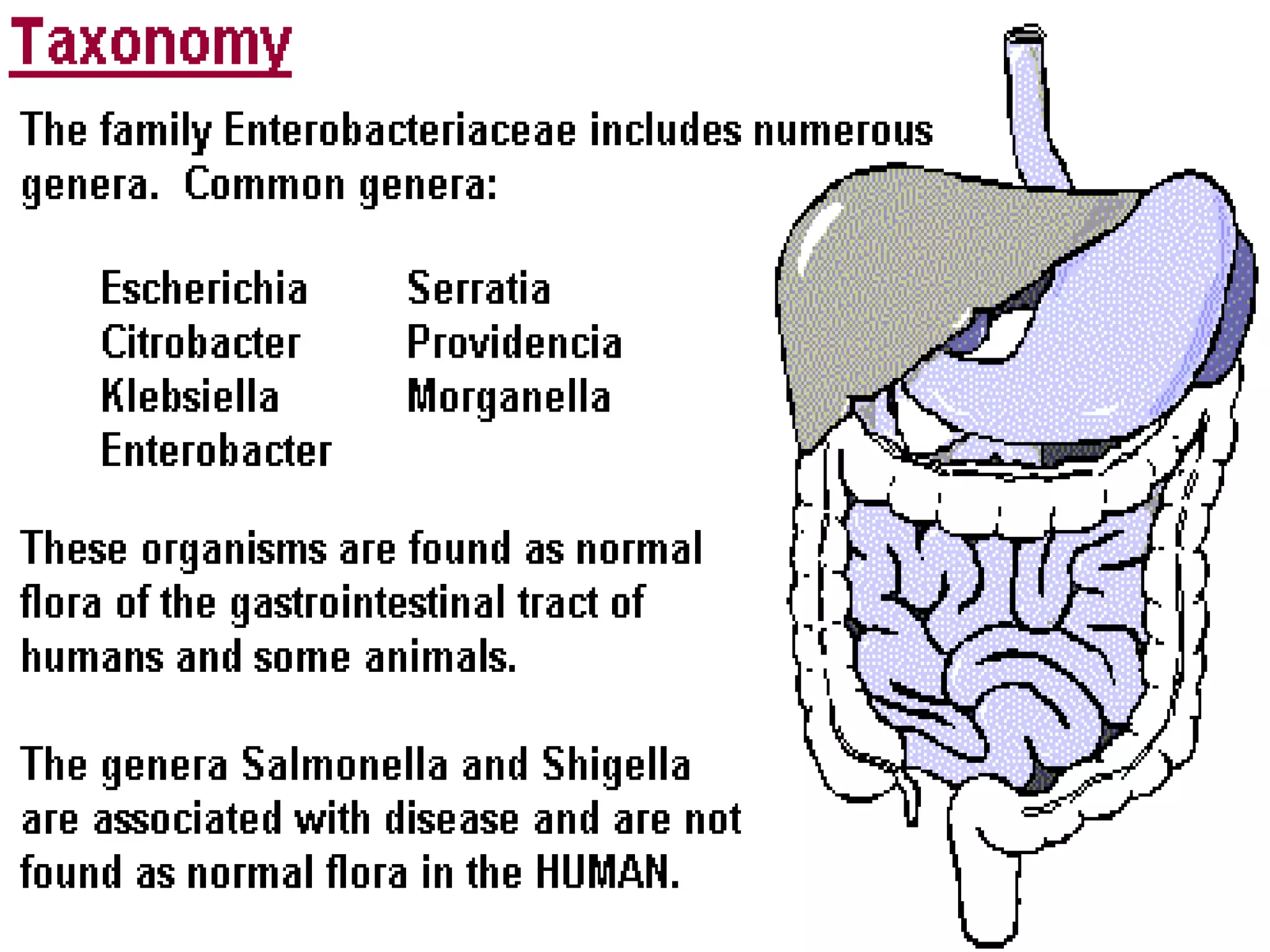
