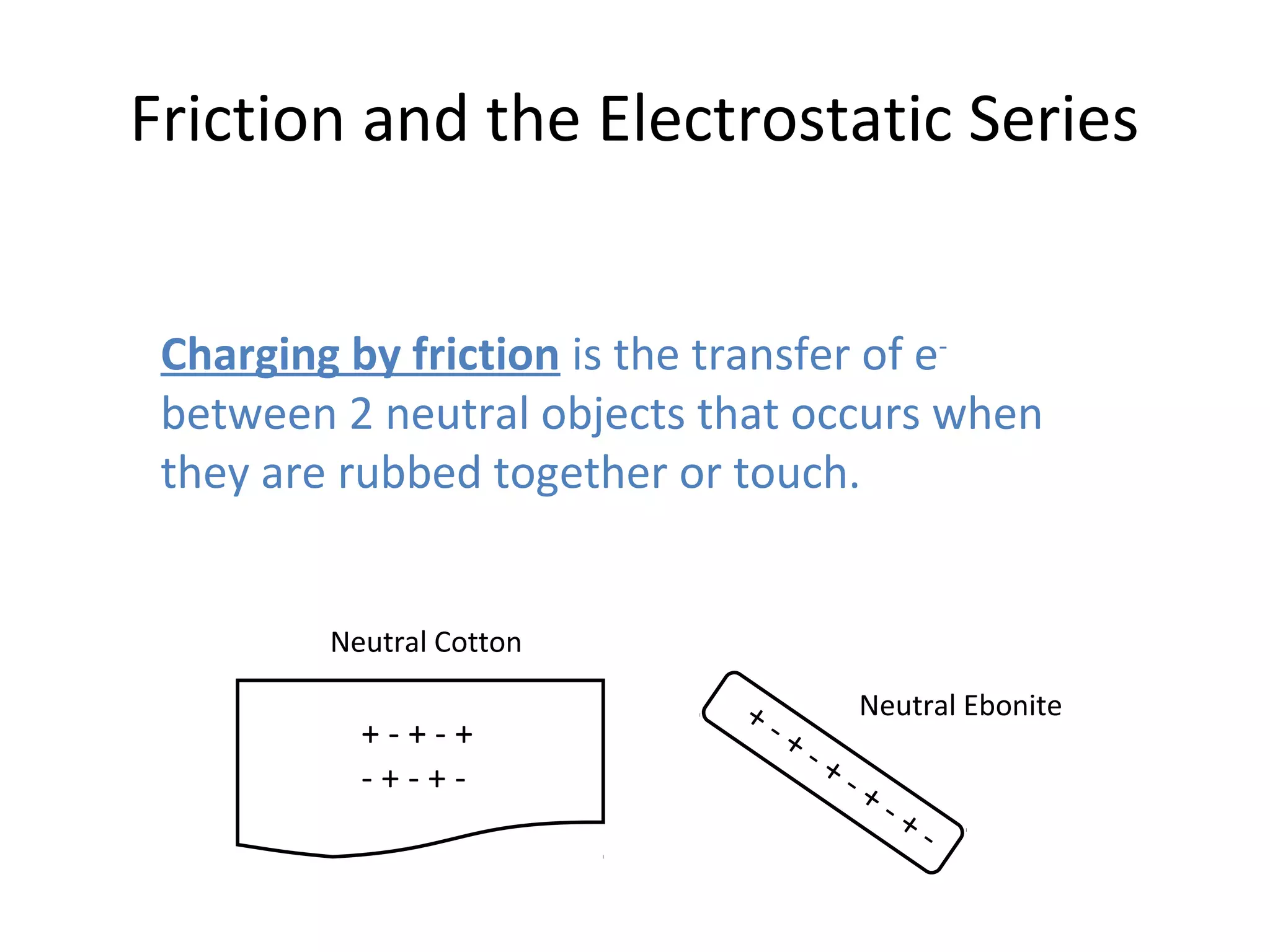
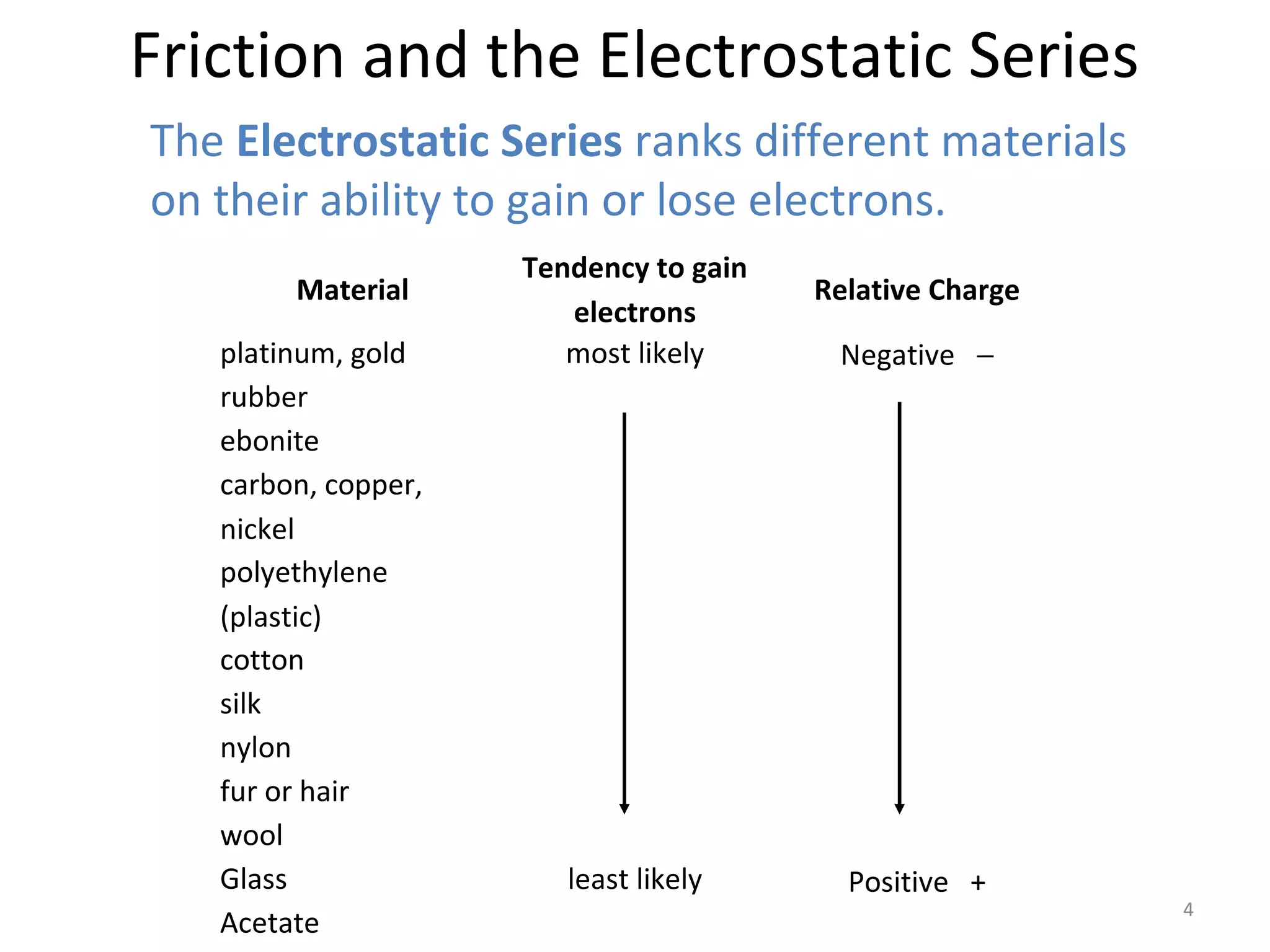
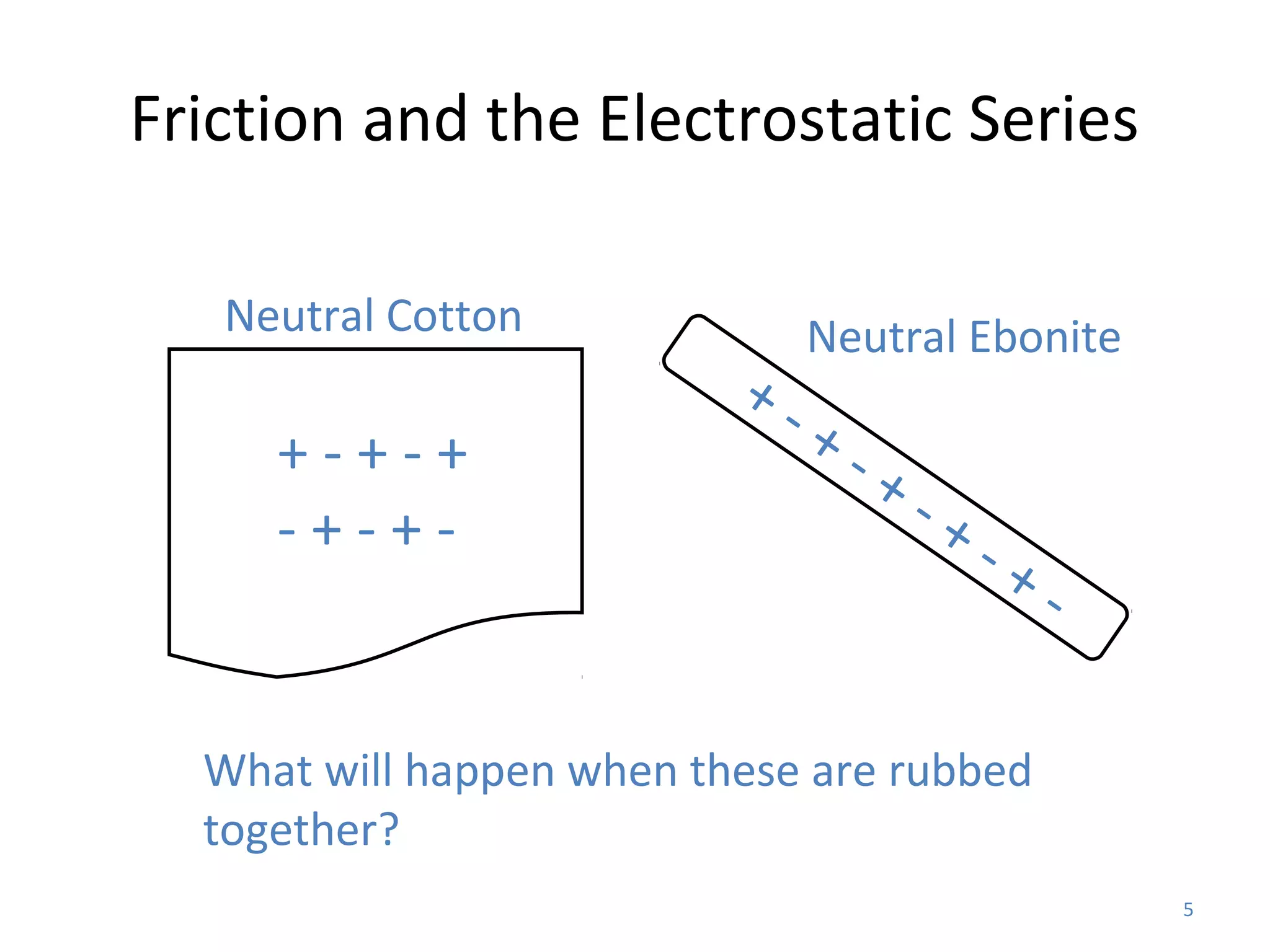
