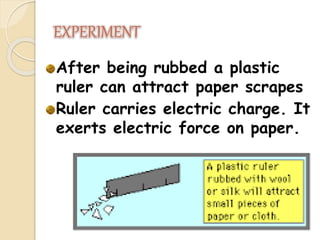
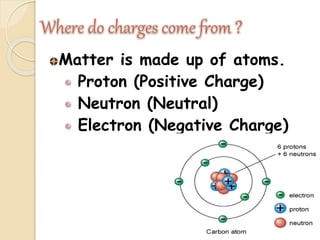
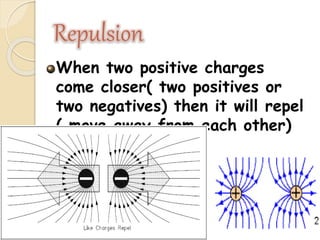
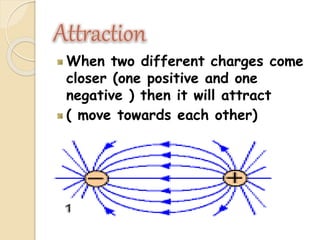
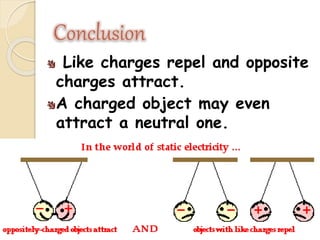
Static electricity is a stationary electrical charge that builds up on the surface of a material. It is called "static" because the charges do not move. Rubbing two materials together, like a plastic ruler and wool cloth, can transfer electrons between them, leaving one material positively charged and the other negatively charged. Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract, explaining why a negatively charged ruler may attract scraps of paper.