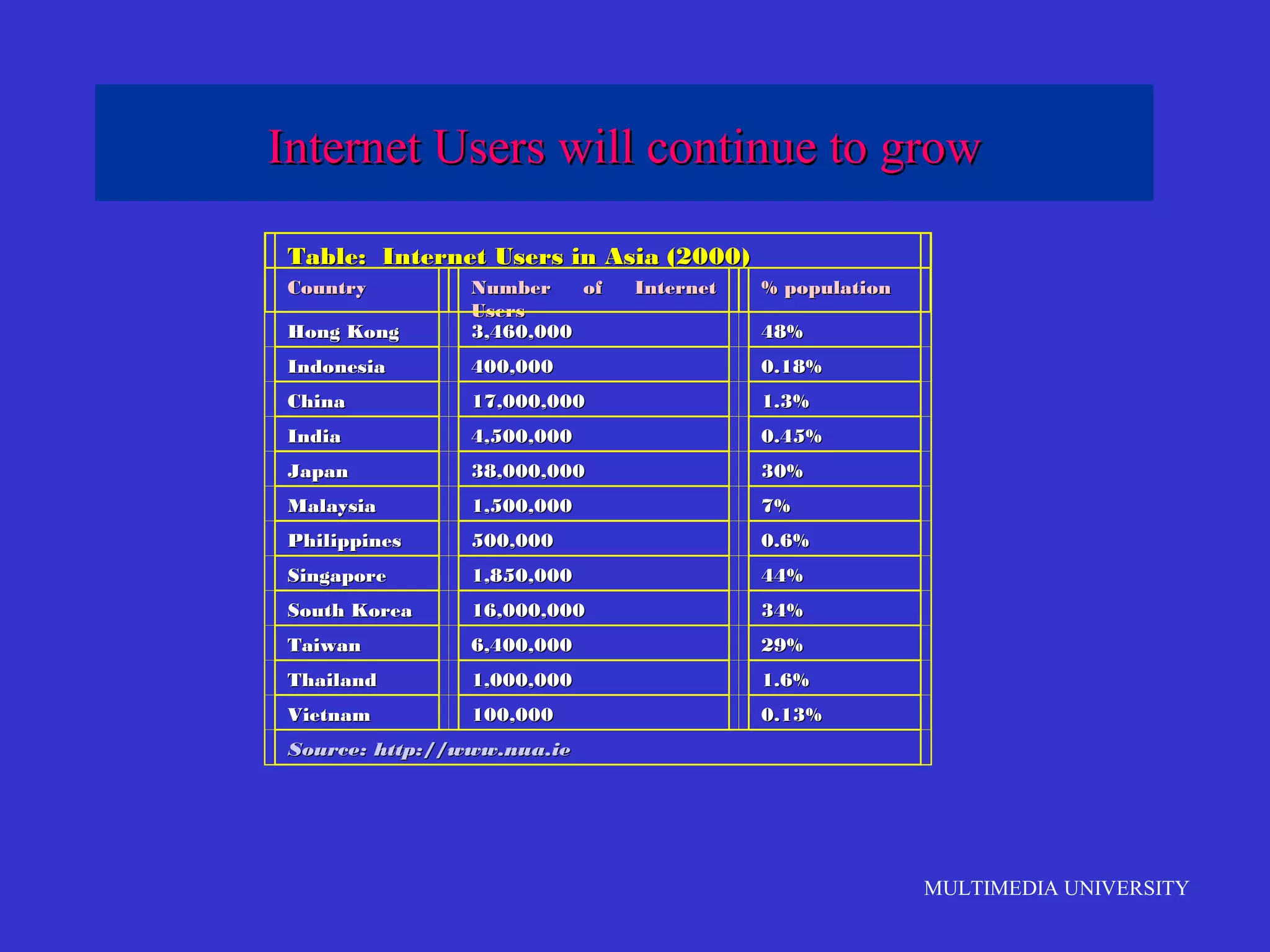
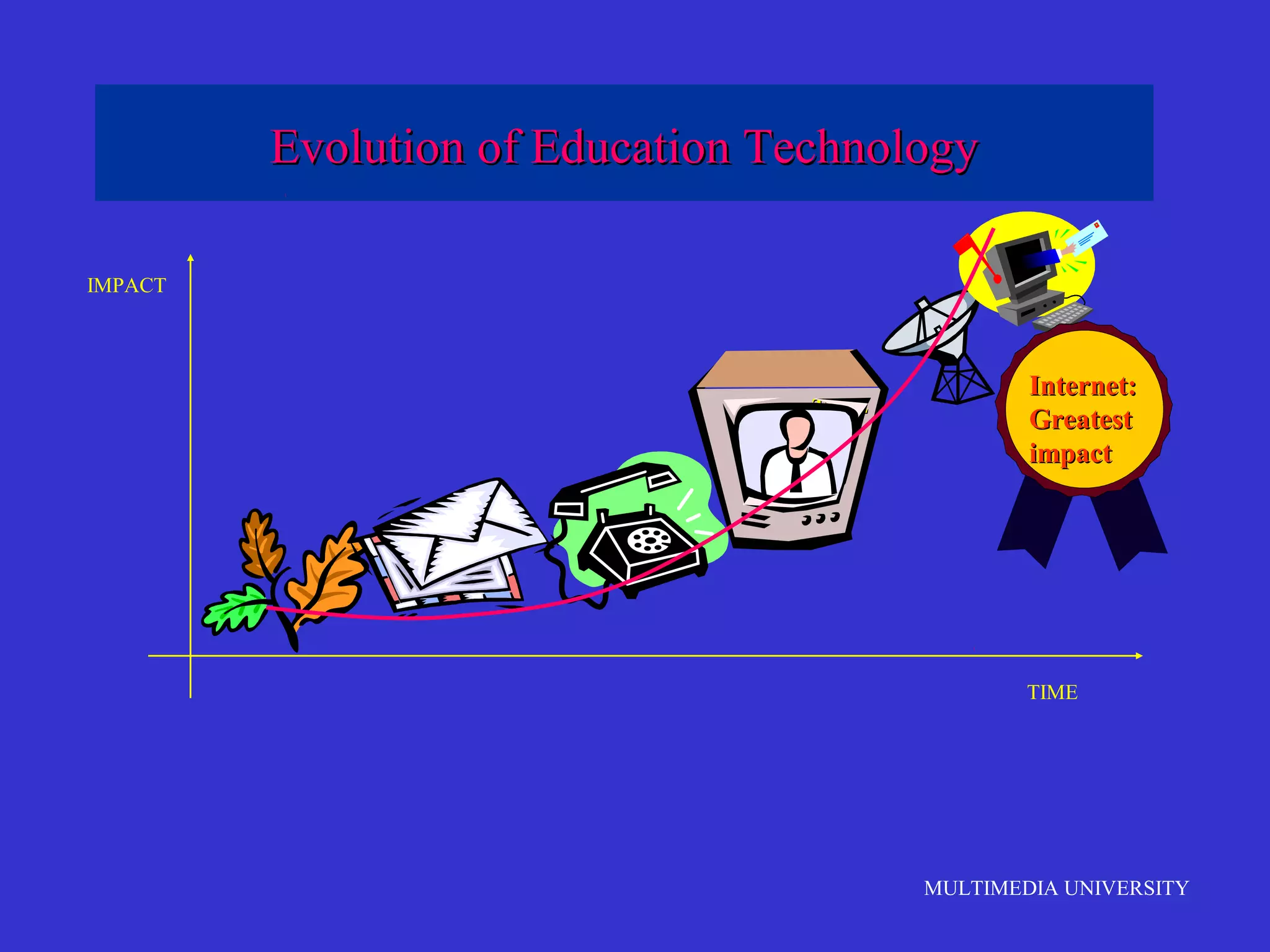
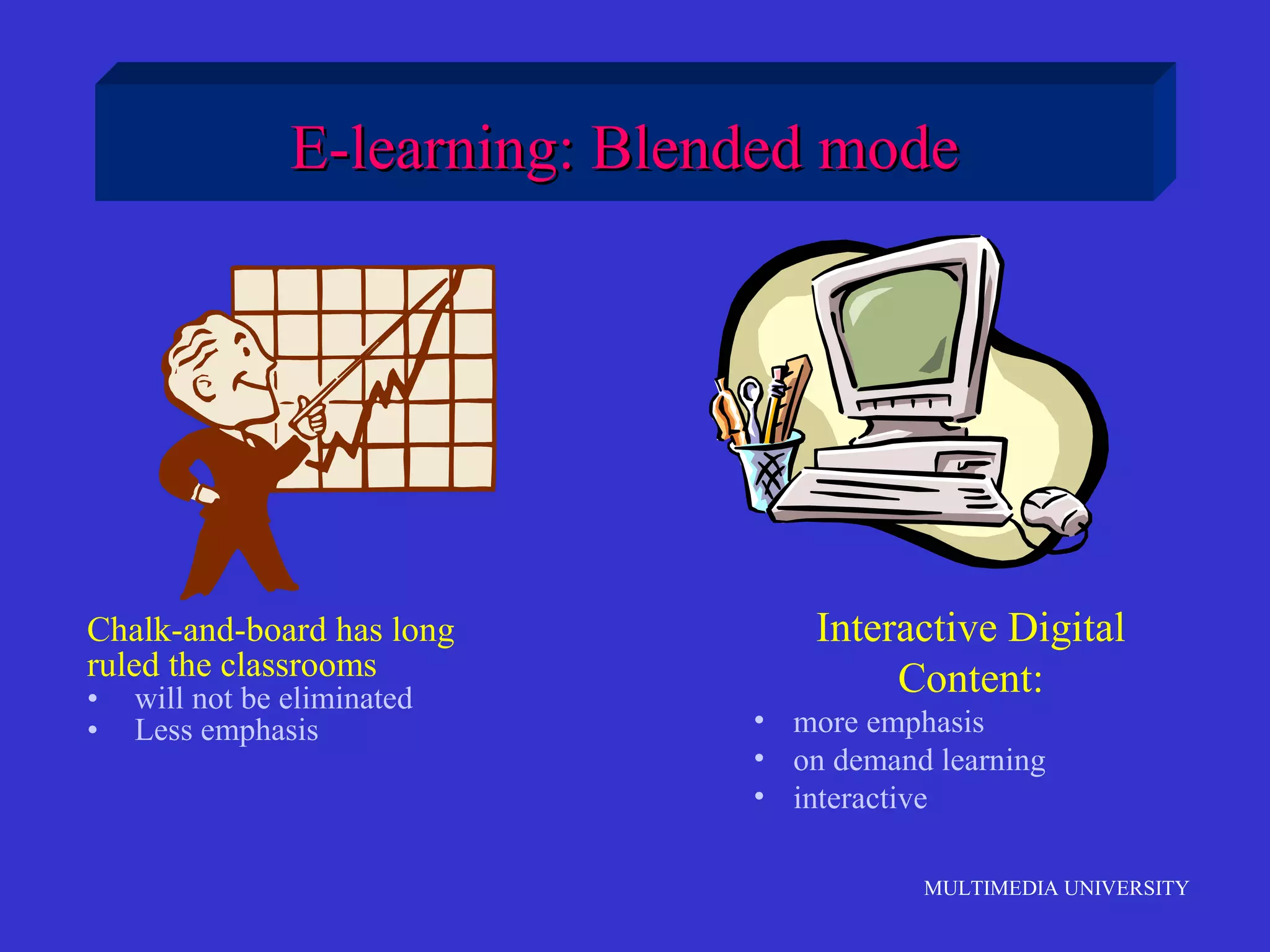
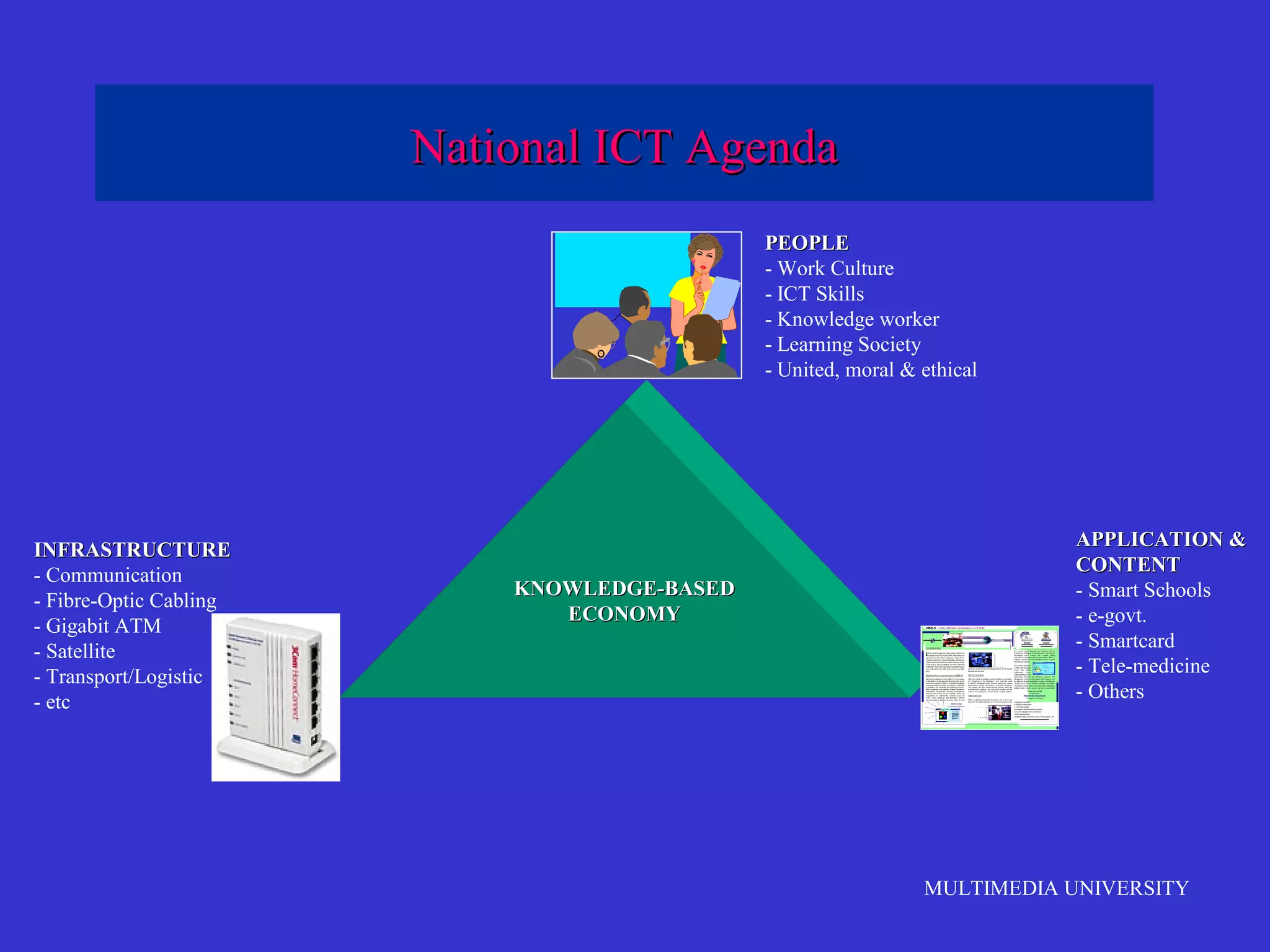
