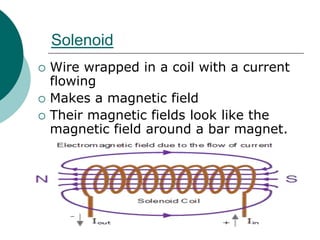
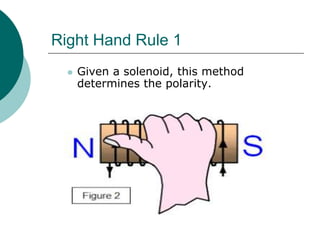
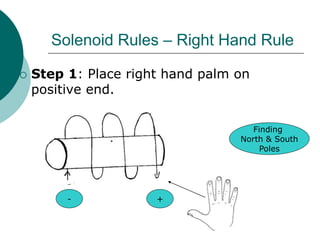
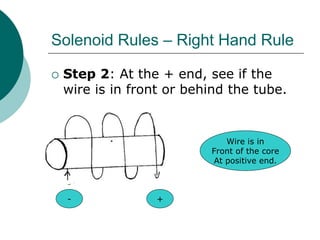
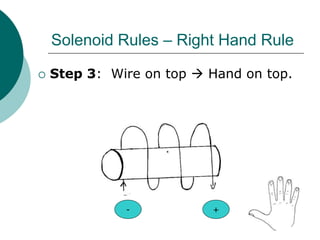
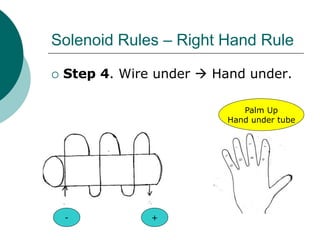
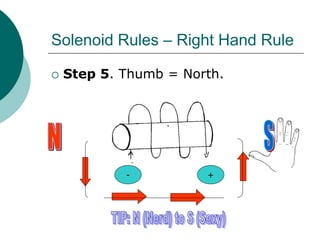
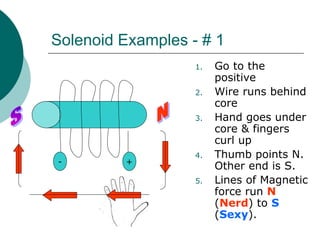
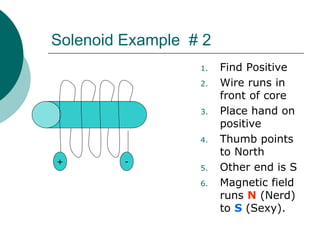
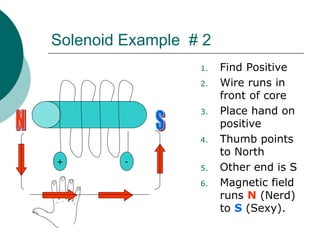
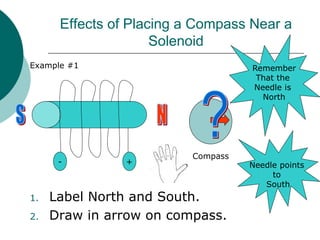
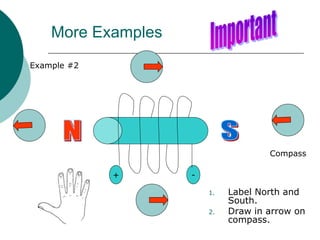
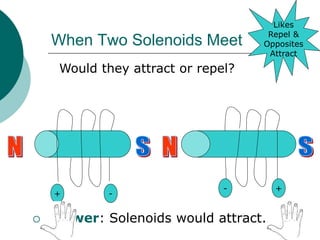
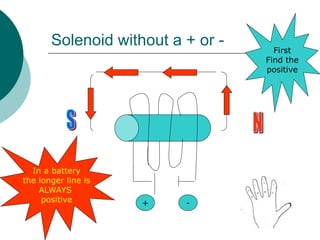
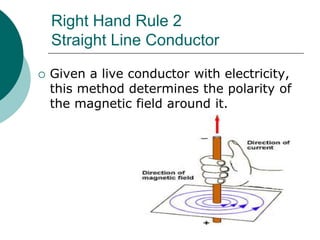
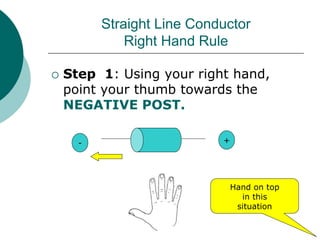
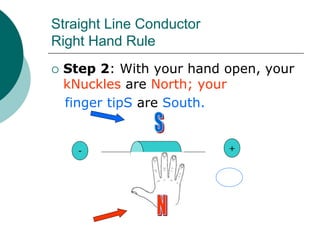
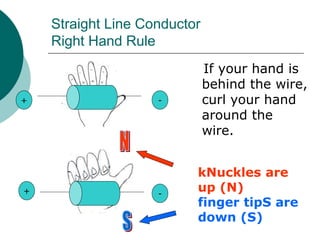
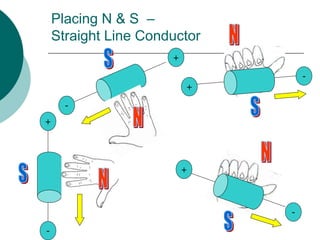
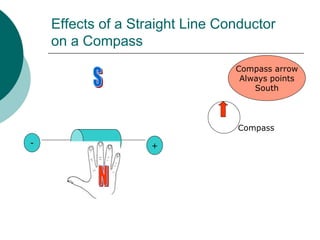
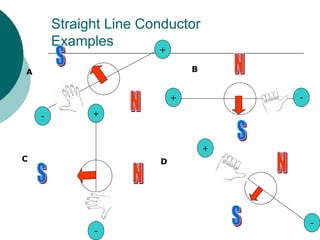
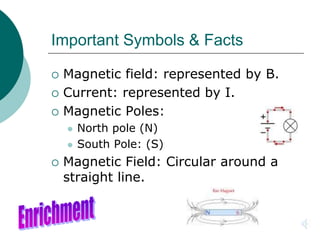
This document discusses solenoids and how to determine the magnetic field around them. It explains that a solenoid is a coil of wire that produces a magnetic field similar to a bar magnet when electric current flows through it. The right hand rule is used to determine the north and south poles of a solenoid by placing the hand at the positive end and orienting the thumb to point north. Examples are given to demonstrate how to apply the right hand rule to identify pole orientation in different solenoid setups.