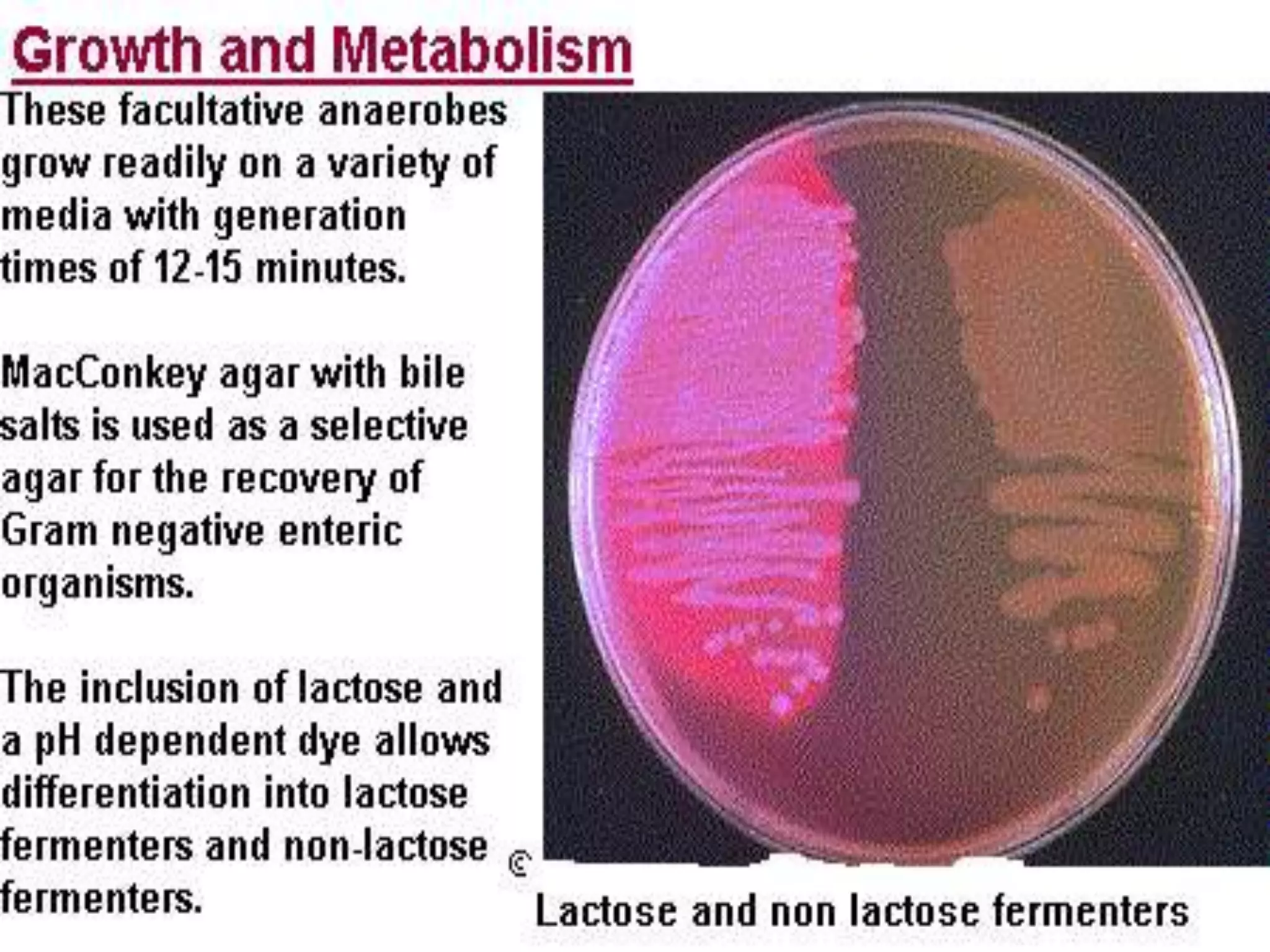
