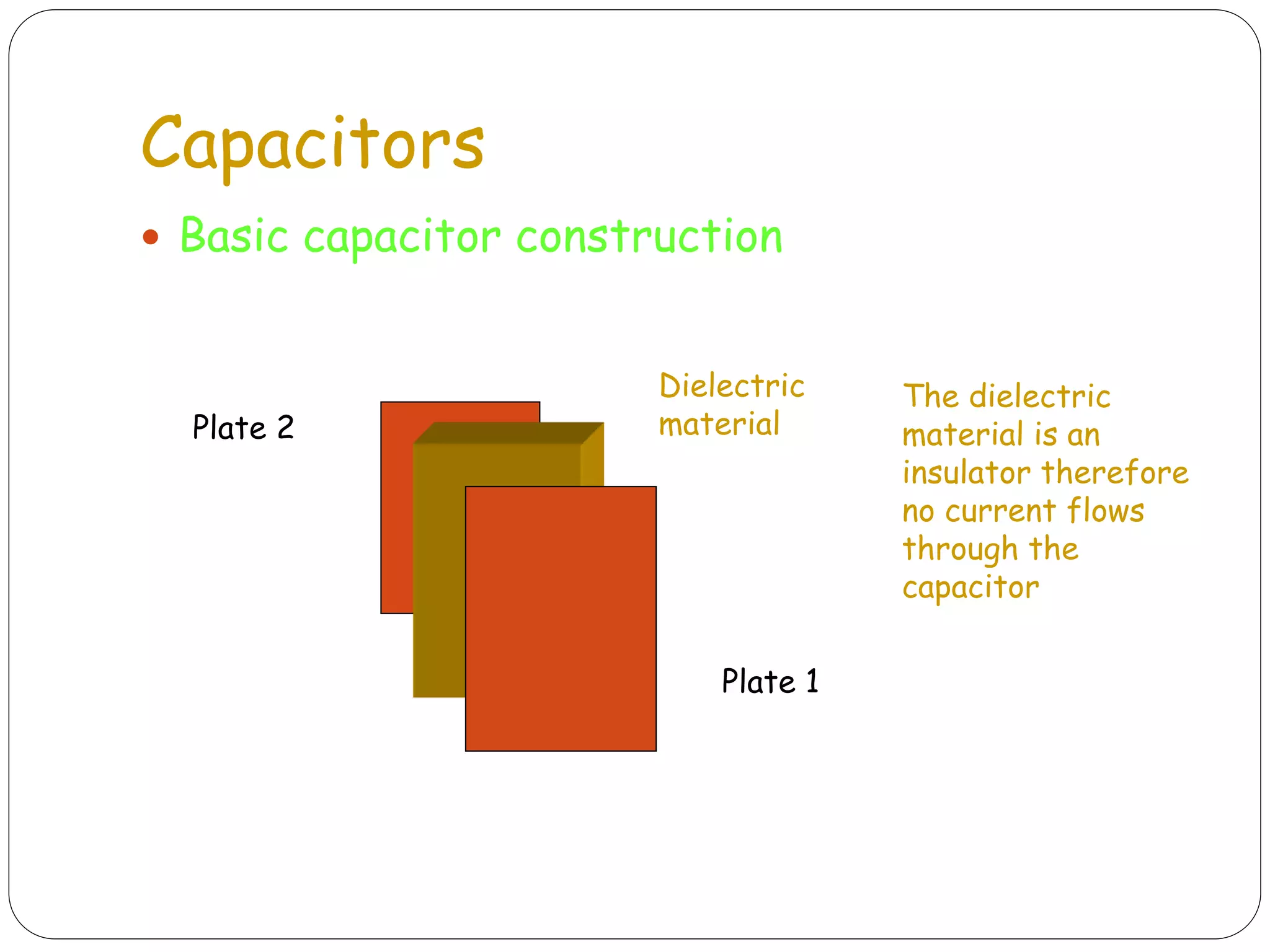
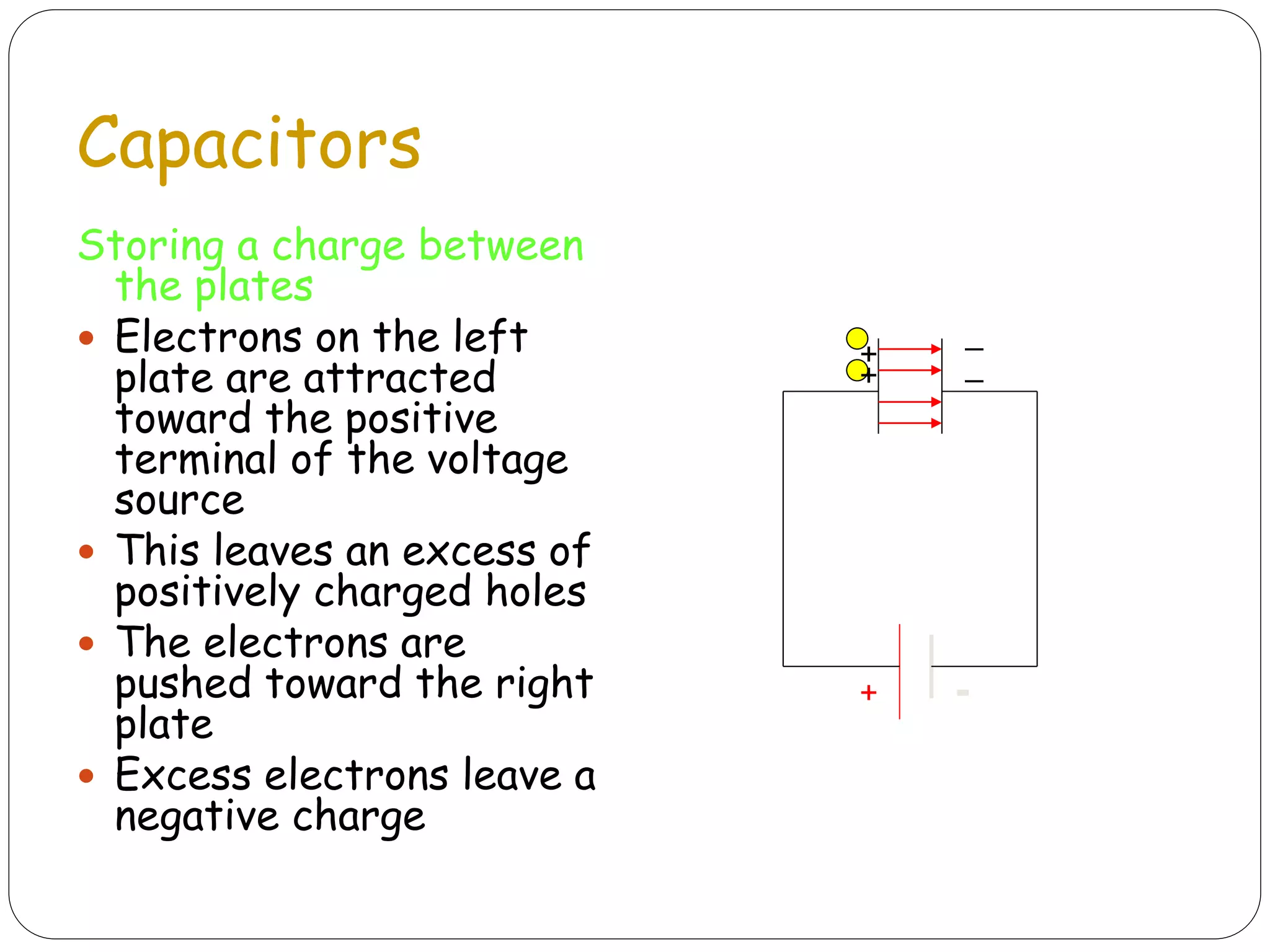
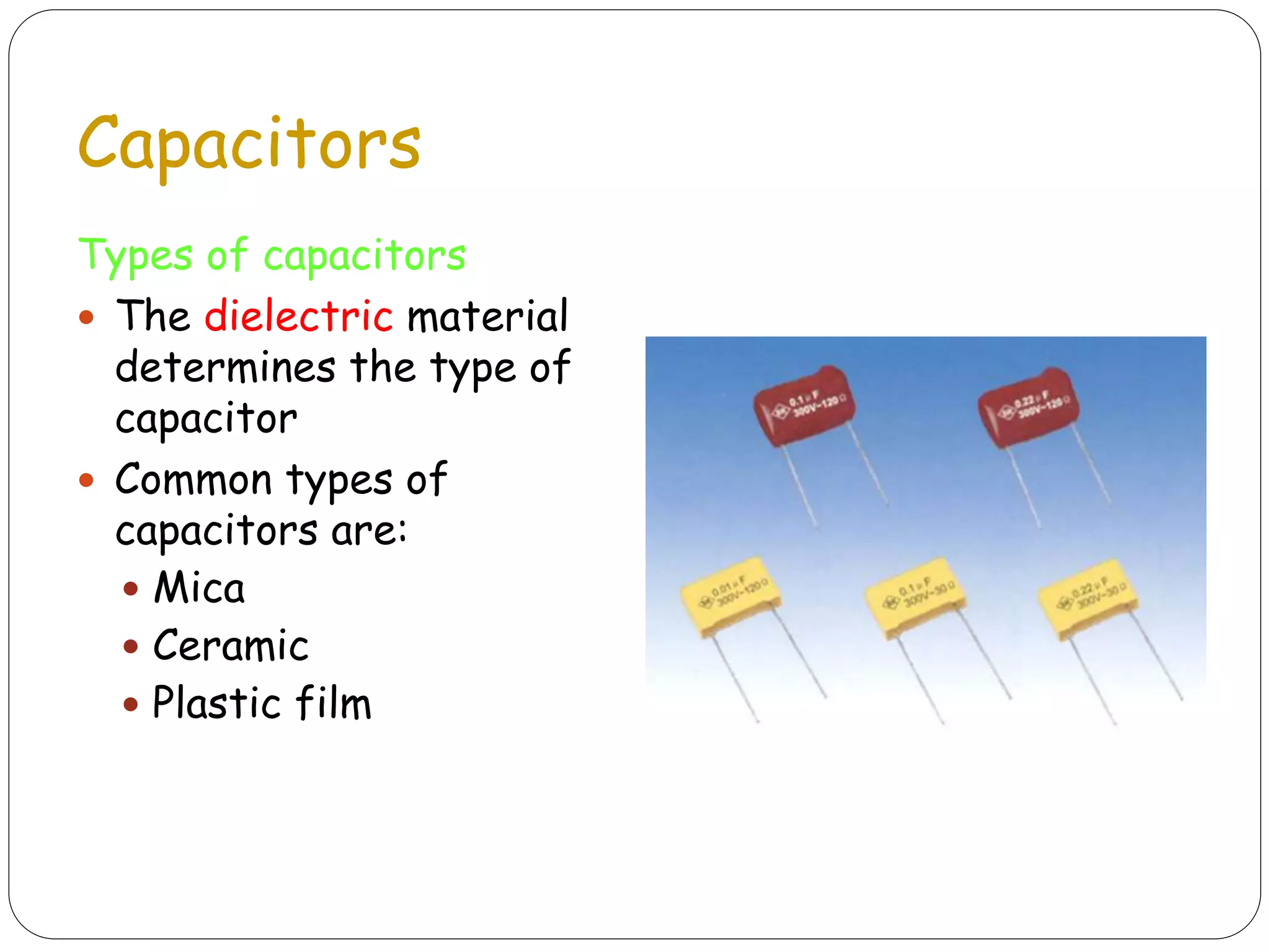
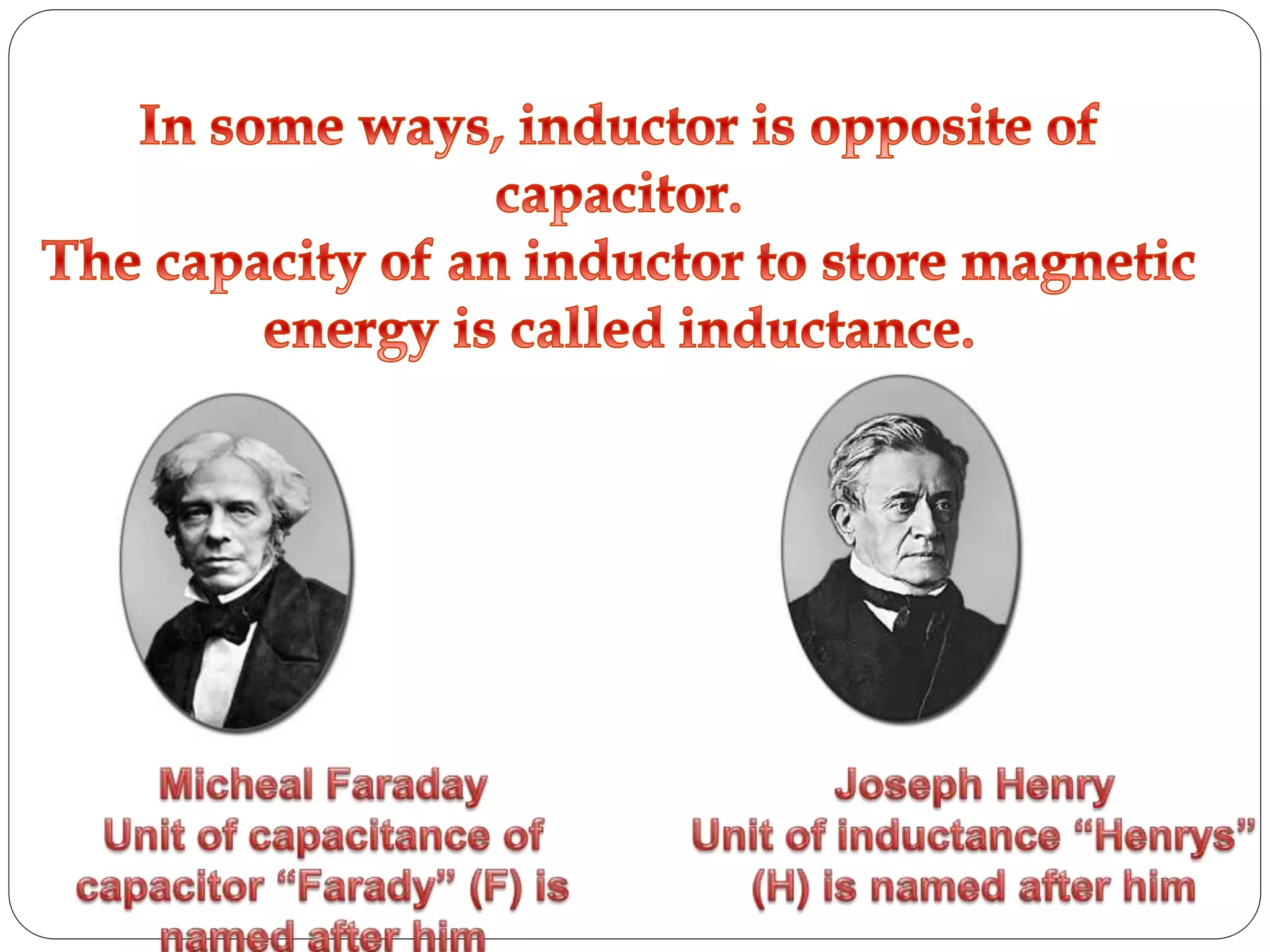