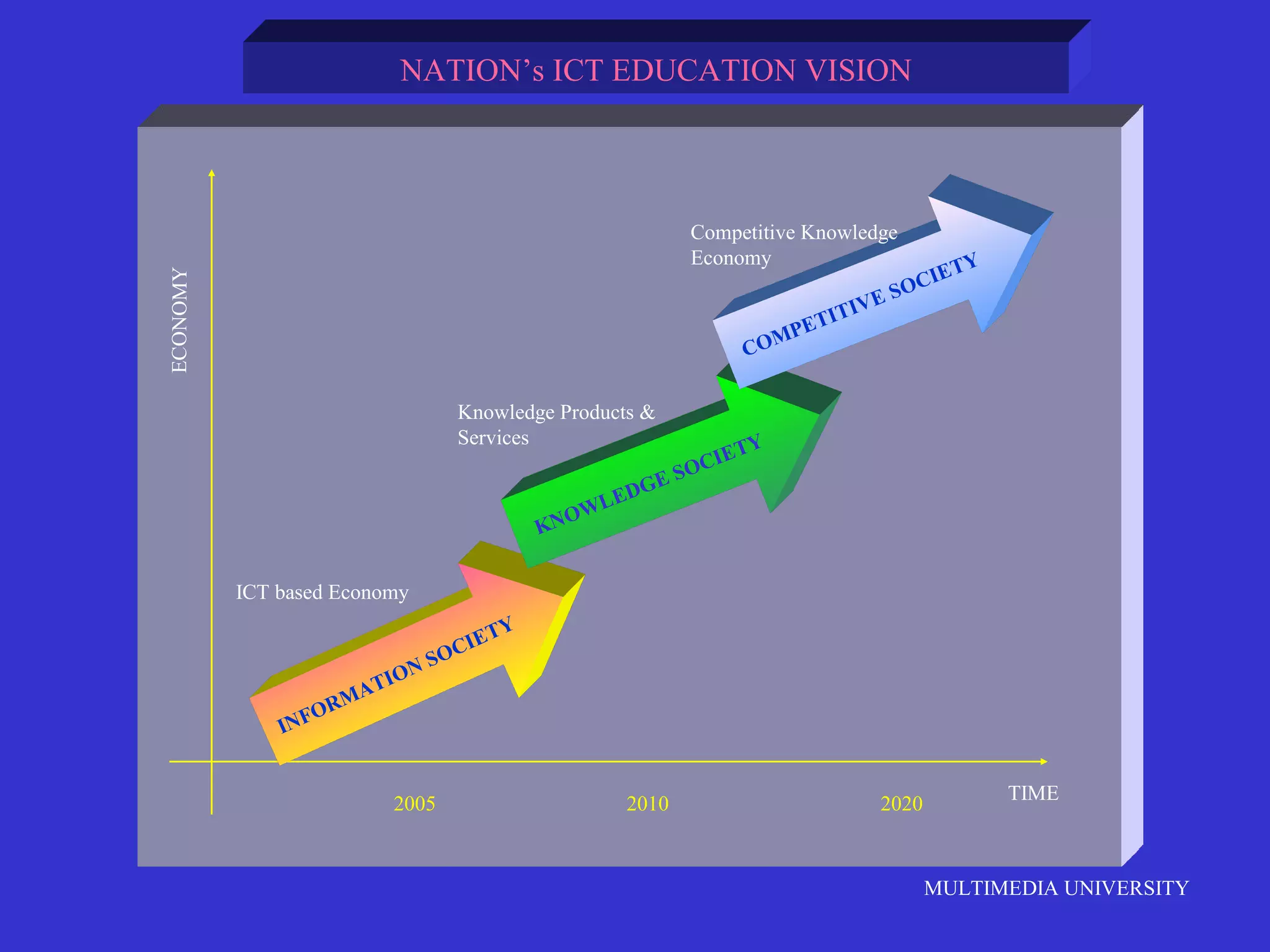
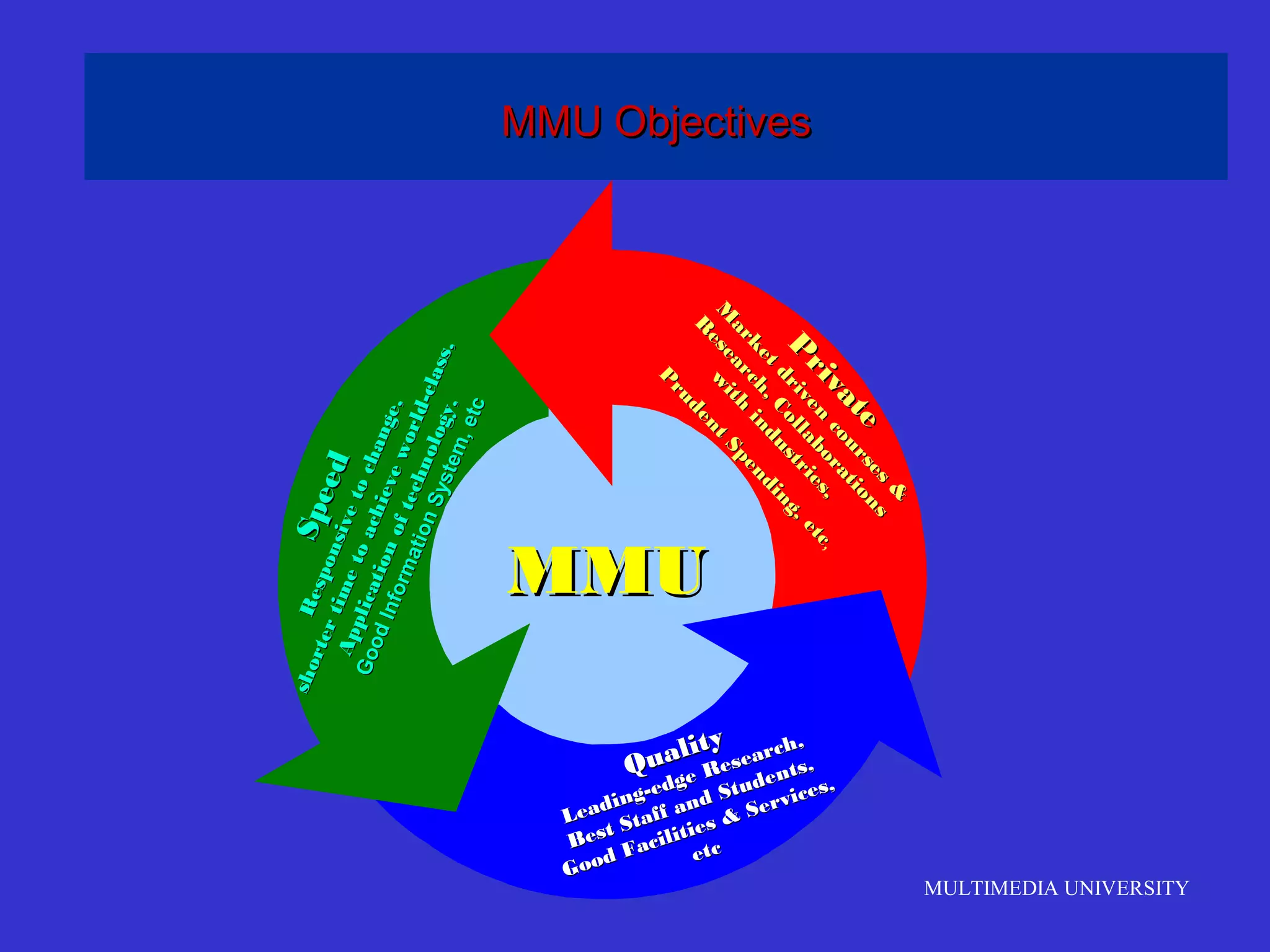
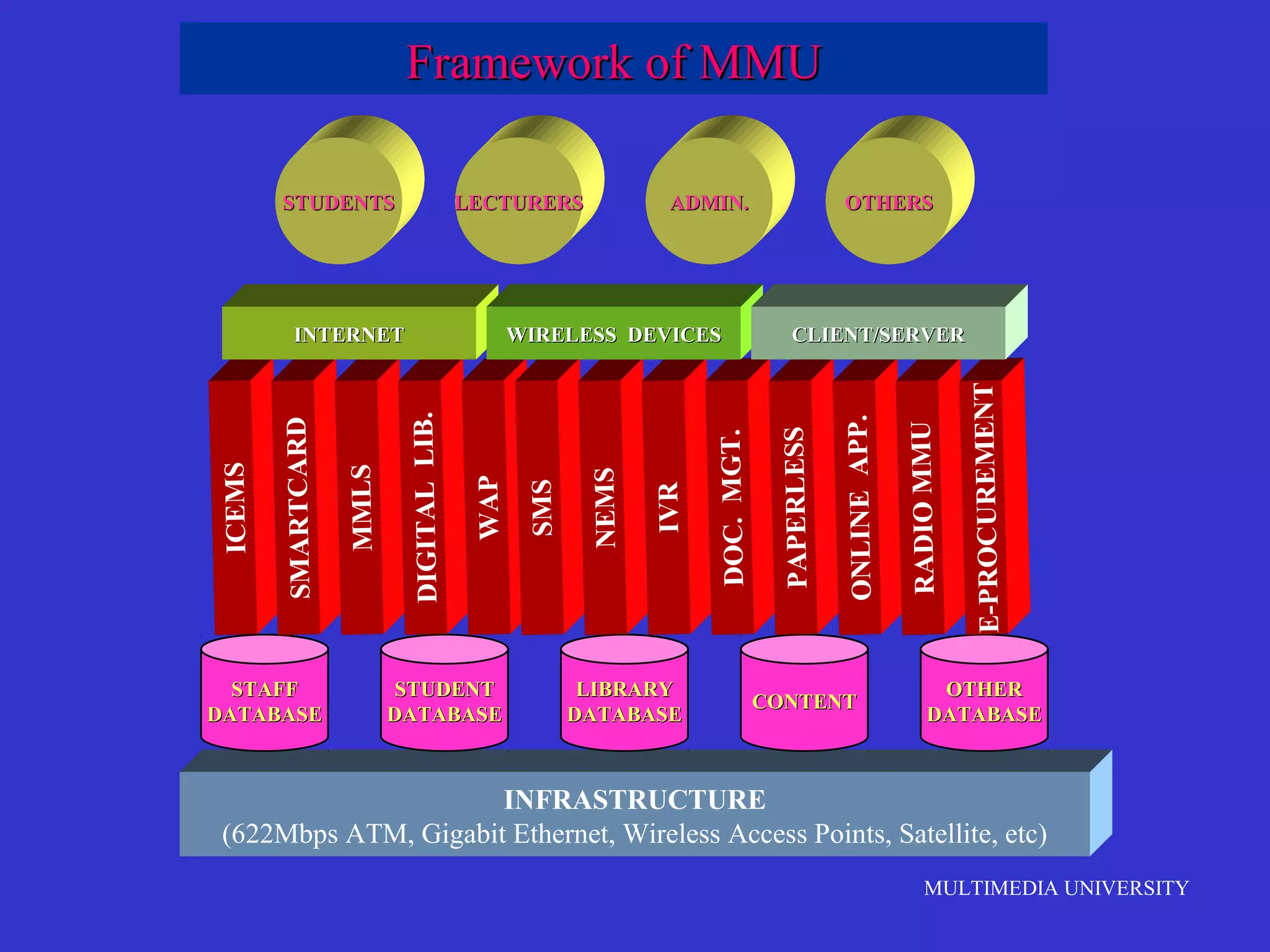
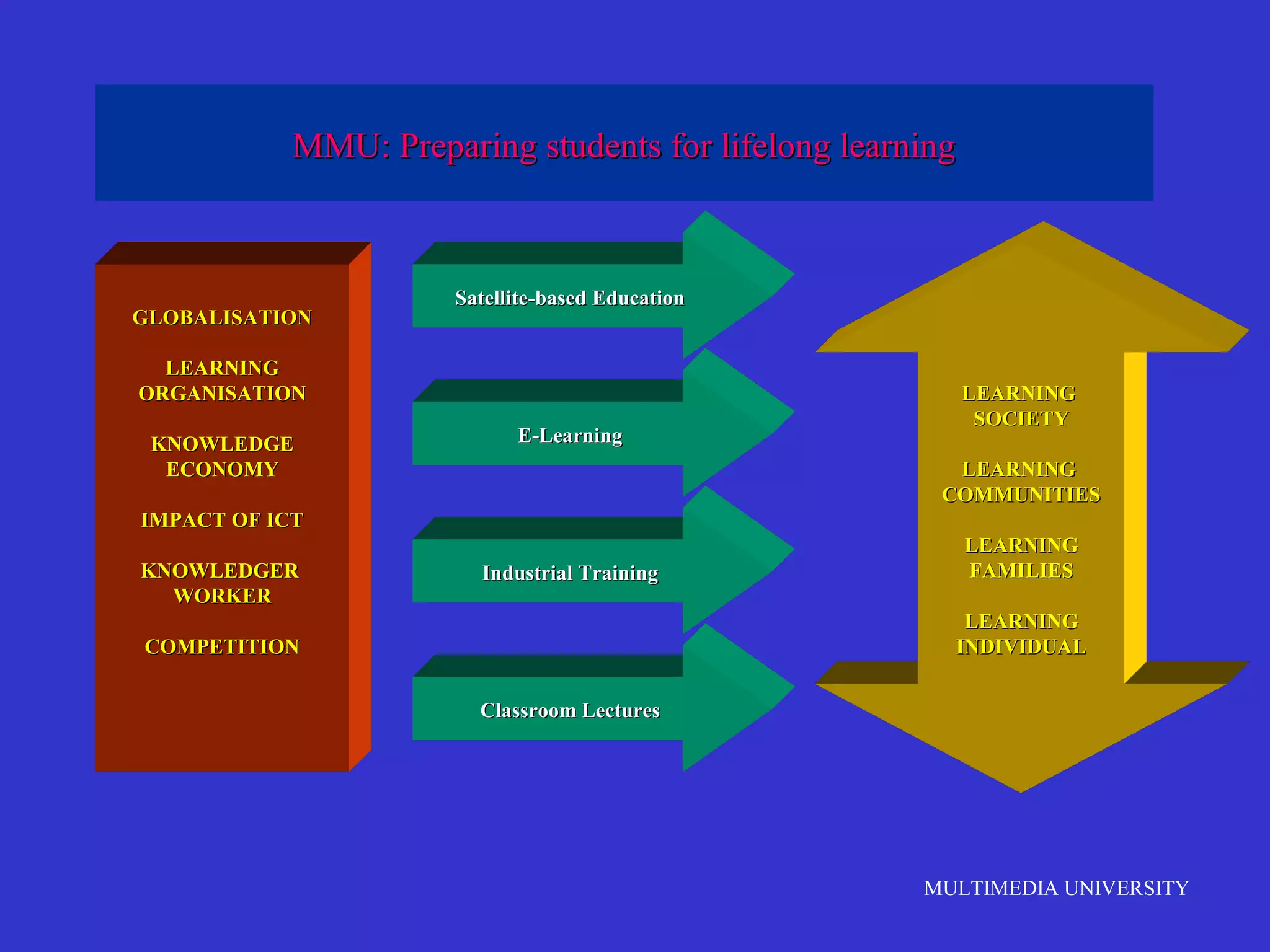