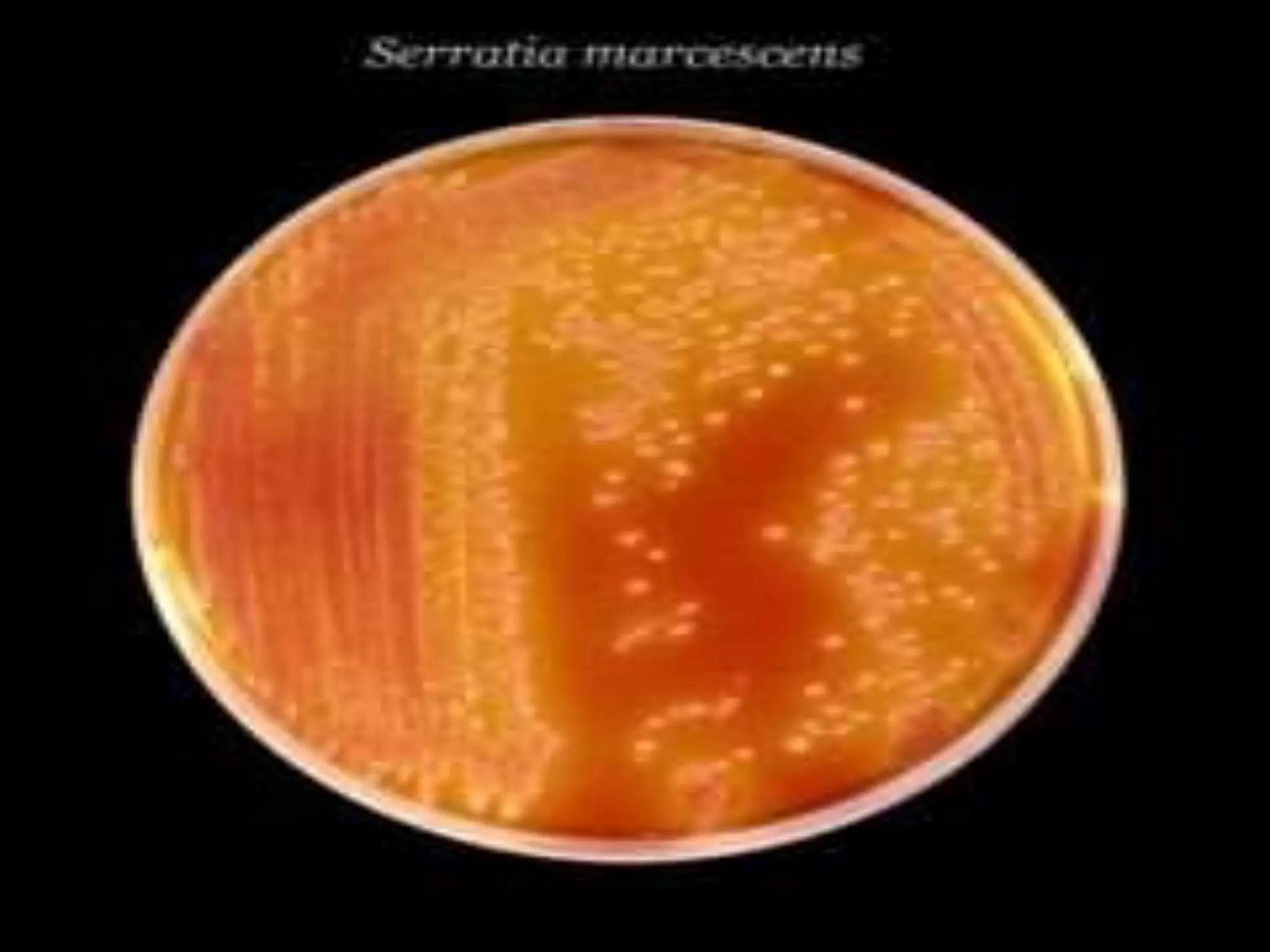
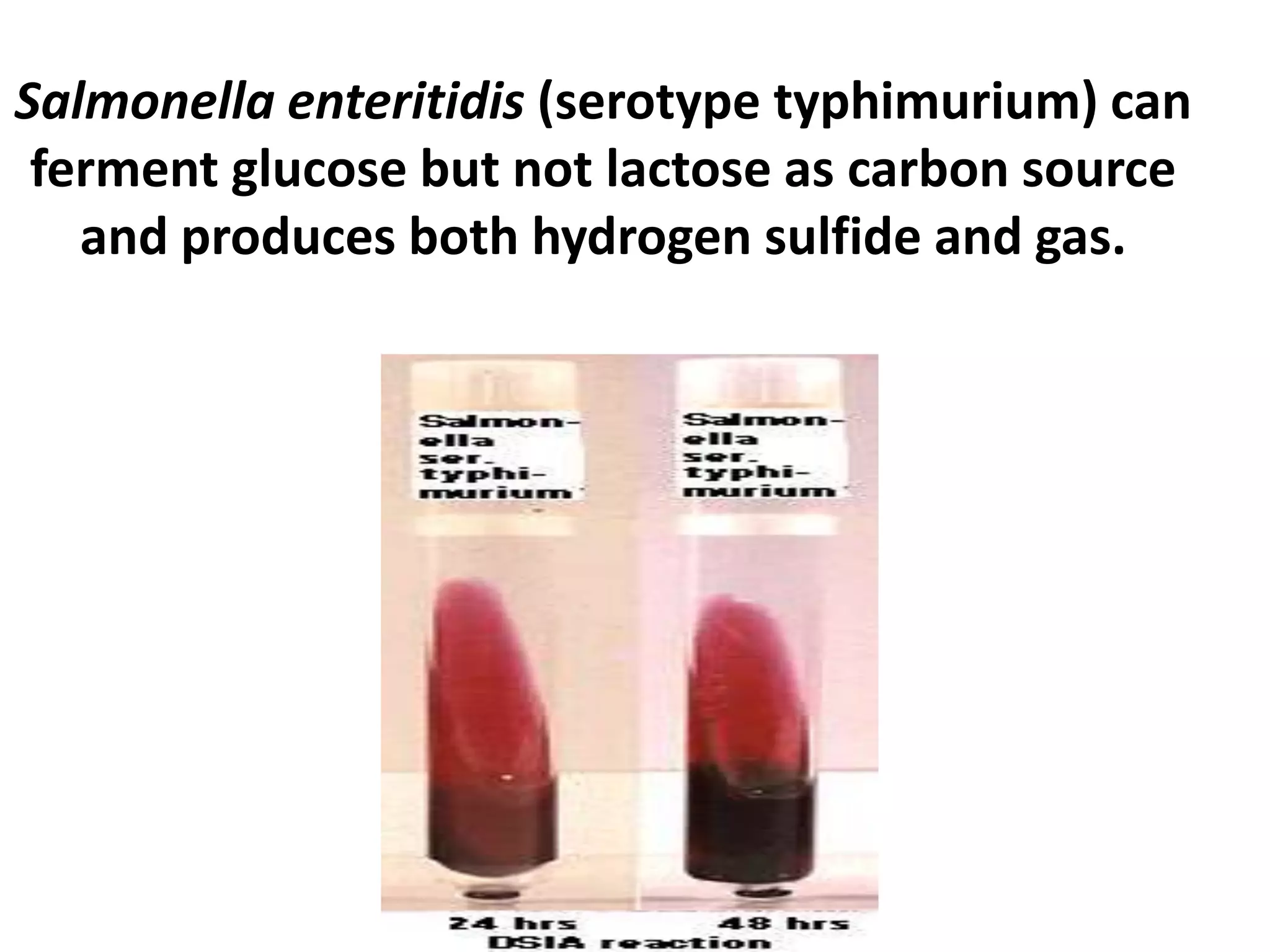
