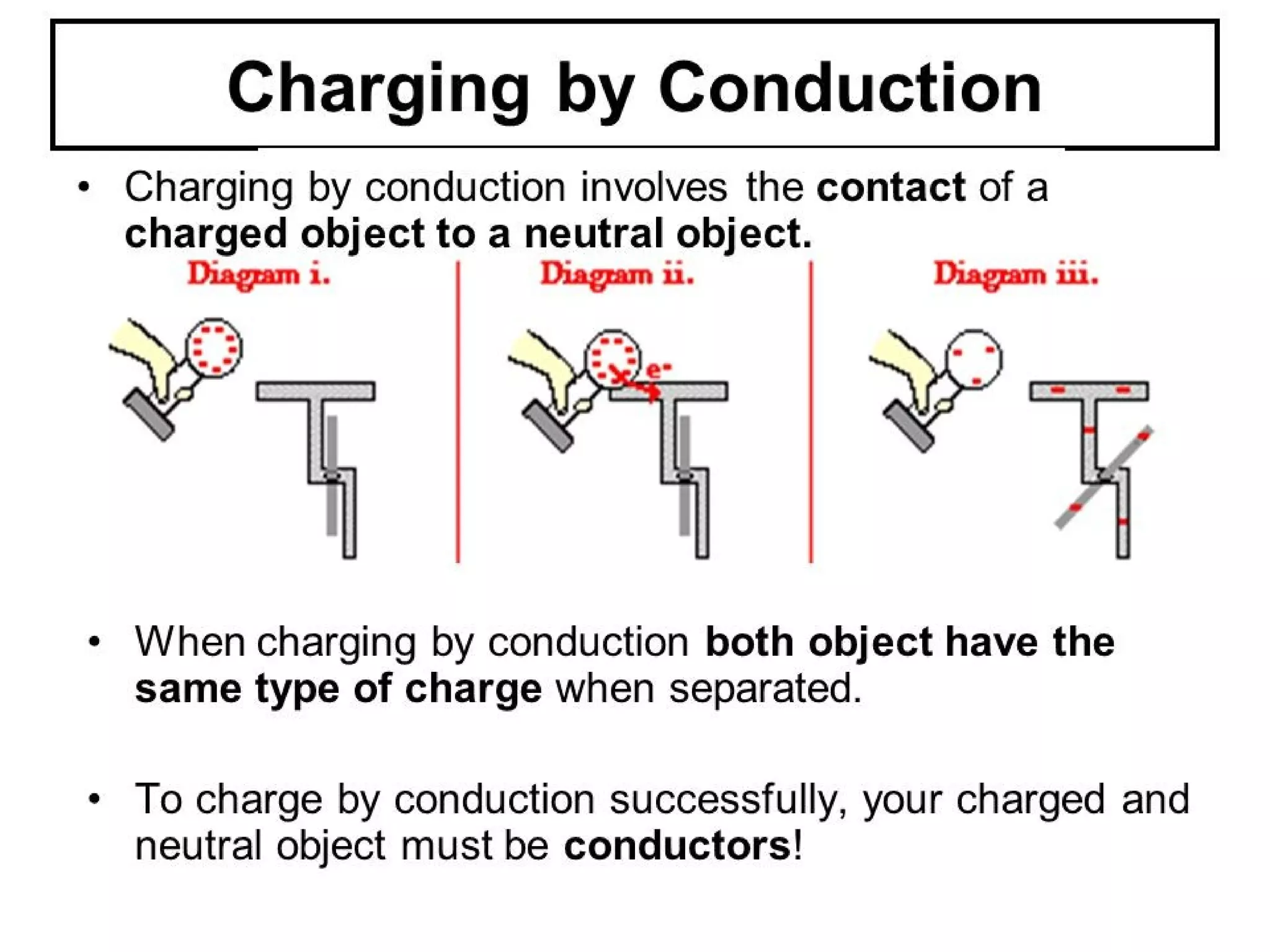
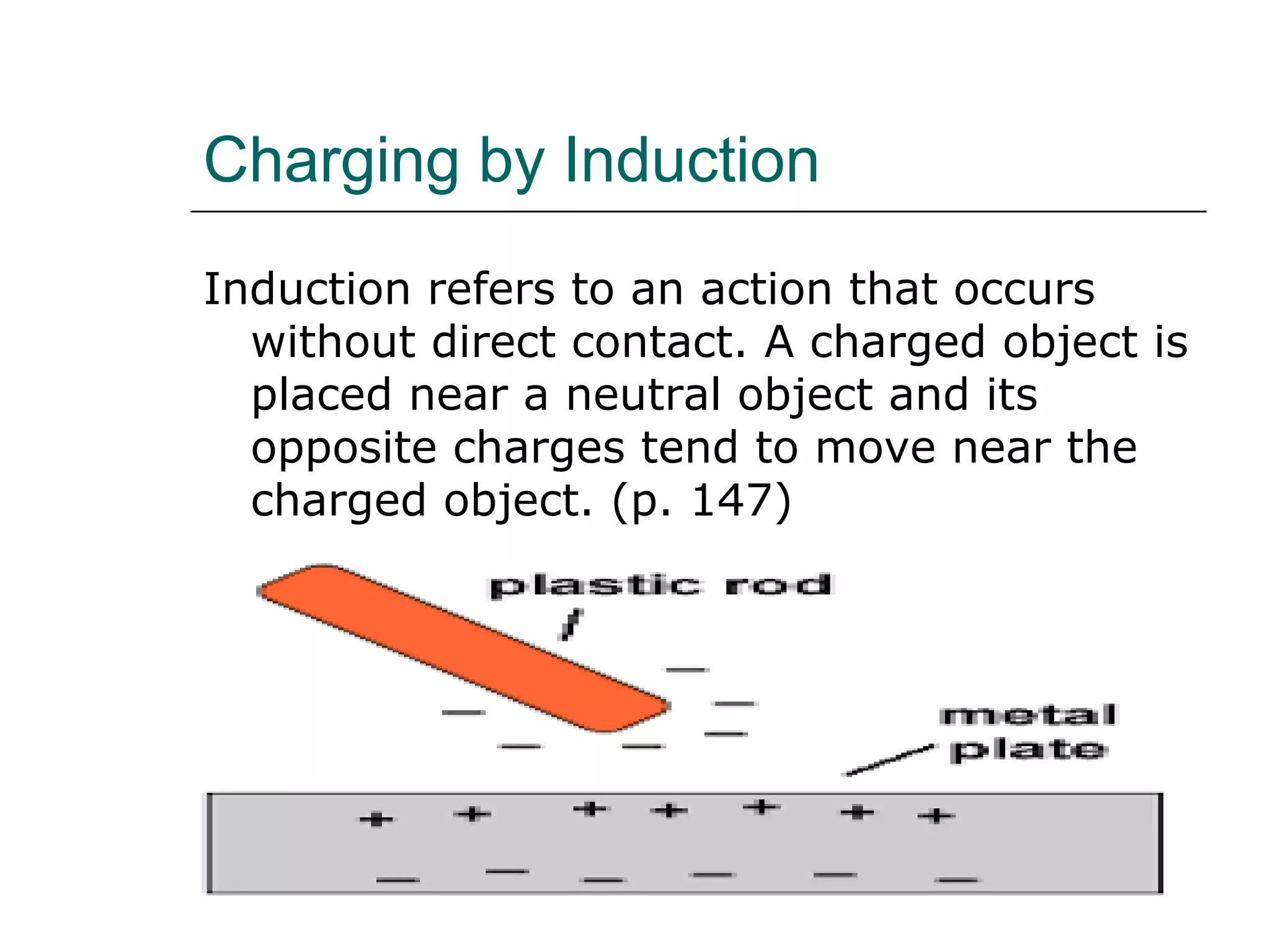
Electrical charges are caused by positive and negative charges from protons and electrons. All objects begin neutral but can become positively or negatively charged by gaining or losing electrons. There are two forces between charged objects - attraction between opposite charges and repulsion between like charges. Charges can be induced through friction, conduction, or induction without direct contact. The triboelectric series ranks materials based on their ability to gain or lose electrons through friction charging.