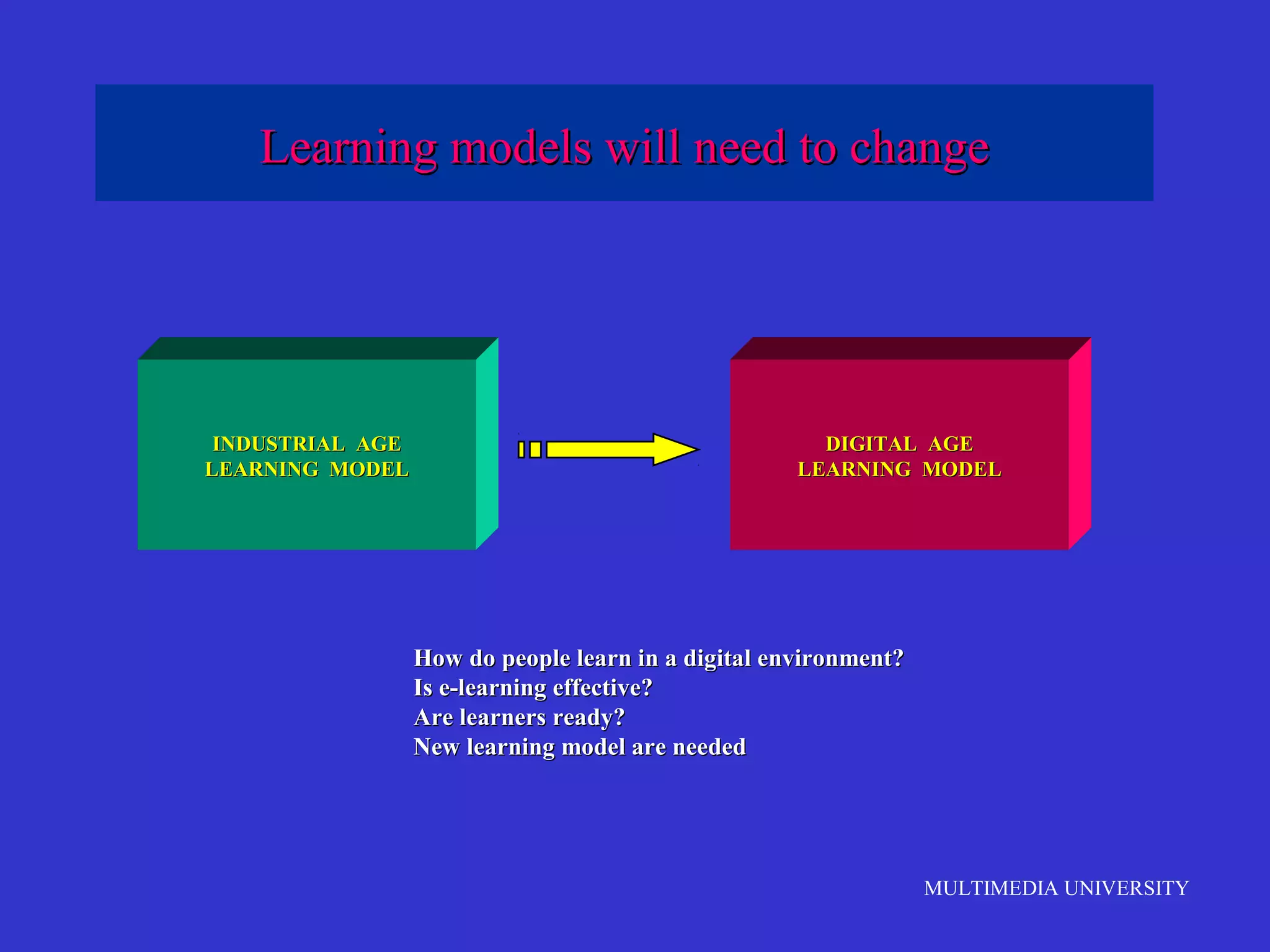
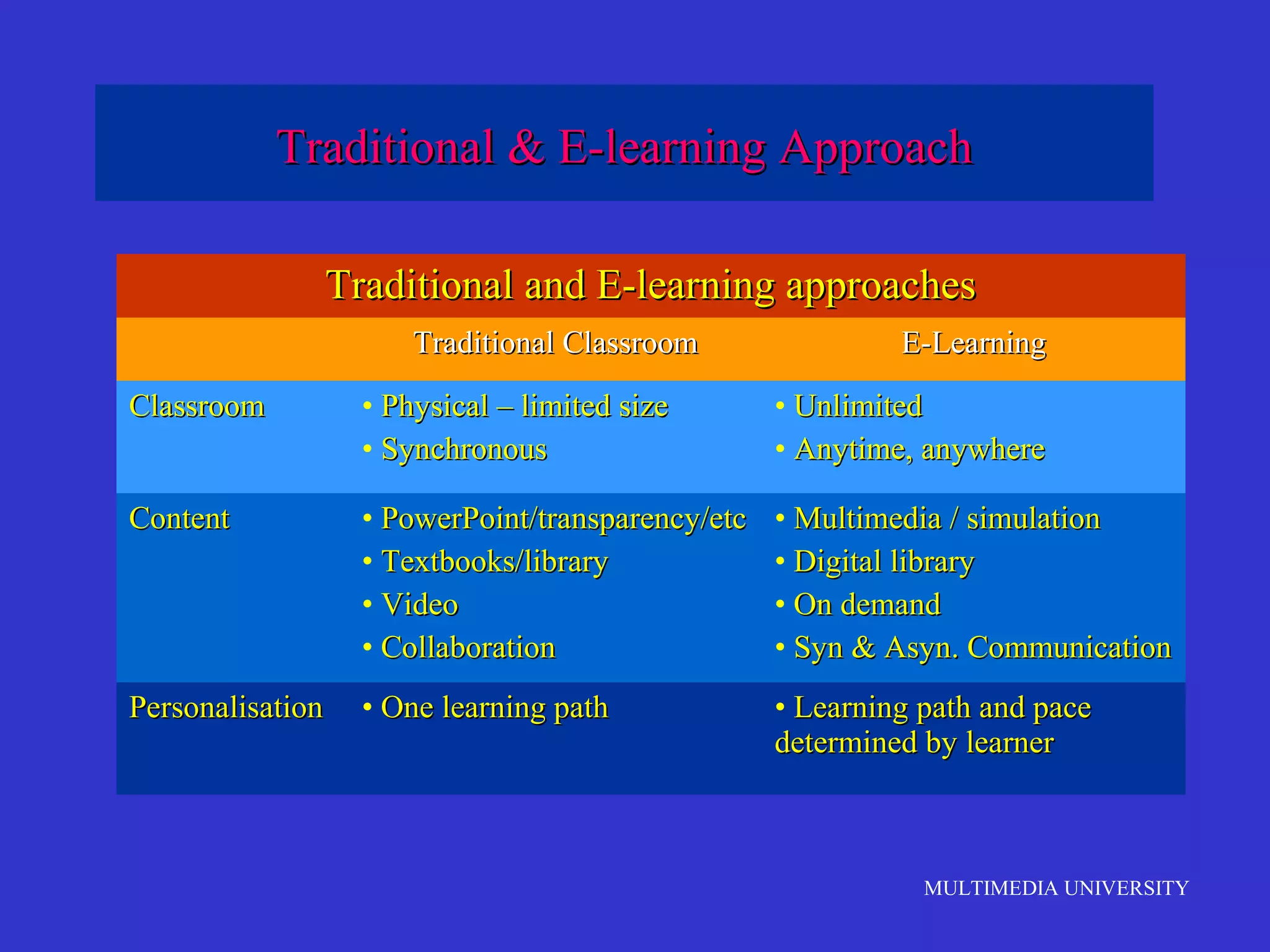
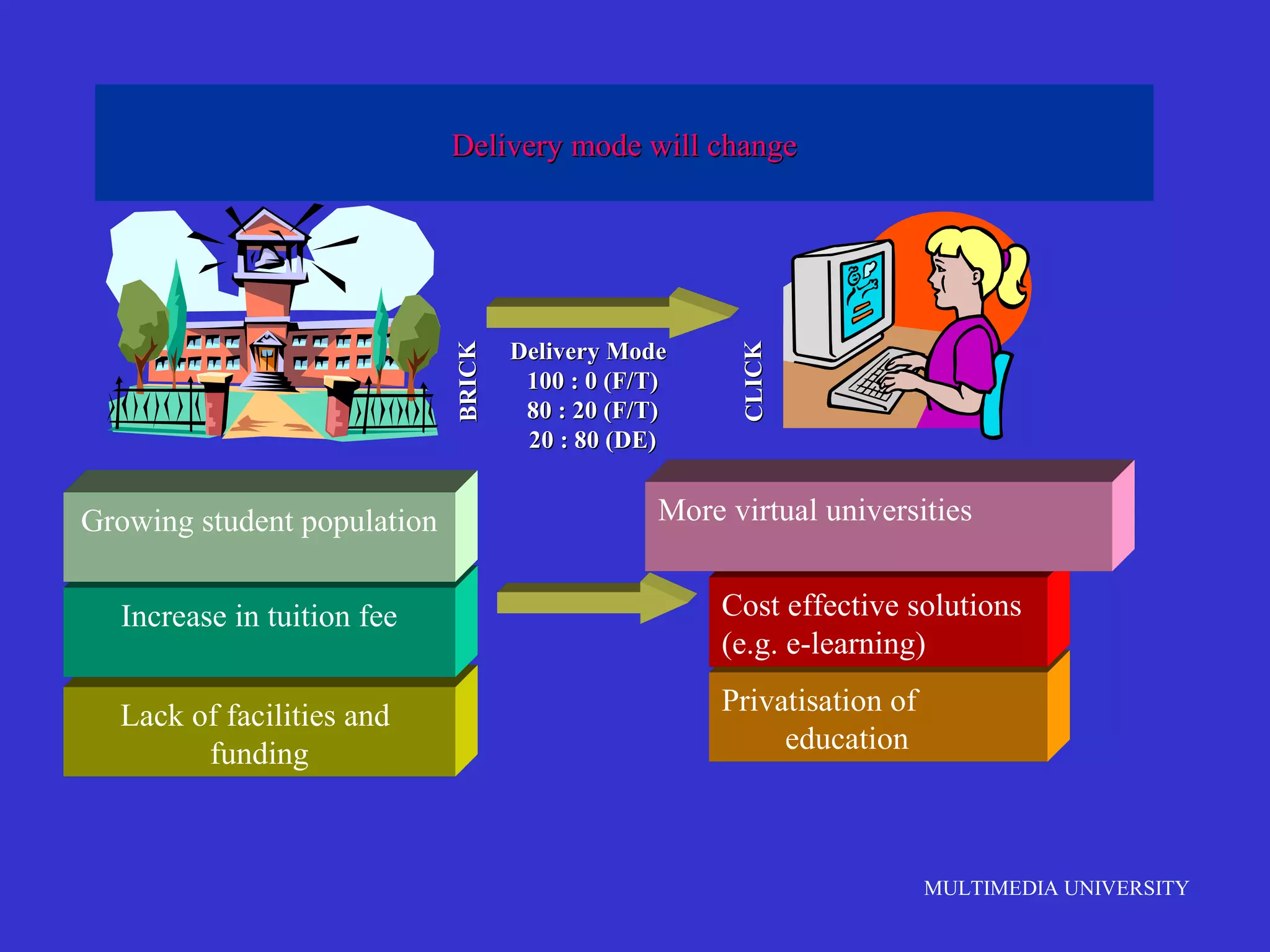
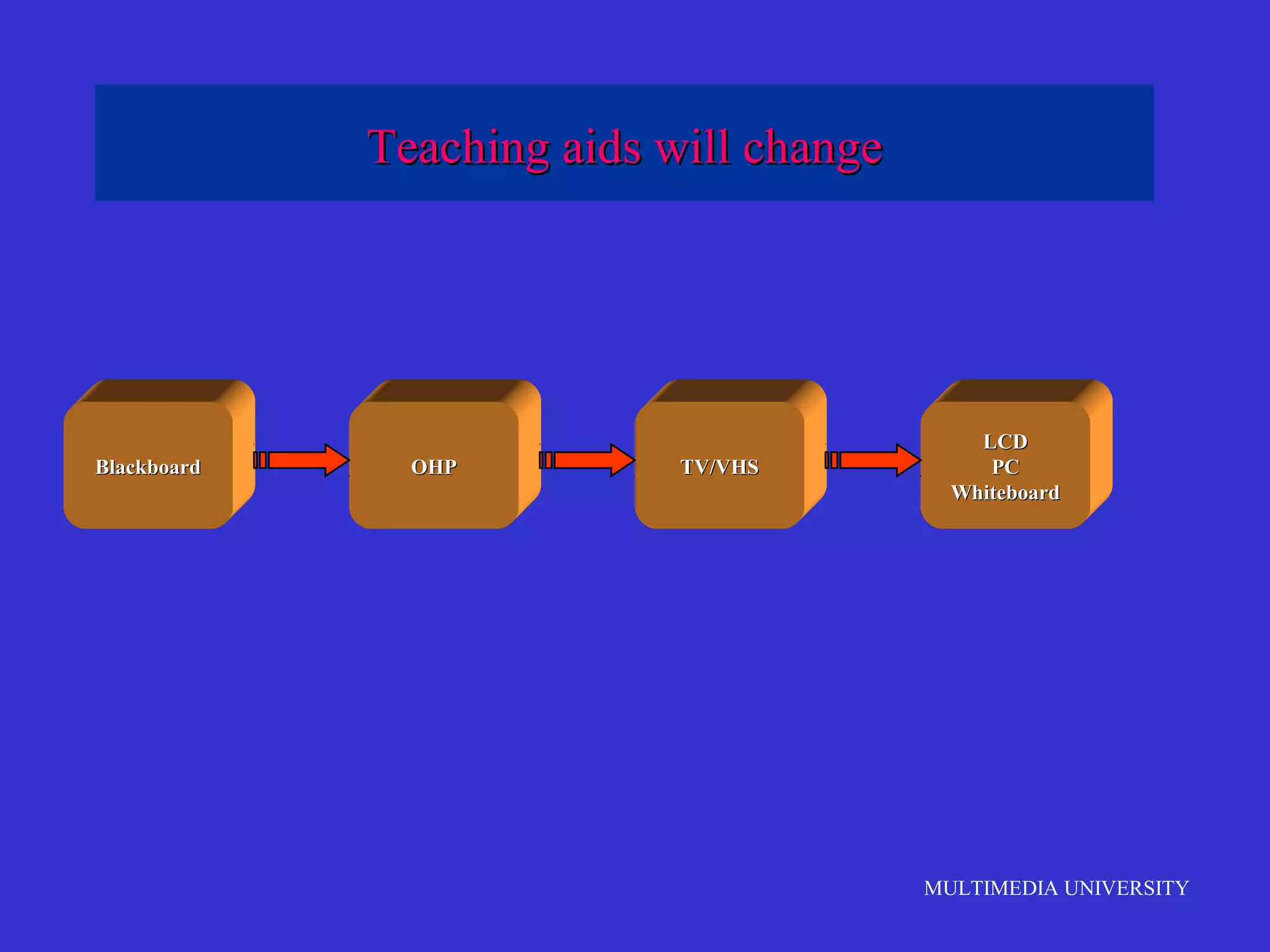