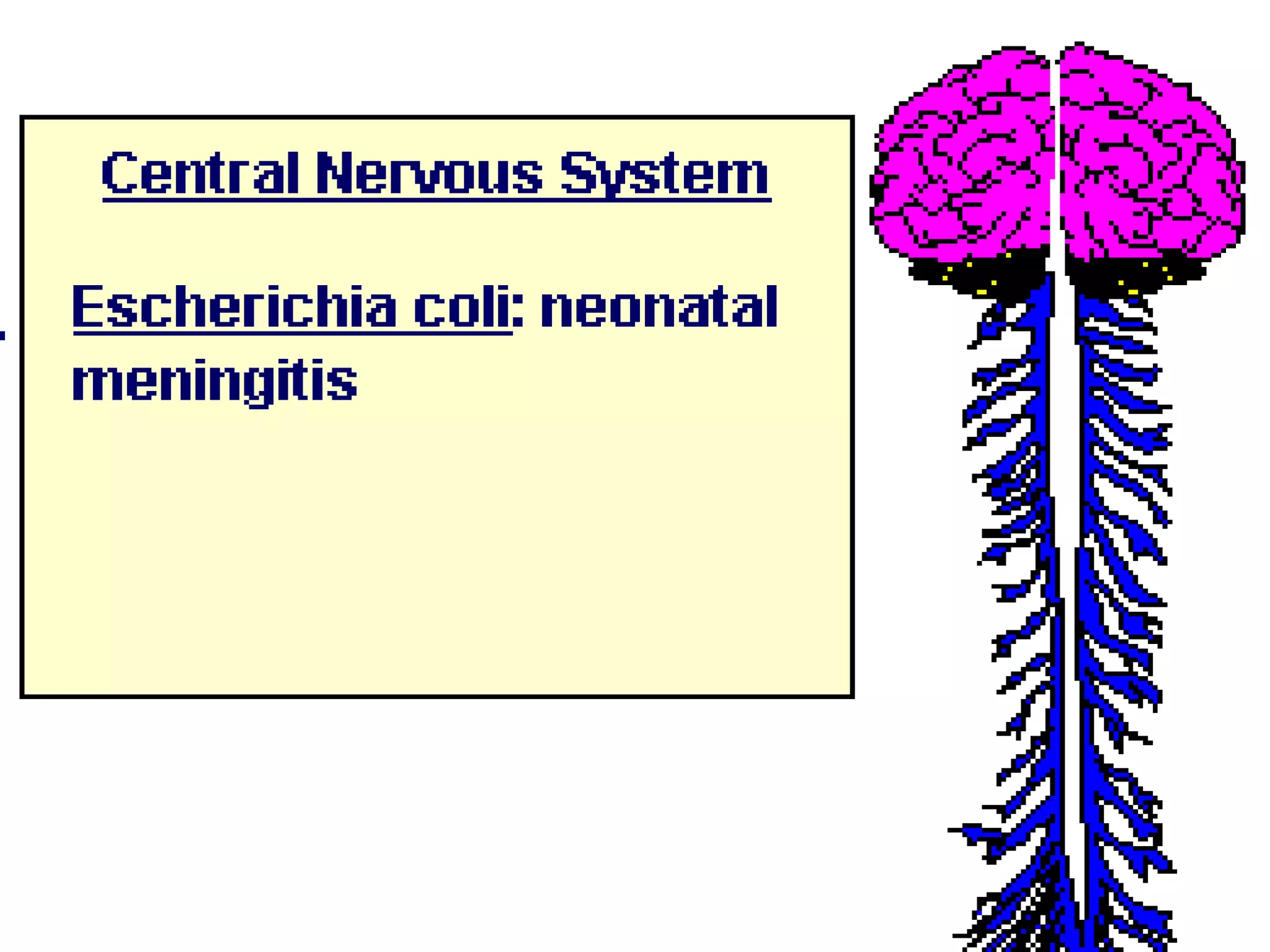
