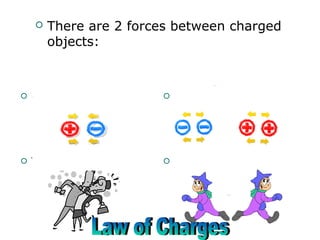
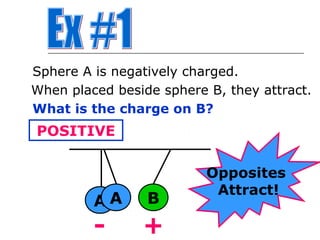
The document discusses electrical charges, noting that there are two types - positive and negative - and that opposites attract while likes repel. It explains how some materials are more likely to take on or lose negative charges than others according to their placement in the electrostatic series. Various examples are provided to illustrate the concepts of attraction and repulsion between charged objects.