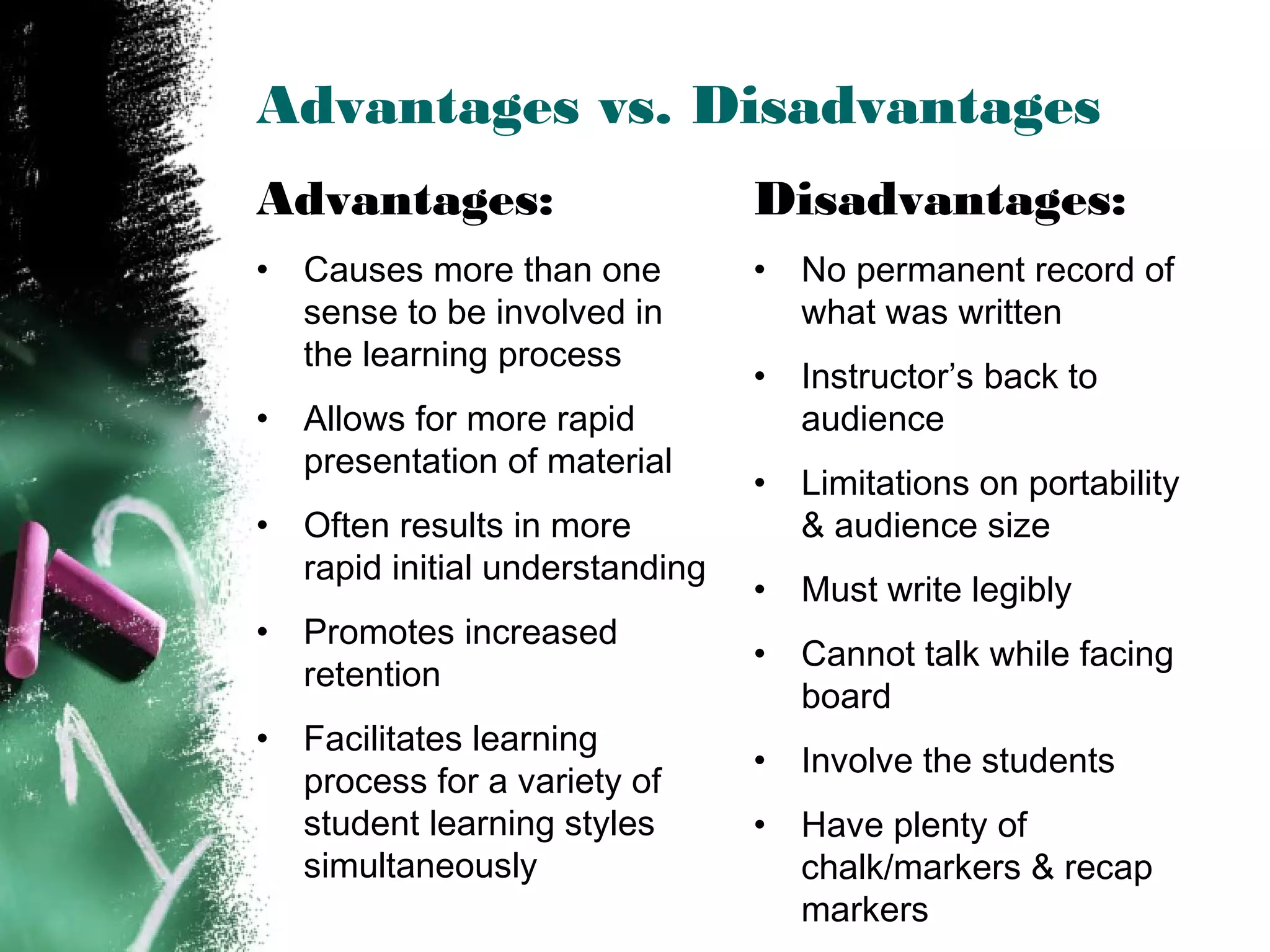
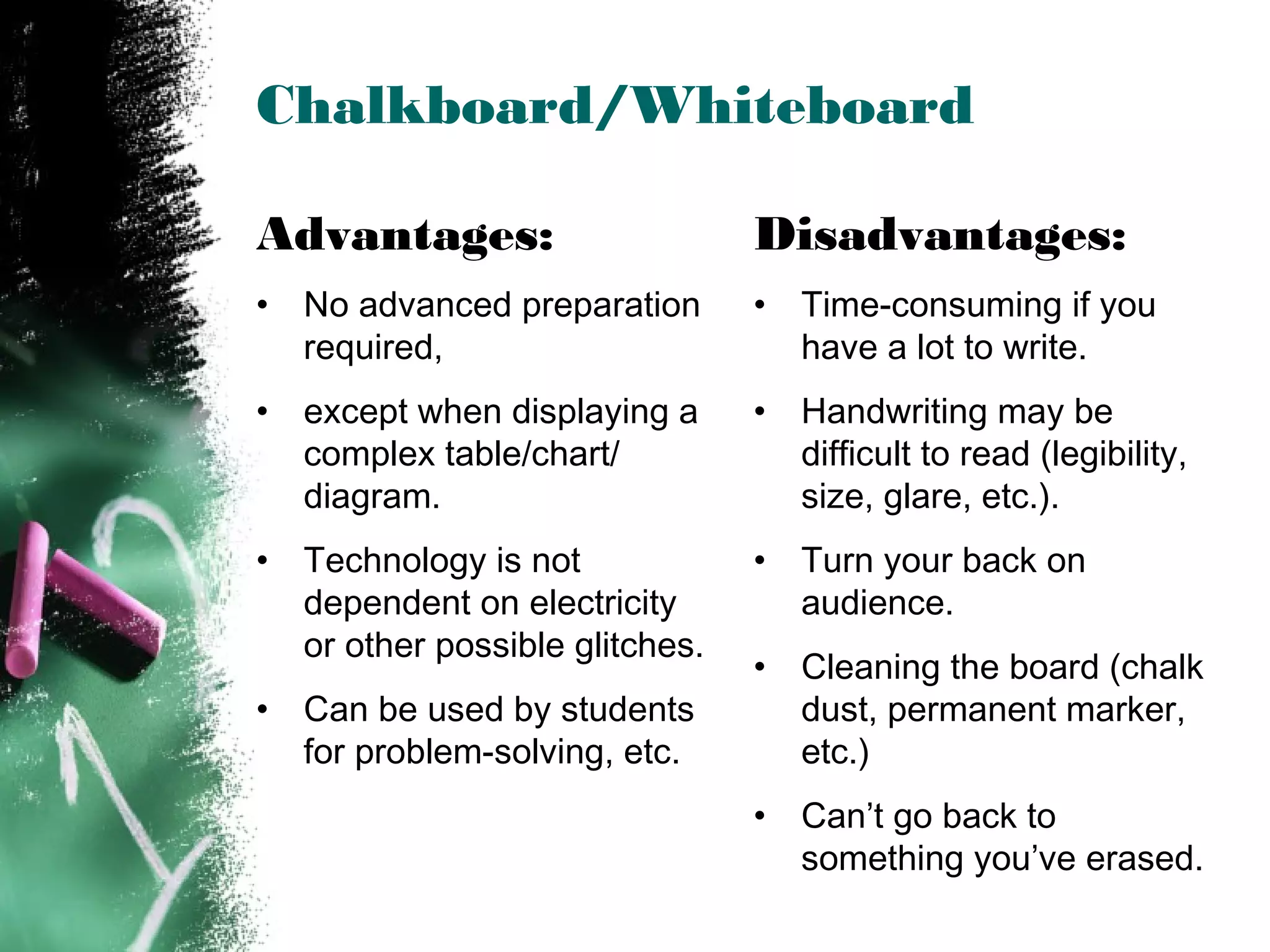
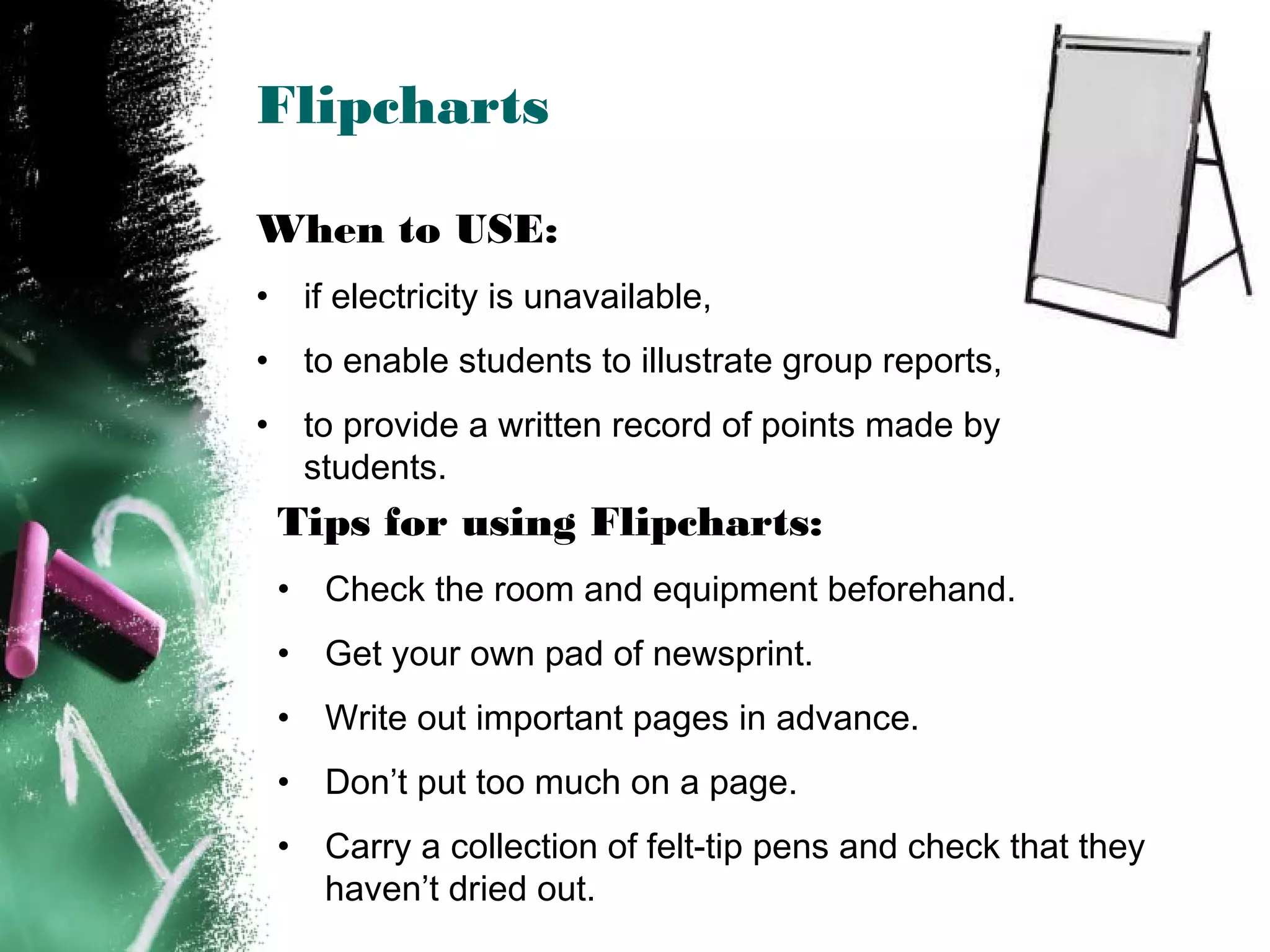
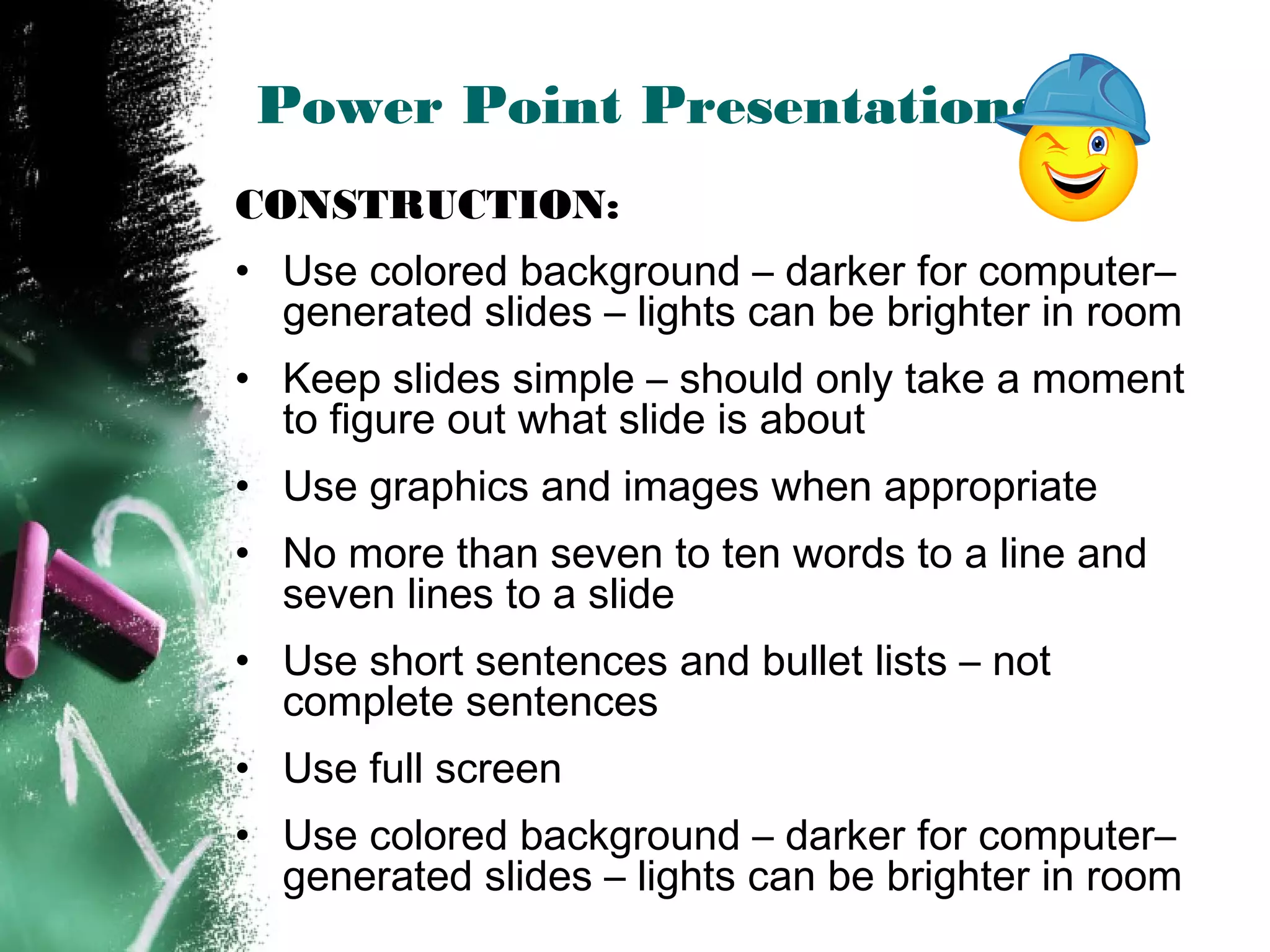
The document discusses effective use of teaching aids. It provides tips on choosing the appropriate visual aid based on context, and how to effectively use common teaching aids like whiteboards, overhead projectors, PowerPoint, and various media. The advantages and disadvantages of different teaching aids are outlined to help instructors select options that best support their learning objectives and engage students. Key considerations for using teaching aids effectively include preparation, presentation skills, readability, and relevance to the topic.