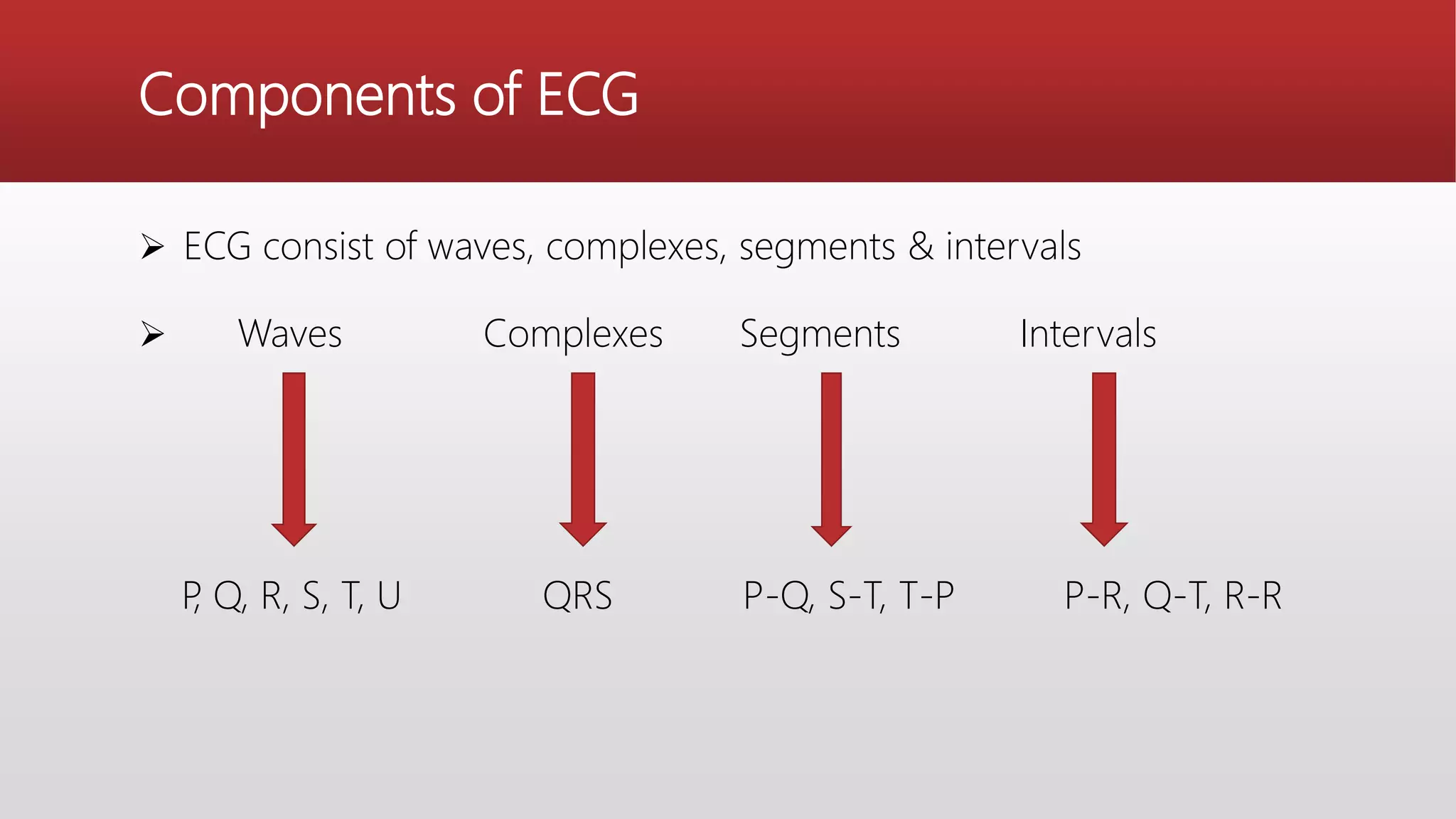
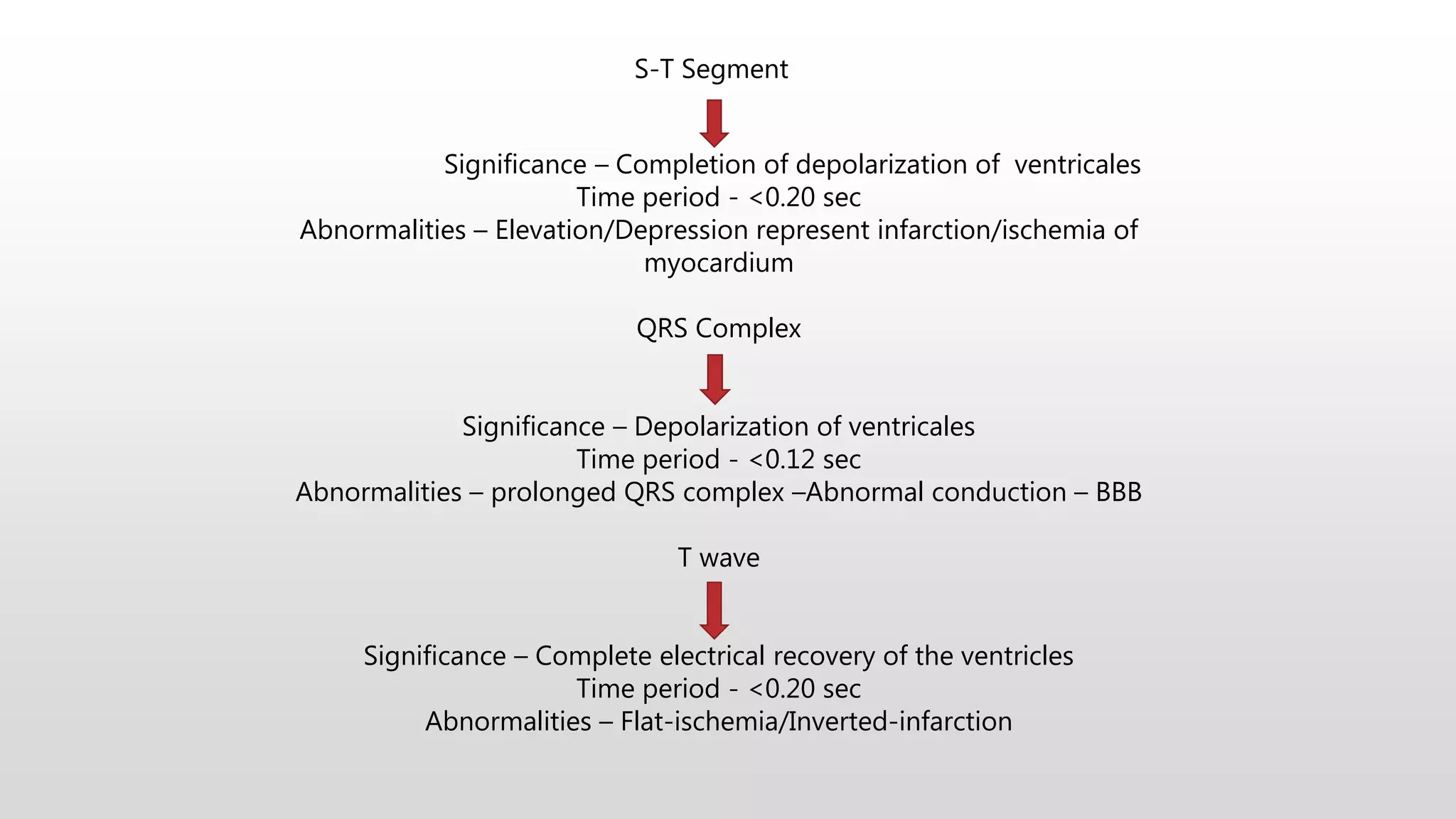
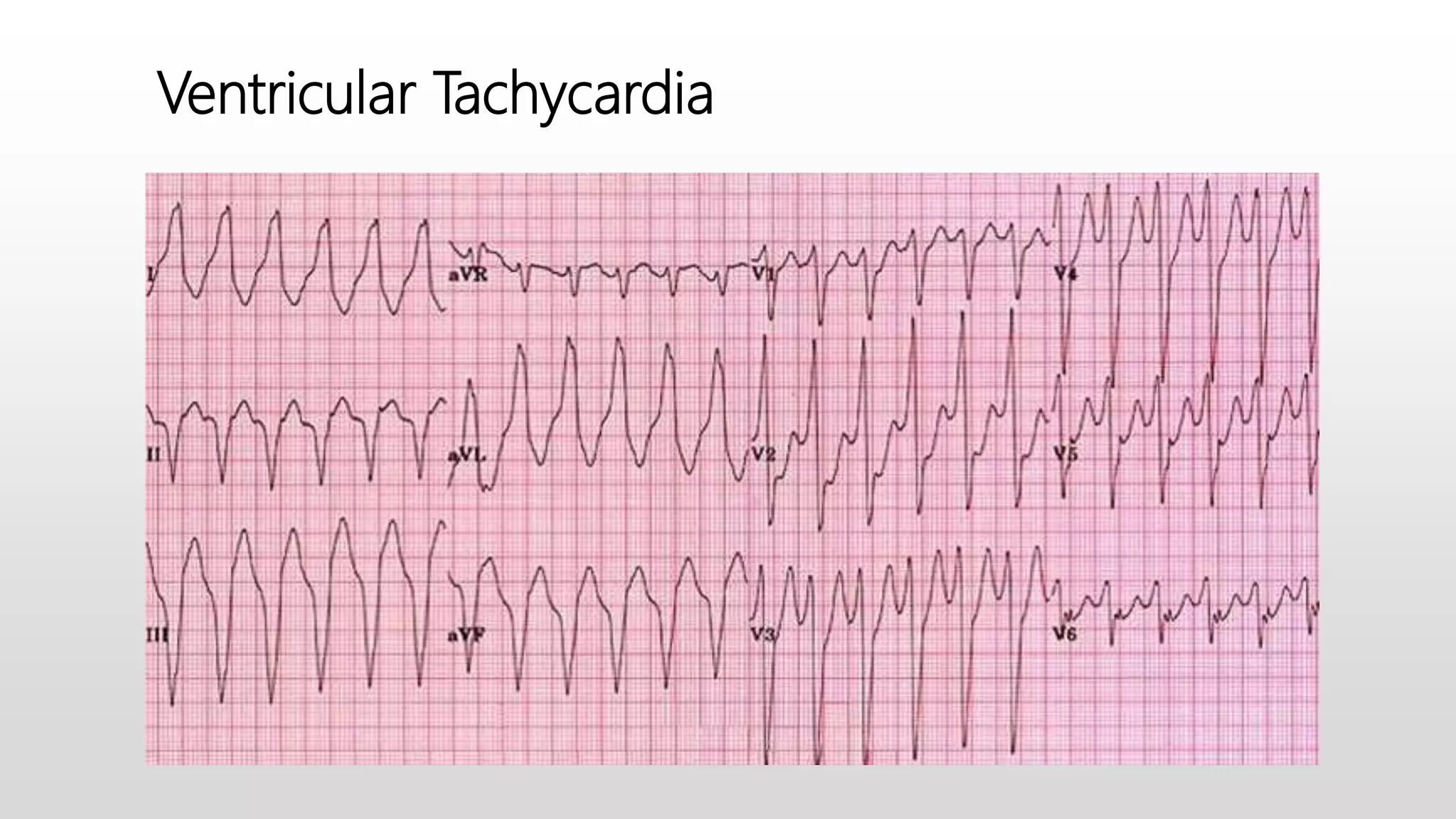
An electrocardiogram (ECG) records the electrical impulses of the heart, helping to assess cardiac function, diagnose disorders, and evaluate treatment effects. It consists of various leads and components including waves, complexes, segments, and intervals that indicate different heart activities and abnormalities. Proper lead placement and understanding of the ECG paper are essential for accurate interpretation and diagnosing conditions like myocardial infarction and arrhythmias.