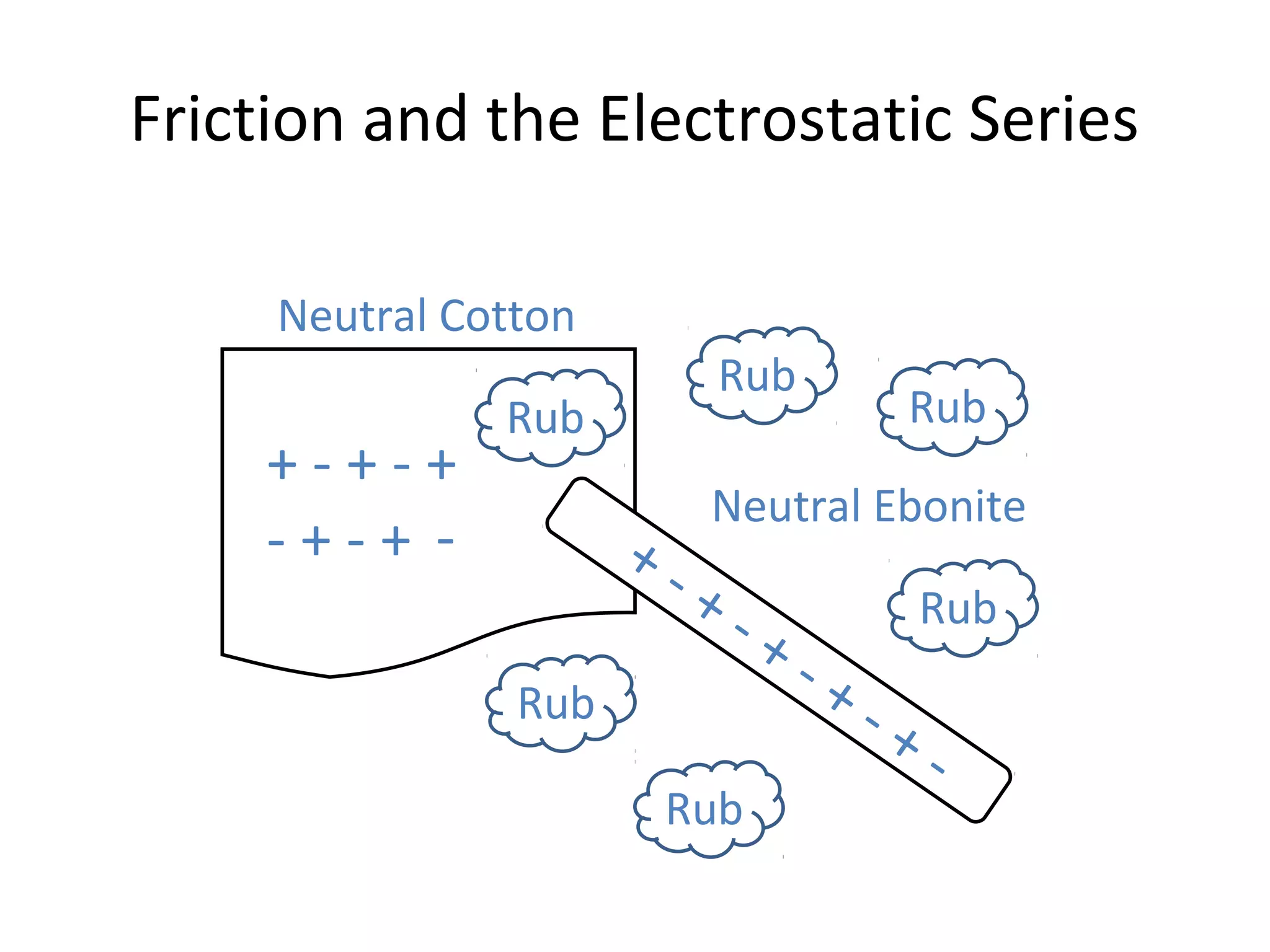
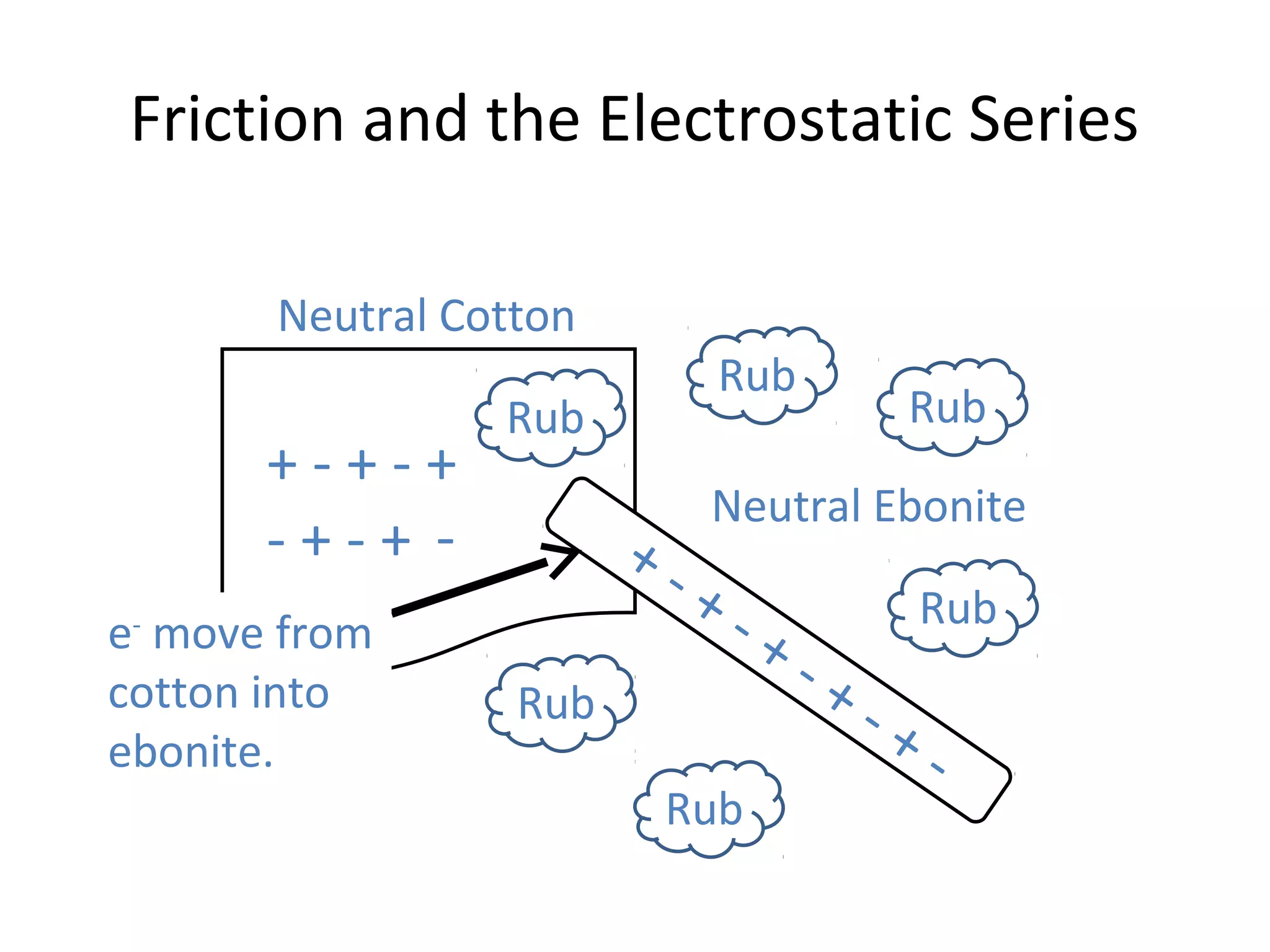