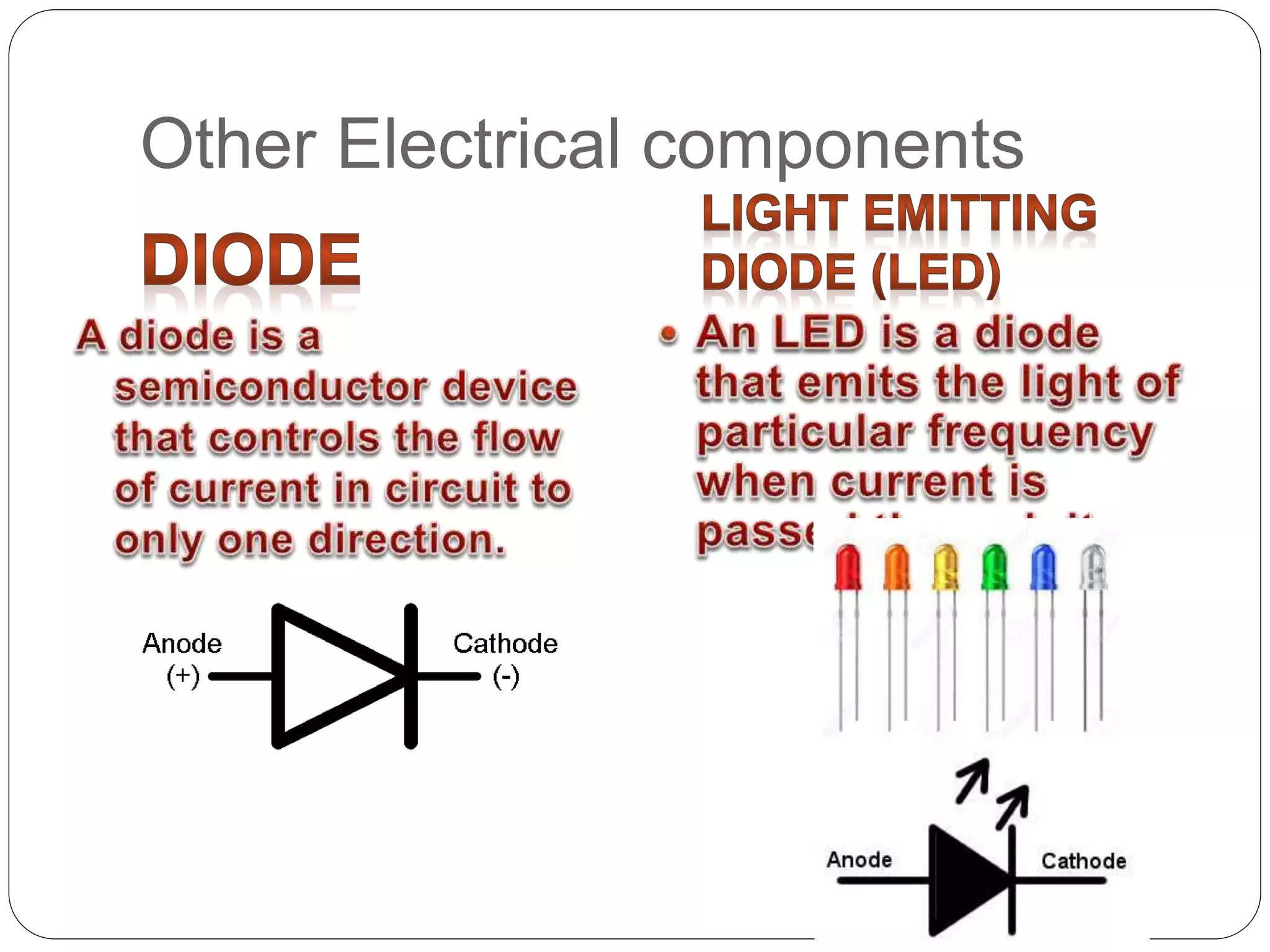
The document discusses several basic electrical components. It describes batteries as having three parts - an anode, cathode, and electrolyte. Chemical reactions in the battery cause a build up of electrons at the anode. Common battery types are also listed. Resistors are described as passive components that increase electrical resistance and reduce current flow. Capacitors are explained as storing electrical charge between two parallel plates separated by an insulating material. Inductors are coils of wire that can do interesting things due to magnetic properties. Transformers are used to increase or decrease alternating current. Fuses and jumpers are also briefly introduced.