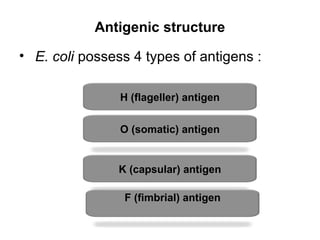
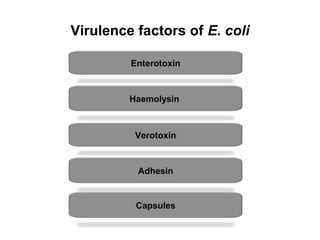
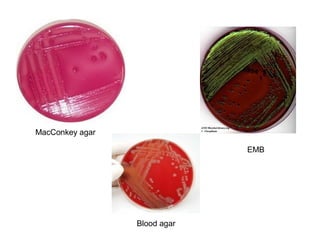
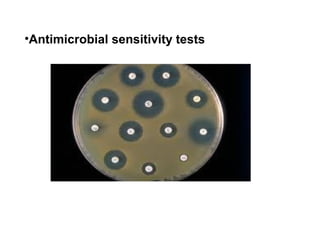
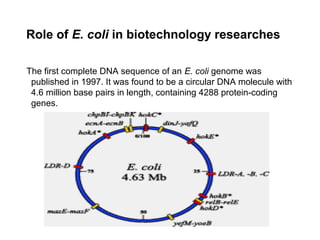
Escherichia coli is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic and non-sporulating bacteria that grows optimally at 37°C. It possesses flagella that allow it to swim and is motile. E. coli has four types of antigens and several virulence factors that allow some strains to cause diseases like gastroenteritis, urinary tract infections, and neonatal meningitis. It is normally found in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and animals, where it plays an important role. While some pathogenic strains cause disease, nonpathogenic strains like E. coli Nissle 1917 are used as probiotics. E. coli is also widely used in biotechnology research due to its well-known genetics.