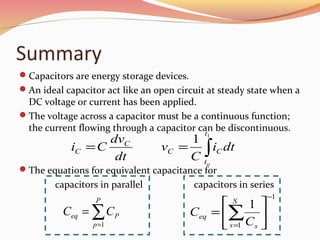
Capacitors are energy storage devices composed of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric, with their capacitance determined by the surface area, plate spacing, and dielectric constant. They can be fixed, electrolytic, or variable, and behave as open circuits in steady state with DC voltages, while voltage across a capacitor must be continuous, though current can be discontinuous. The document also details techniques for charging and discharging a capacitor and the equations for calculating equivalent capacitance in parallel and series configurations.















![Ceq for Capacitors in Series
i
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )[ ] 1
4321eq
t
t
t
t4
t
t3
t
t2
t
t1
t
t4
4
t
t3
3
t
t2
2
t
t1
1
4321
1111C
idt
1
idt
1
idt
1
idt
1
idt
1
idt
1
idt
1
idt
1
idt
1
1
o
1
o
1
o
1
o
1
o
1
o
1
o
1
o
1
o
−
+++=
=
+++=
==
==
+++=
∫
∫∫∫∫
∫∫
∫∫
CCCC
C
v
CCCC
v
C
v
C
v
C
v
C
v
vvvvv
eq
in
in
in](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capacitors-160108113626/85/Capacitors-19-320.jpg)