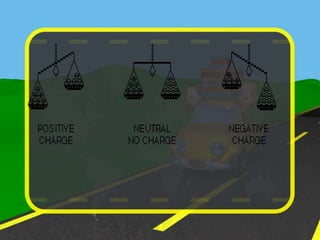
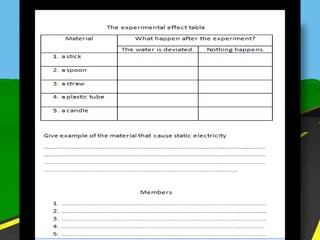
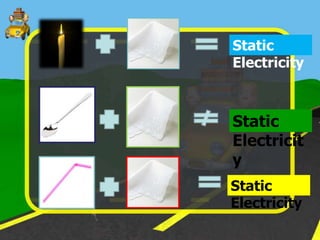
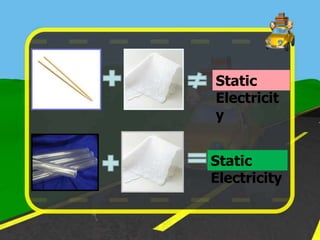
The document discusses static electricity through an experiment. It introduces key terms like electrons, insulators, and conductors. The experiment has students work in groups to observe how rubbing materials like a plastic cup or stick with a handkerchief causes a transfer of electrons, leaving one material positively charged and the other negatively charged. Through pouring water and using other materials, the students can see the effects of this transfer of static charge. The purpose is to demonstrate how static electricity works and which materials more easily allow electron movement.