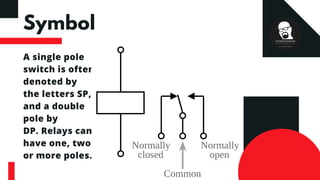
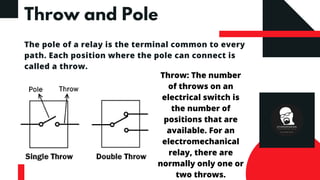
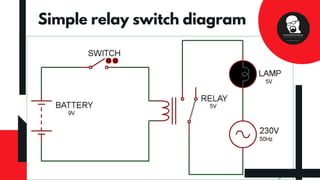
This document discusses relays, including their construction, symbol, types, and advantages. A relay is an electromagnetic switch that uses a small electric current to turn on or off a larger current. It has a coil that becomes a magnet when powered, and uses this magnetism to switch contacts like normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC). Relays have multiple poles and throws to control connections. They allow low-power control of high-power loads, and are used in applications like motor control. Relays provide advantages like low control power requirements and switching of larger loads.