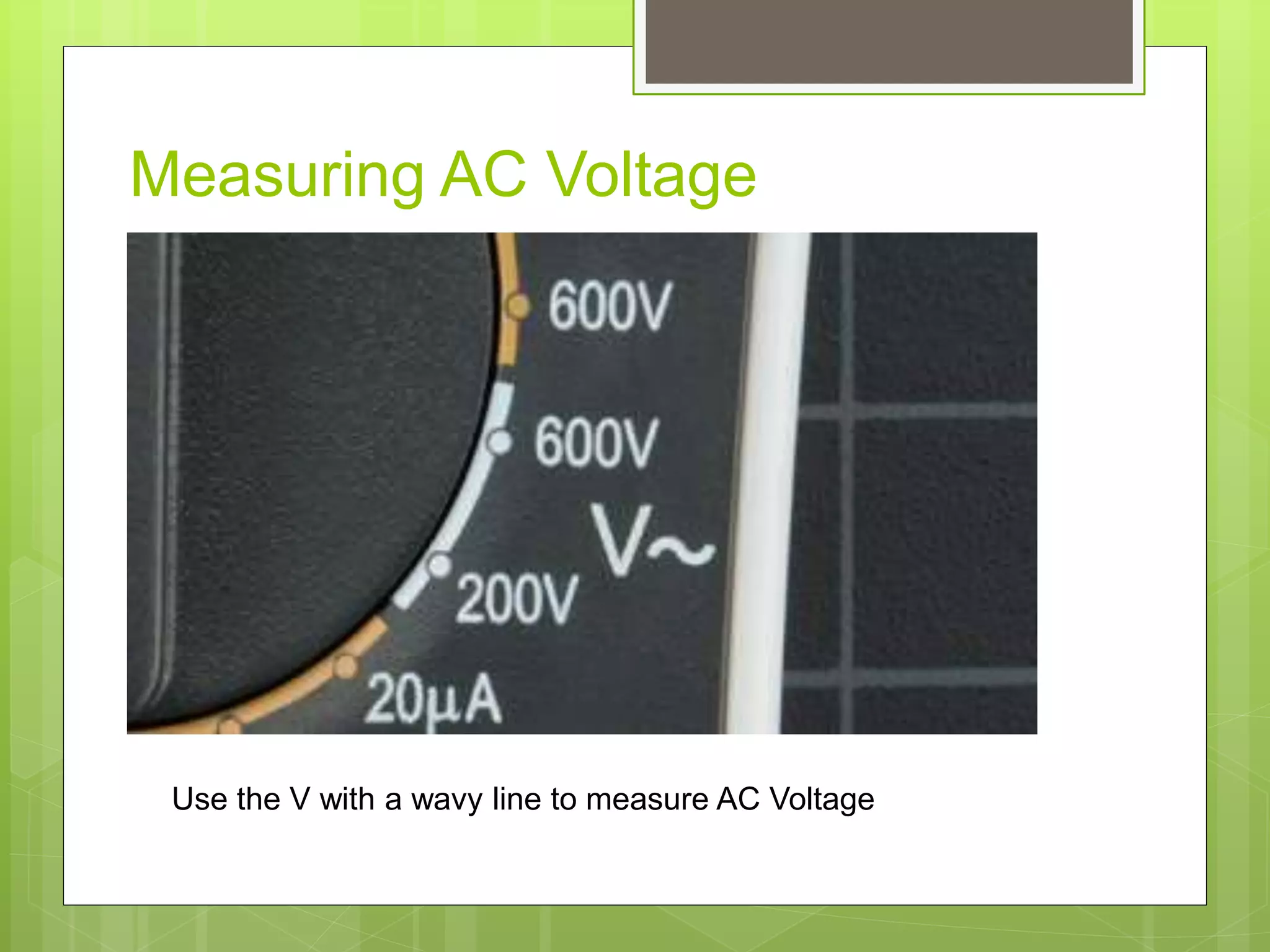
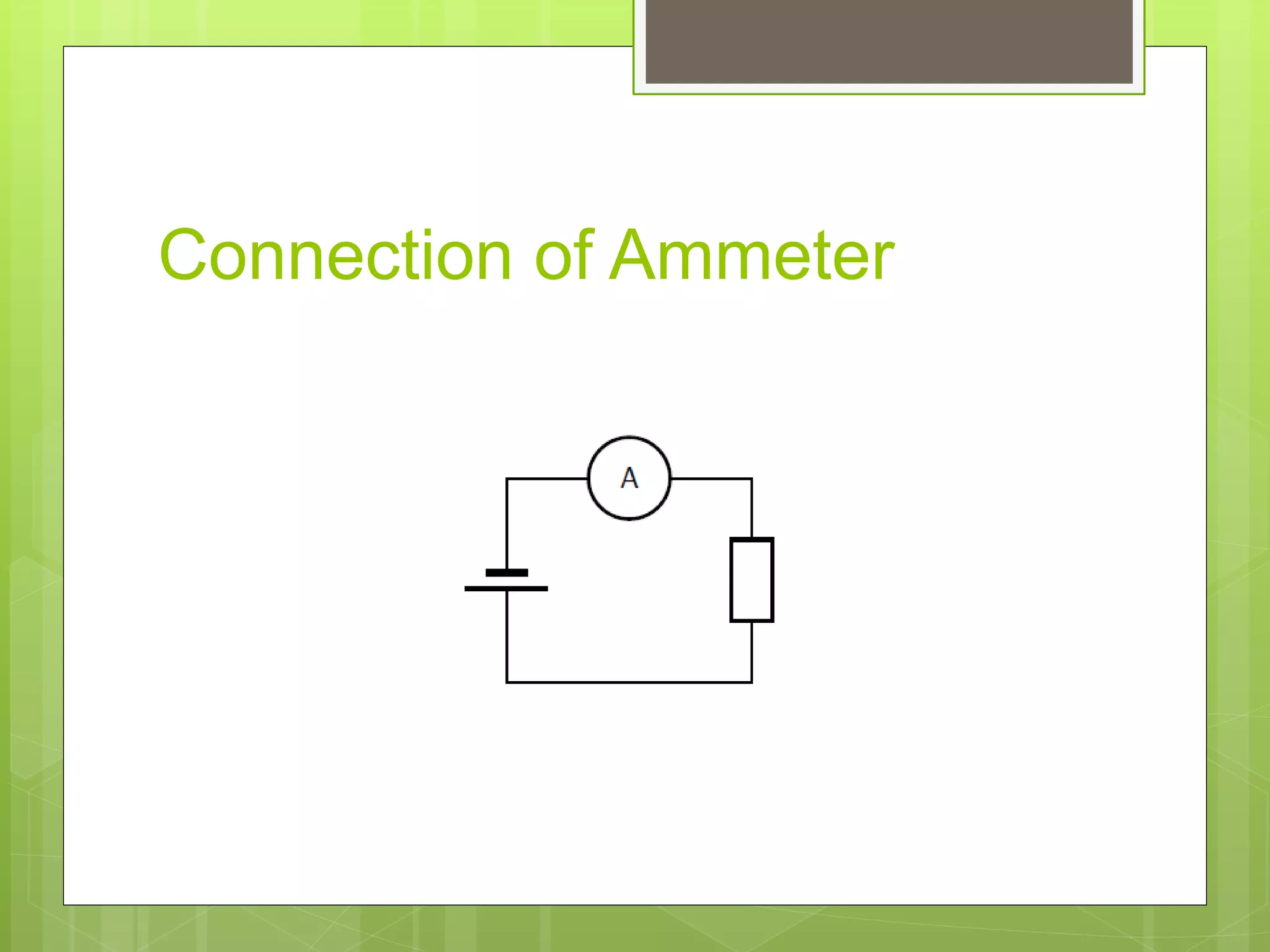
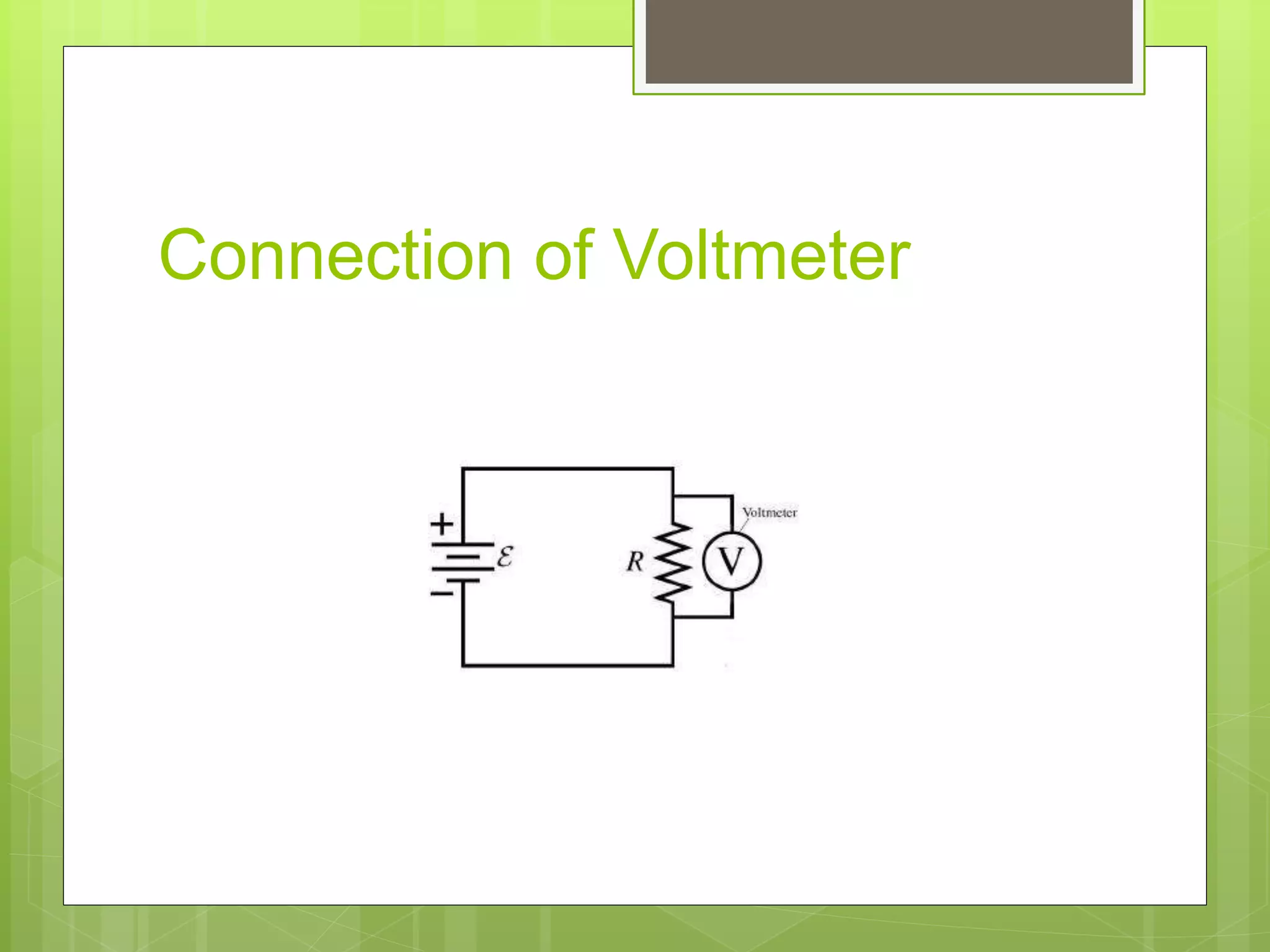
This document discusses different types of basic electrical measuring instruments. It describes absolute instruments, like tangent galvanometers, which directly measure electrical quantities without needing calibration. Secondary instruments require calibration against a standard, examples being multimeters, clamp meters, ammeters and voltmeters. Multimeters are described in detail, including their display, selection knob and ports. The document explains how to use a multimeter to measure AC voltage, DC voltage, resistance, current and test continuity. Clamp meters and the working of ammeters and voltmeters are also briefly covered.