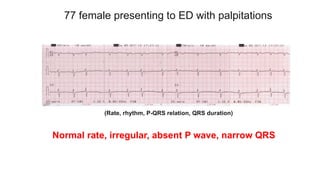
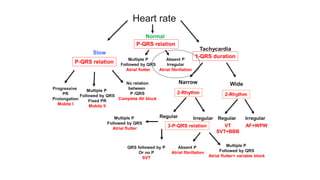
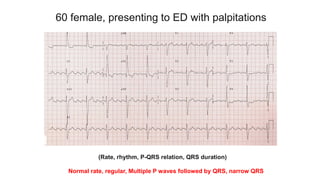
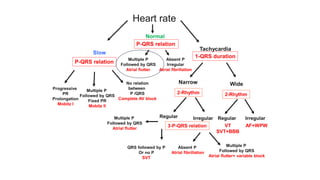
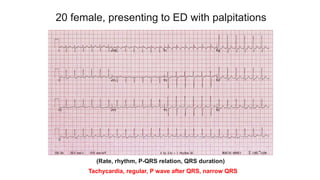
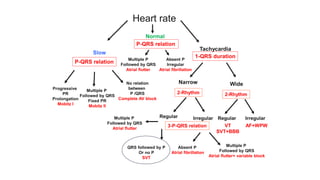
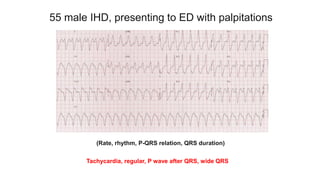
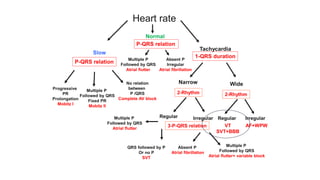
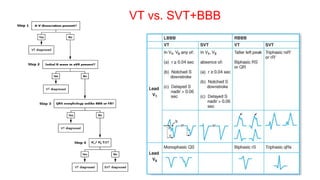
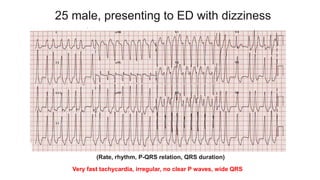
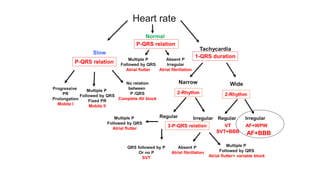
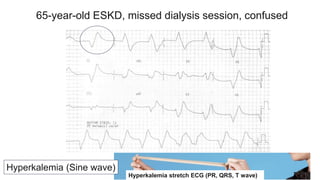
This document provides an overview of how to read an electrocardiogram (ECG). It describes the basic anatomy and electrical conduction system of the heart and how the ECG machine records and displays the heart's electrical activity. It then outlines a systematic approach for interpreting an ECG, including evaluating the rhythm, rate, axes, voltages, waves, segments, intervals, and any signs of ischemia, injury, or arrhythmia. Localization of abnormalities is also addressed. Examples are provided throughout to illustrate various normal and pathological ECG patterns.