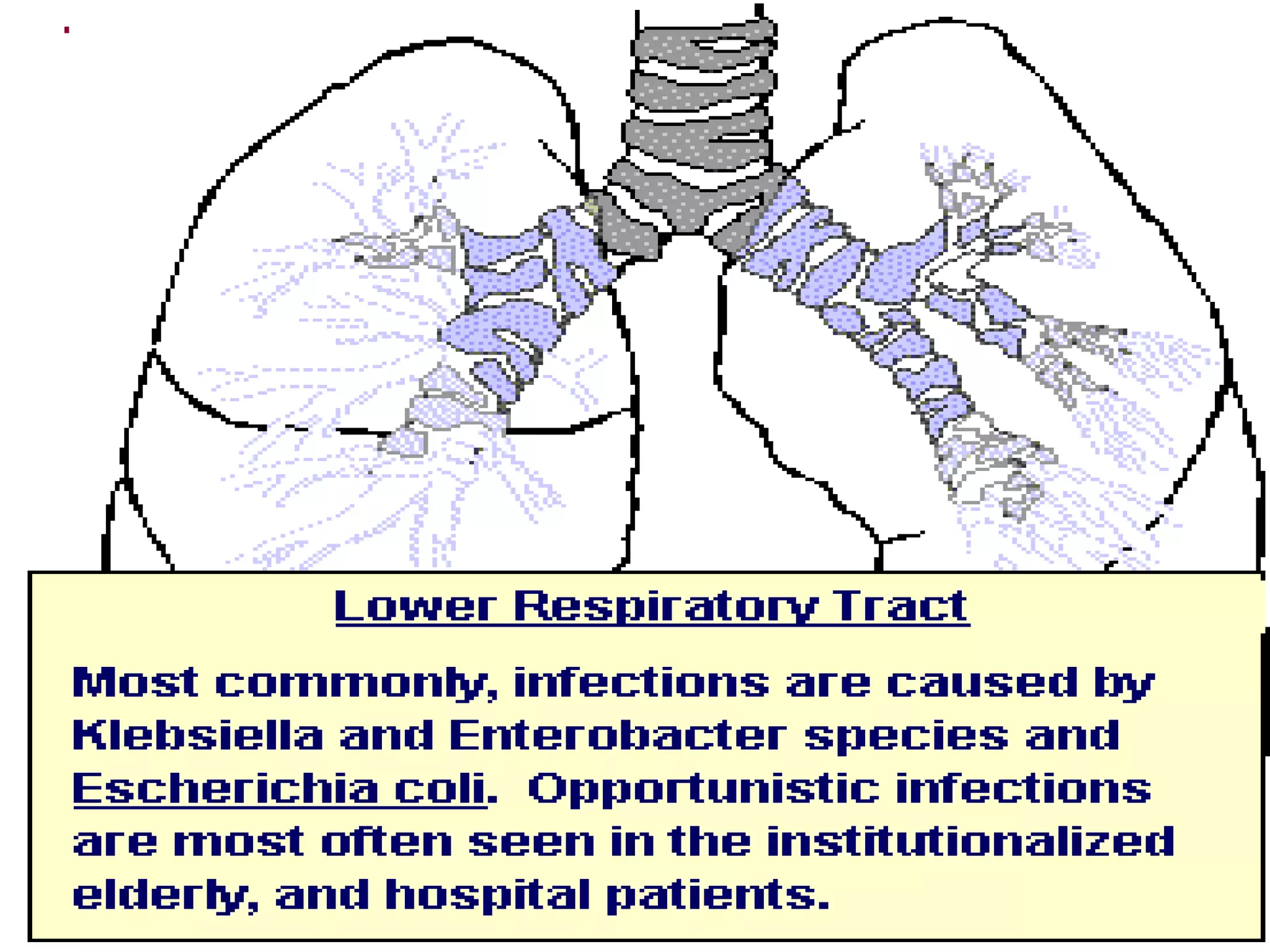
