The document discusses key concepts about the periodic table including:
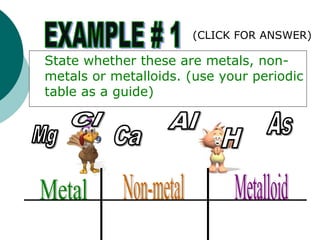
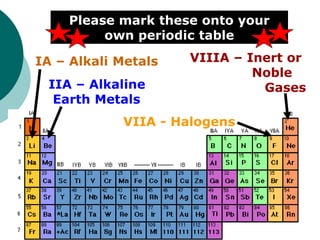
- Locating metals, nonmetals, and metalloids and identifying families such as alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, and inert gases.
- Describing properties of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids and how they differ.
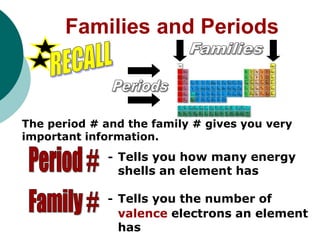
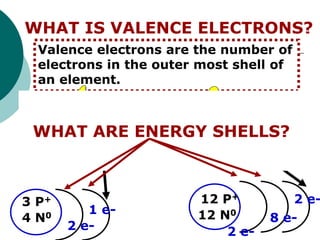
- Explaining that periods indicate the number of electron shells an element has and families indicate the number of valence electrons.
- Identifying important families on the periodic table including alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, and inert gases.