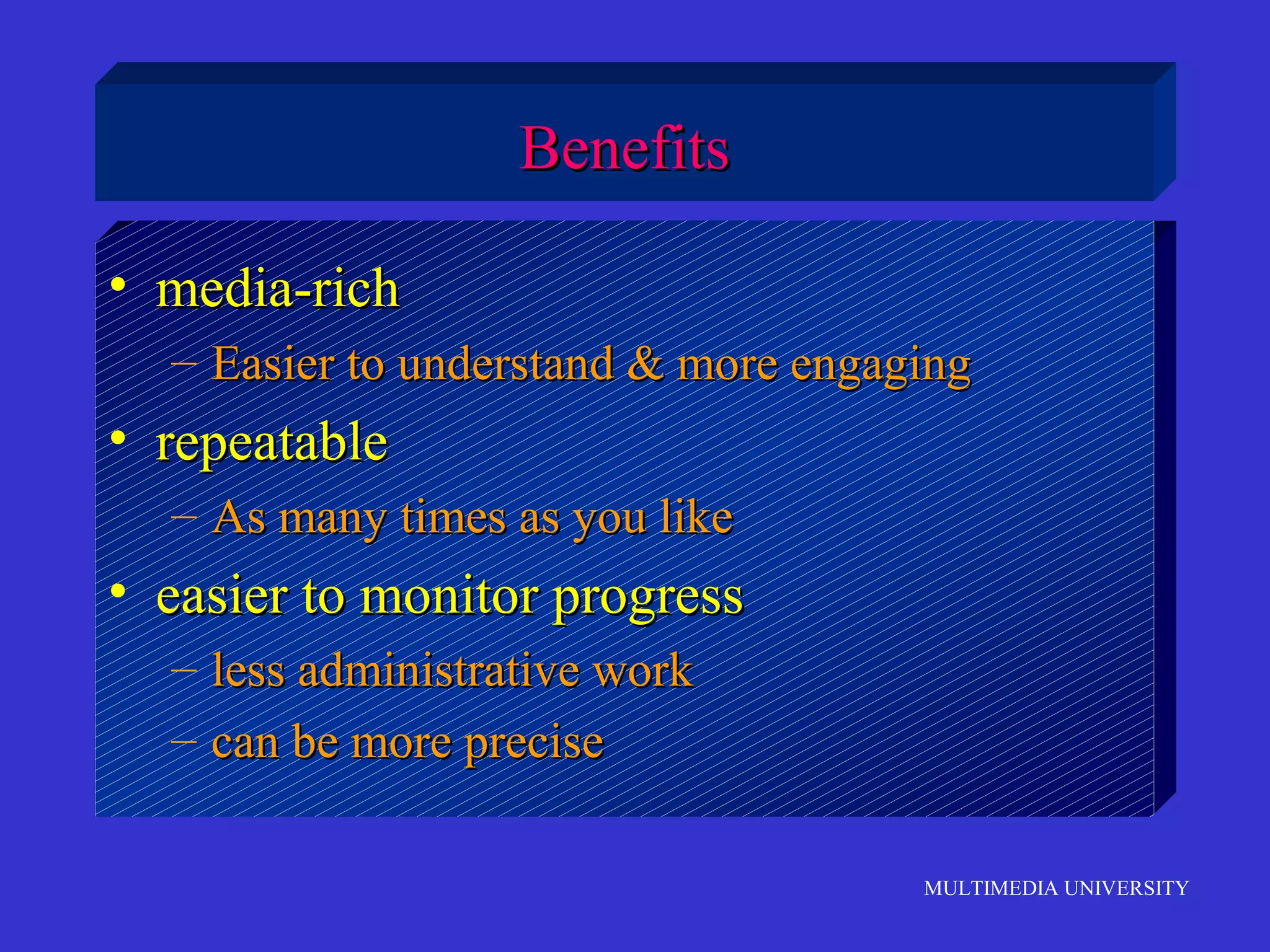
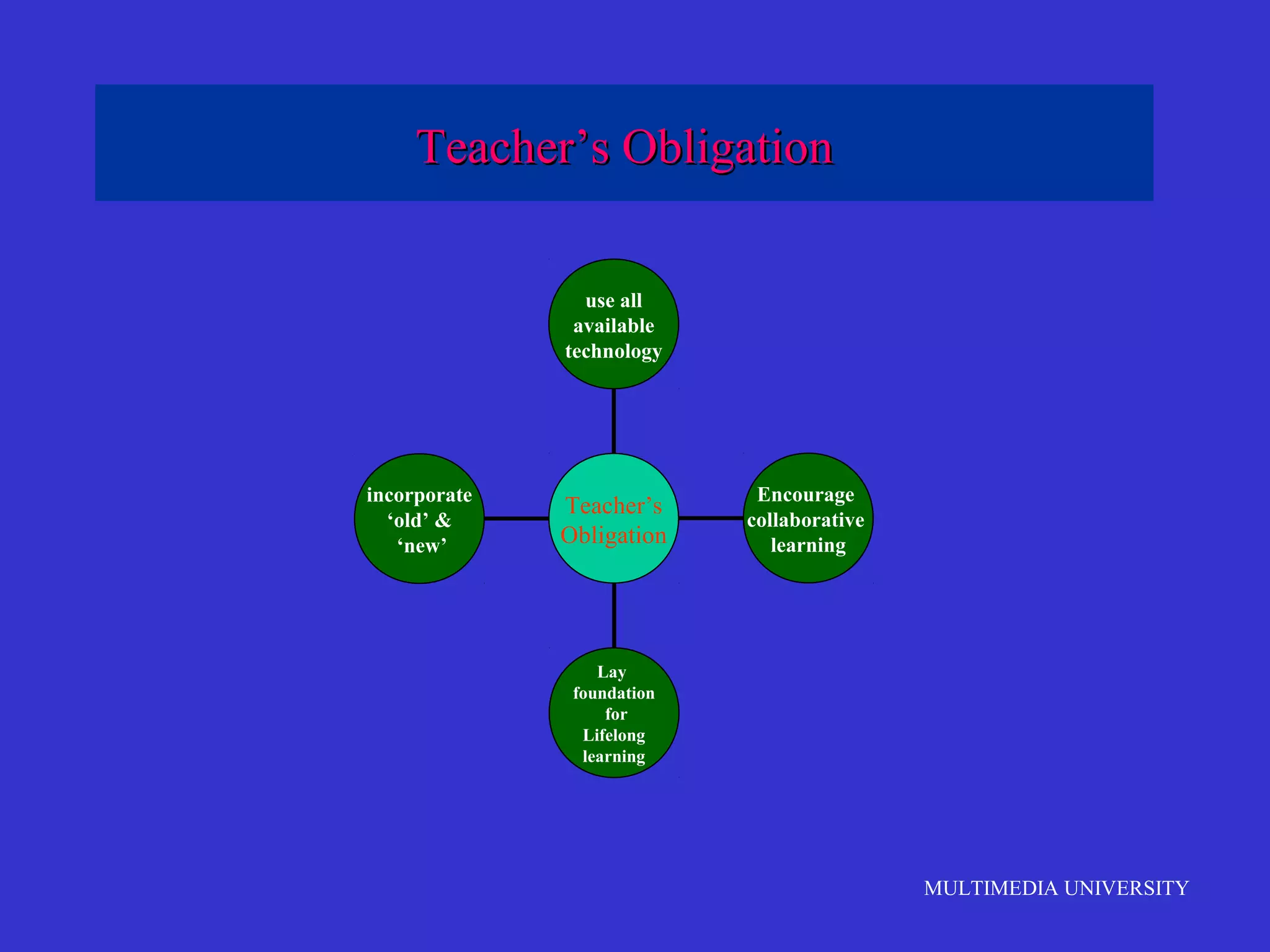
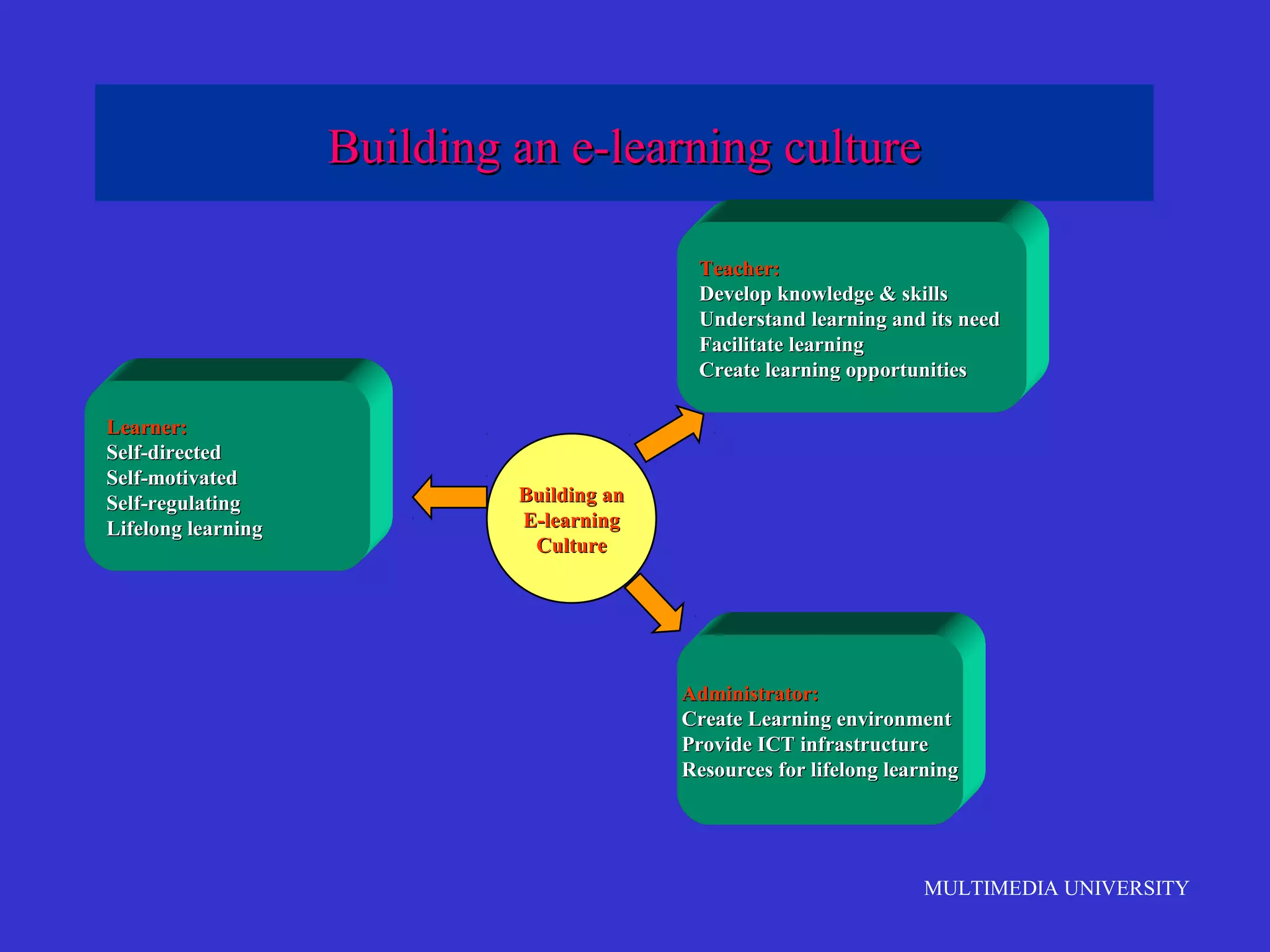
The document discusses the rise of e-learning and its impact on education. It notes that internet technologies are reshaping education and that traditional classrooms will need to be transformed. E-learning is still new, with only about 1% of the population having taken an online course, but it is expected to grow significantly. The education market is also expected to grow substantially to meet rising student populations and skilled job needs. Multimedia University in Malaysia is presented as a case study of an institution adapting to these changes by implementing e-learning tools and strategies to prepare students for lifelong learning in the digital age.