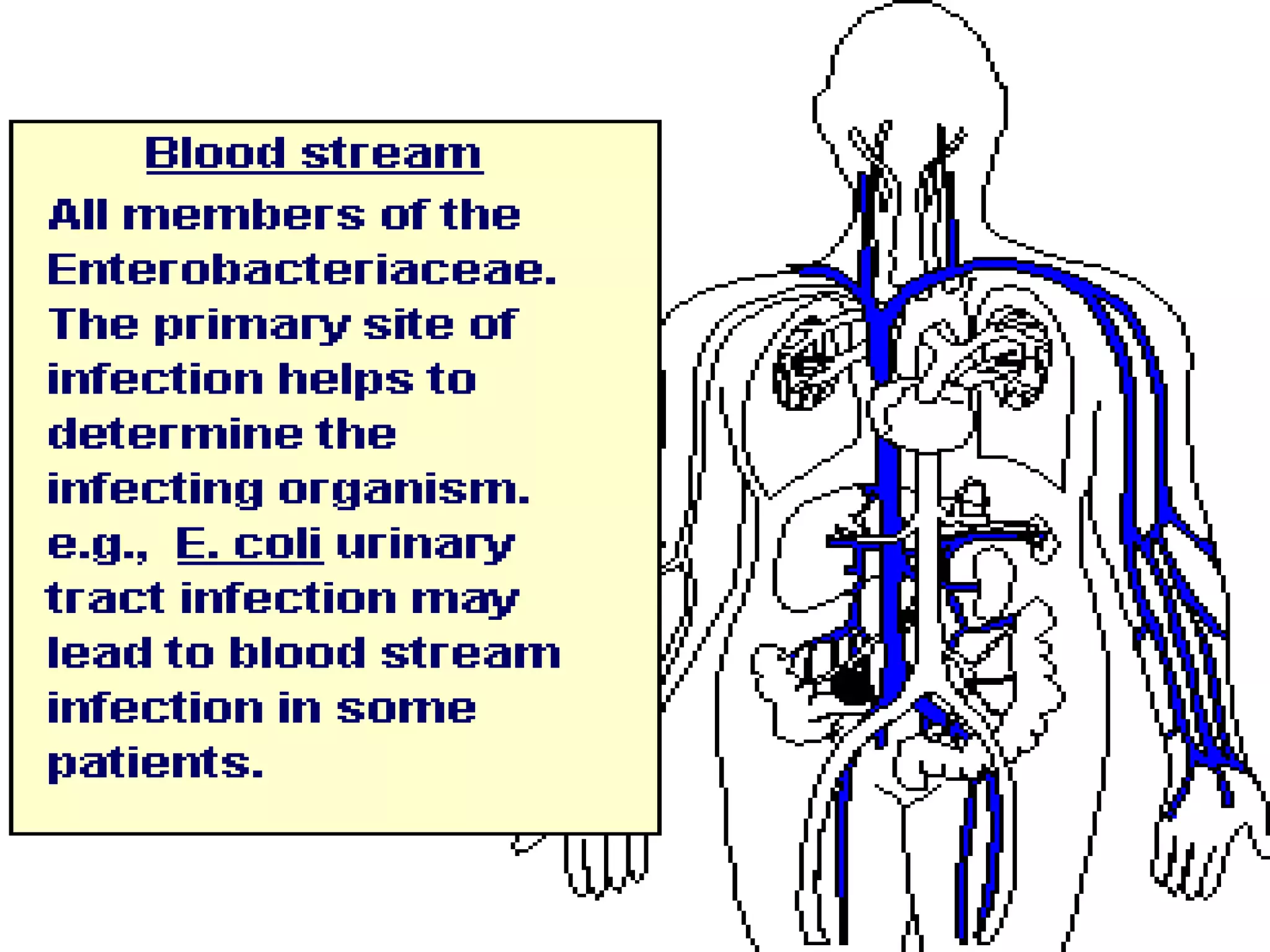
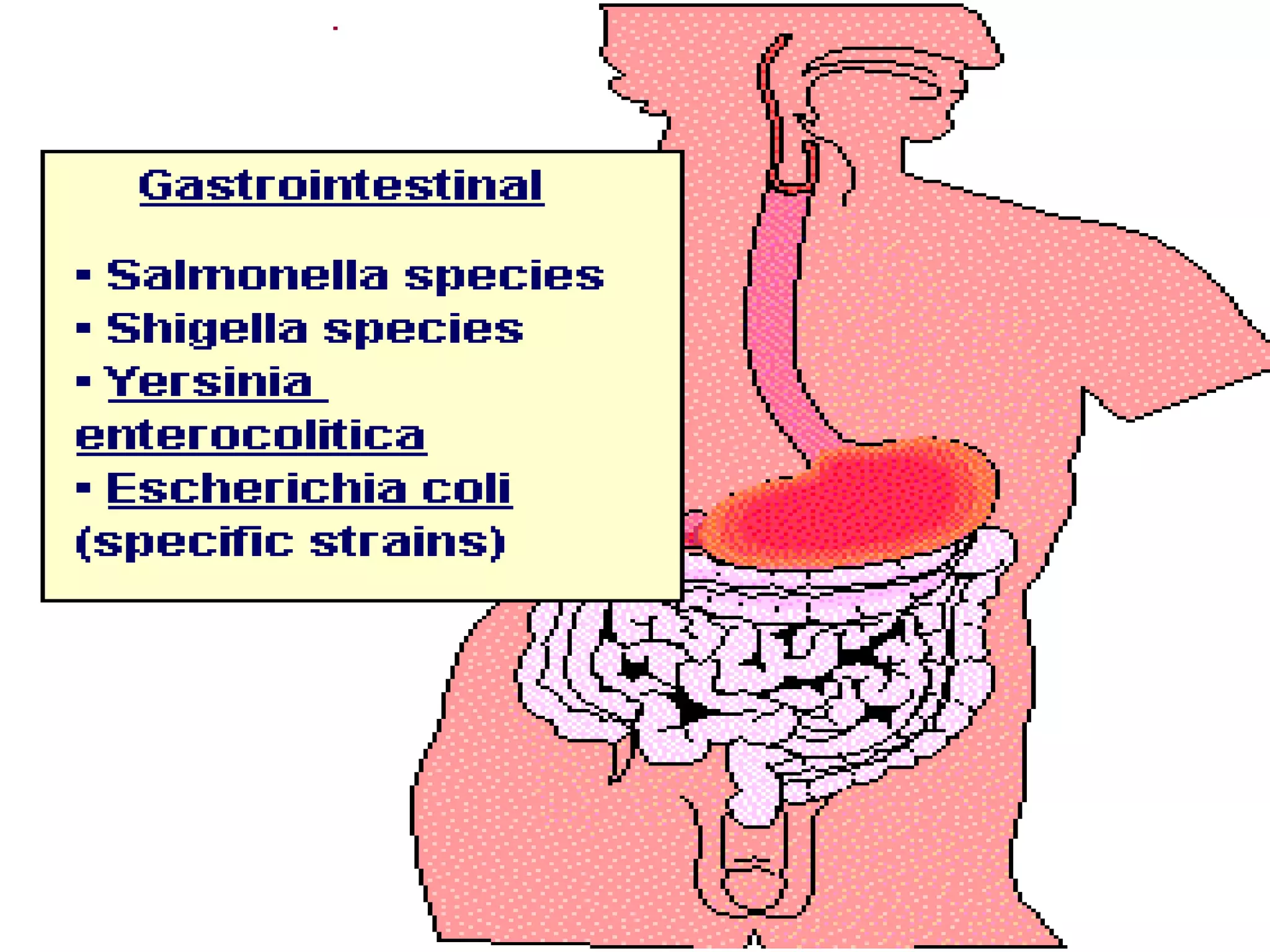