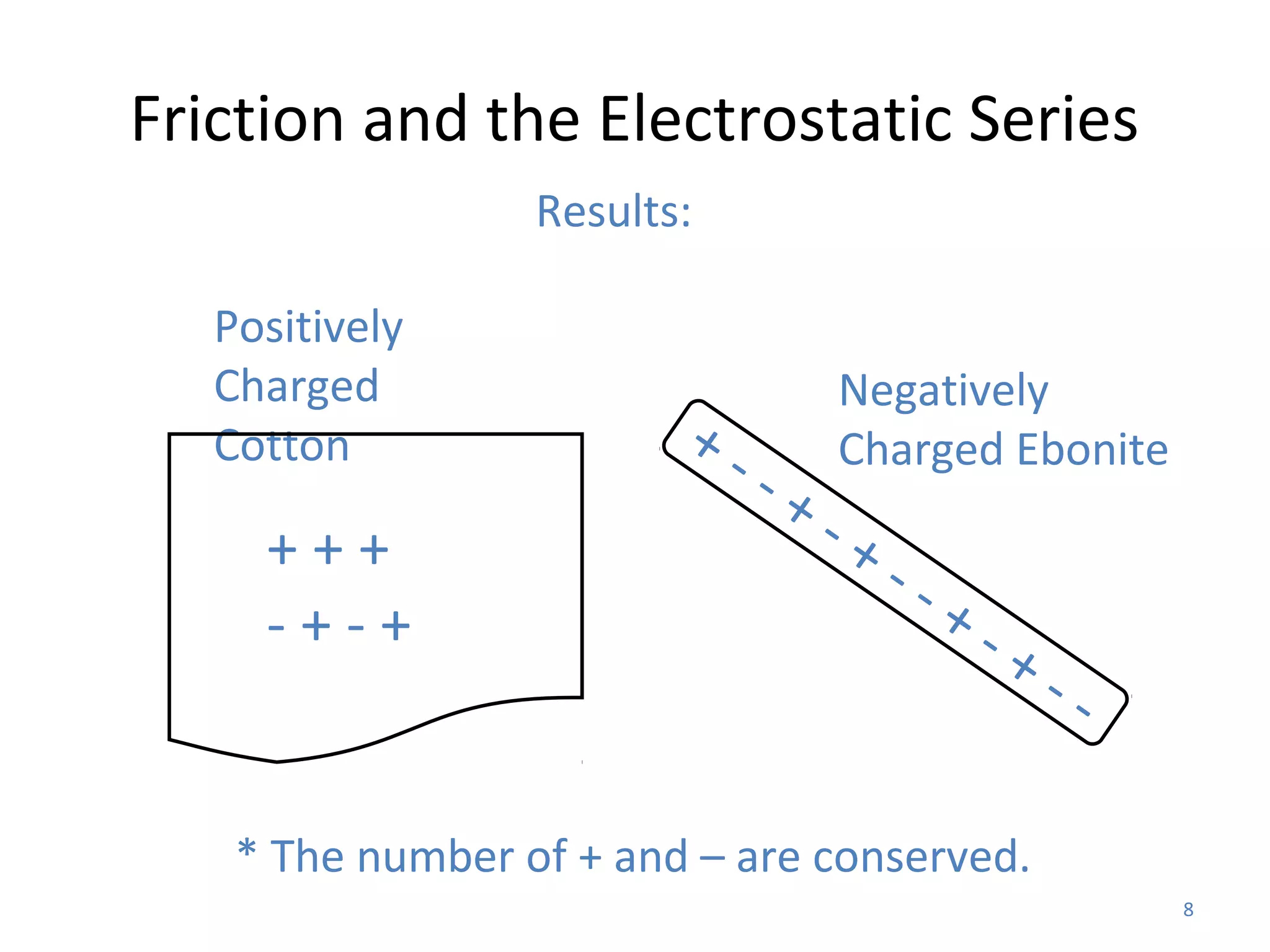
Friction between two neutral materials can cause a transfer of electrons between them. When cotton and ebonite are rubbed together, electrons will move from the cotton into the ebonite, leaving the cotton positively charged and the ebonite negatively charged. Materials can be ranked in an electrostatic series based on their tendency to gain or lose electrons through friction.