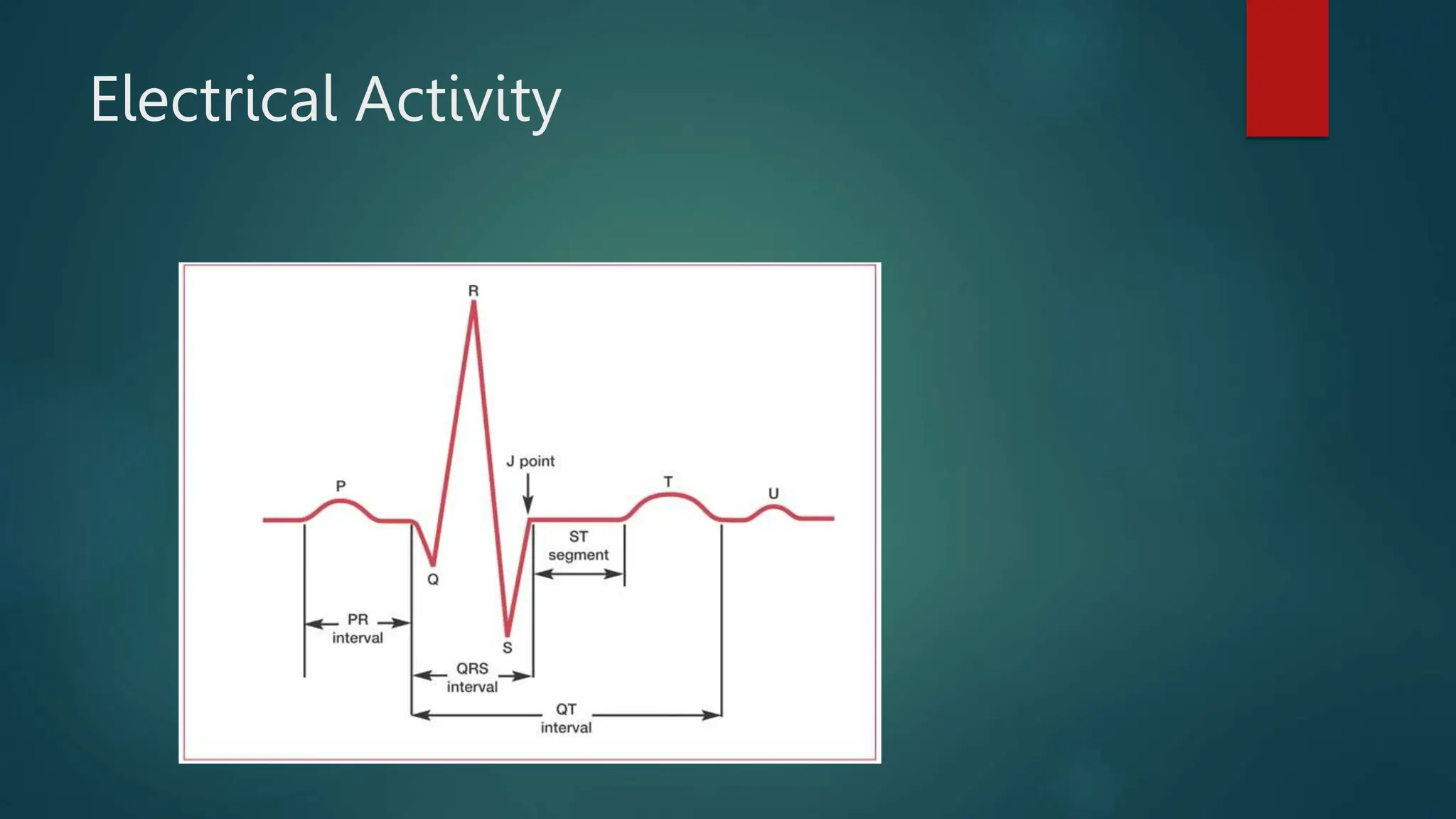
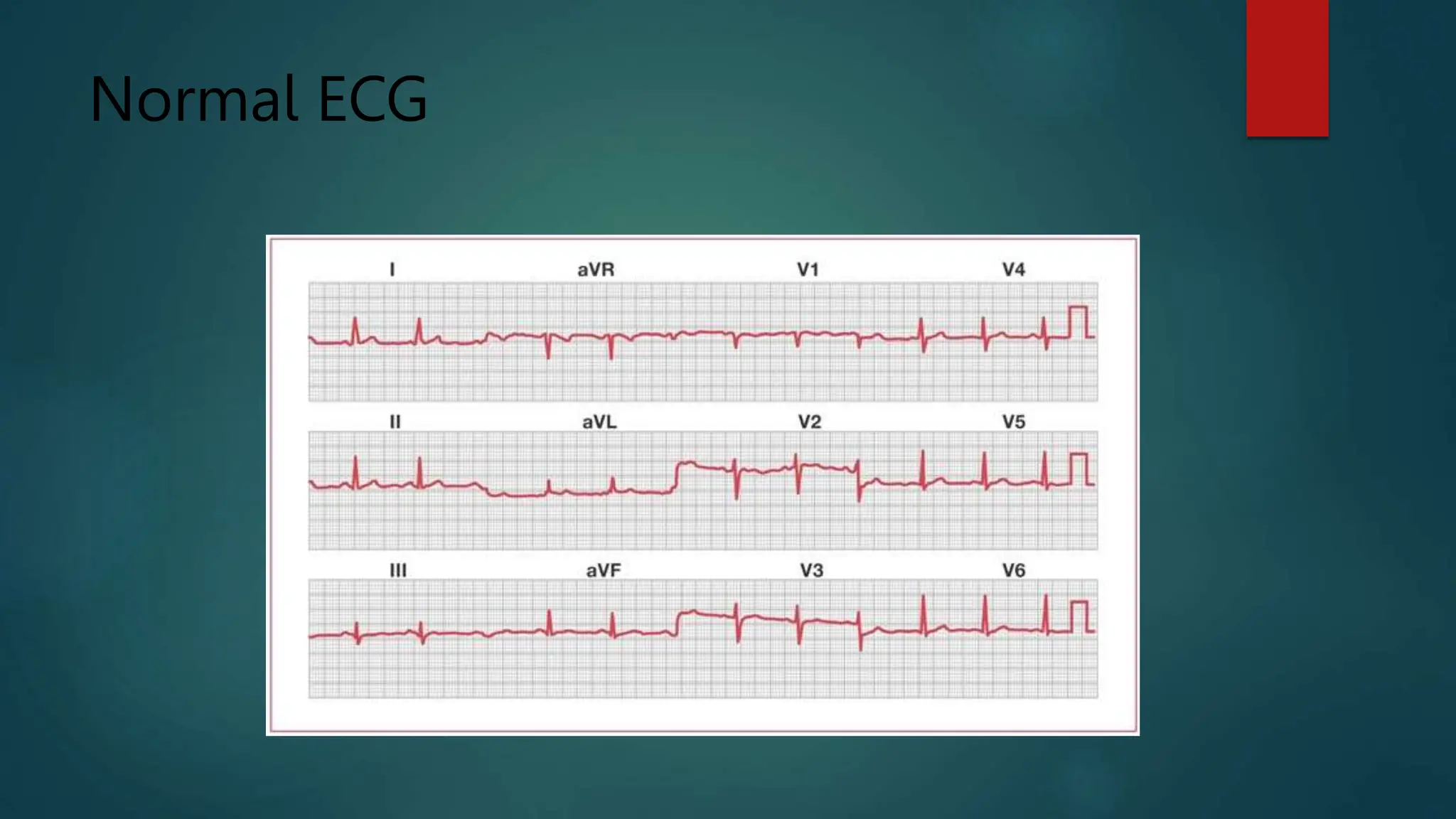
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a noninvasive tool used to diagnose various heart conditions such as arrhythmias, coronary artery disease, and heart attacks. The procedure involves attaching electrodes to the patient's chest and limbs to record the heart's electrical activity, with potential for continuous monitoring using Holter or event monitors. ECG results provide critical insights into heart rate, rhythm, structure, and blood supply, which can guide further medical decision-making.