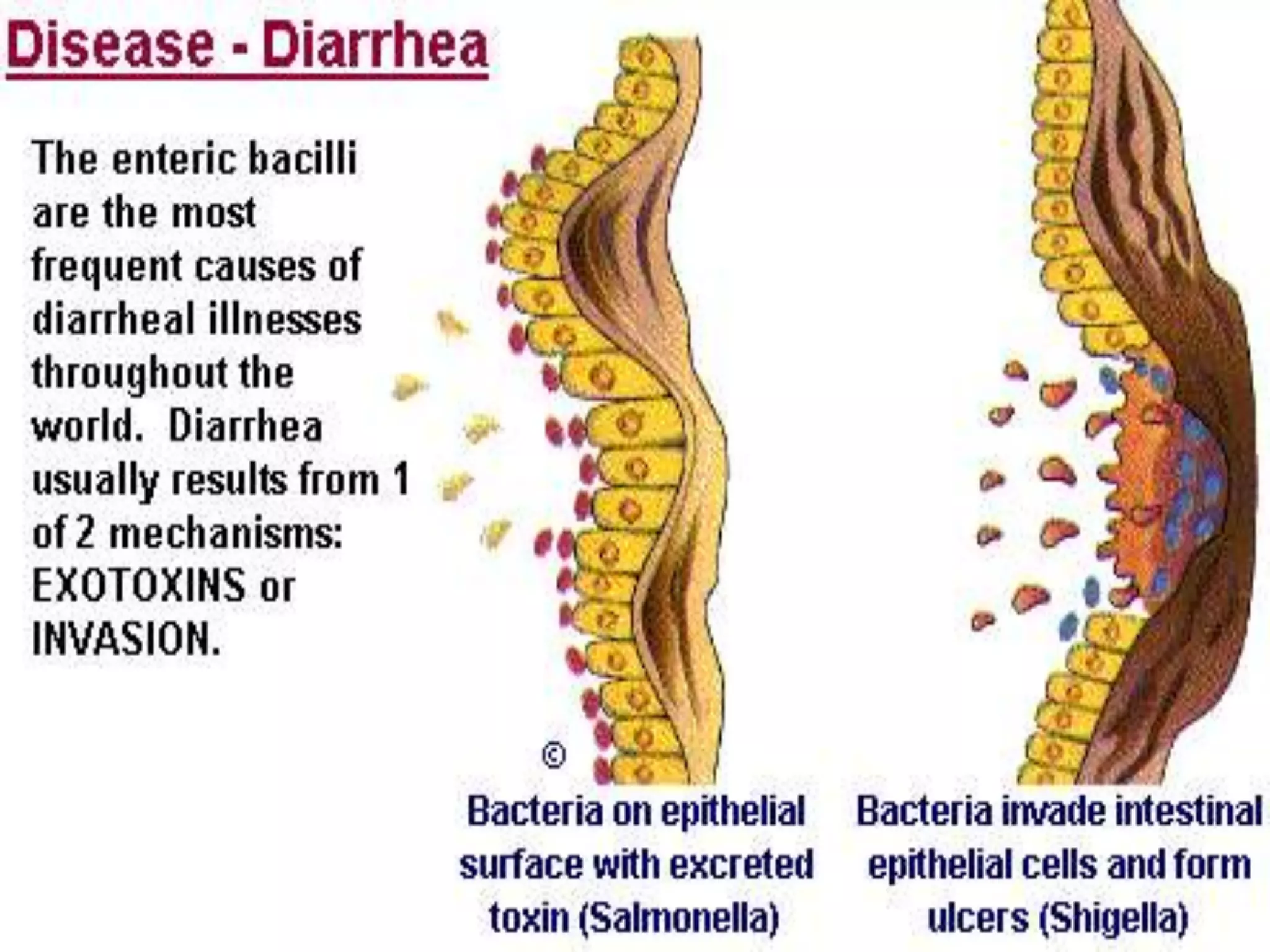
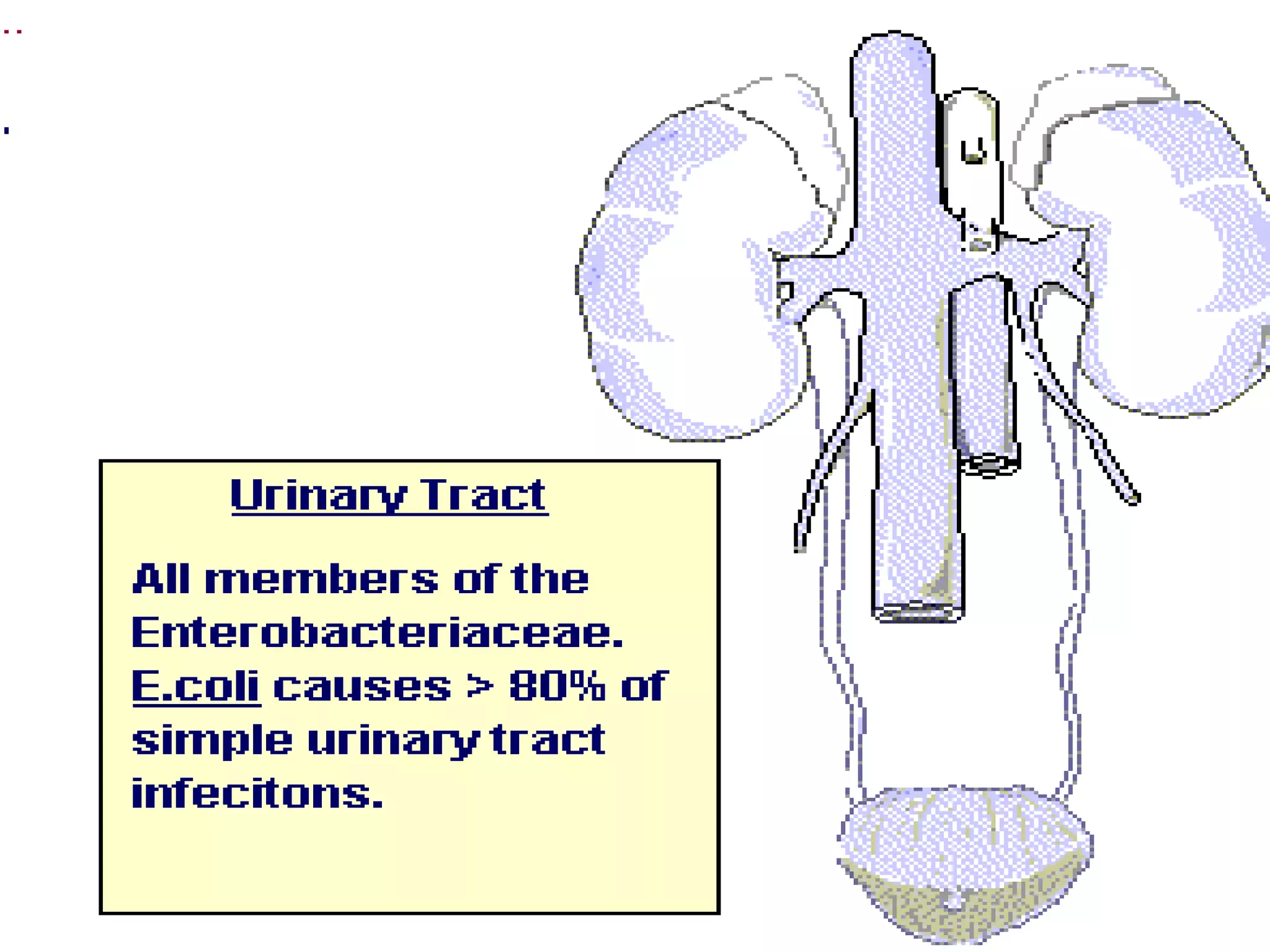
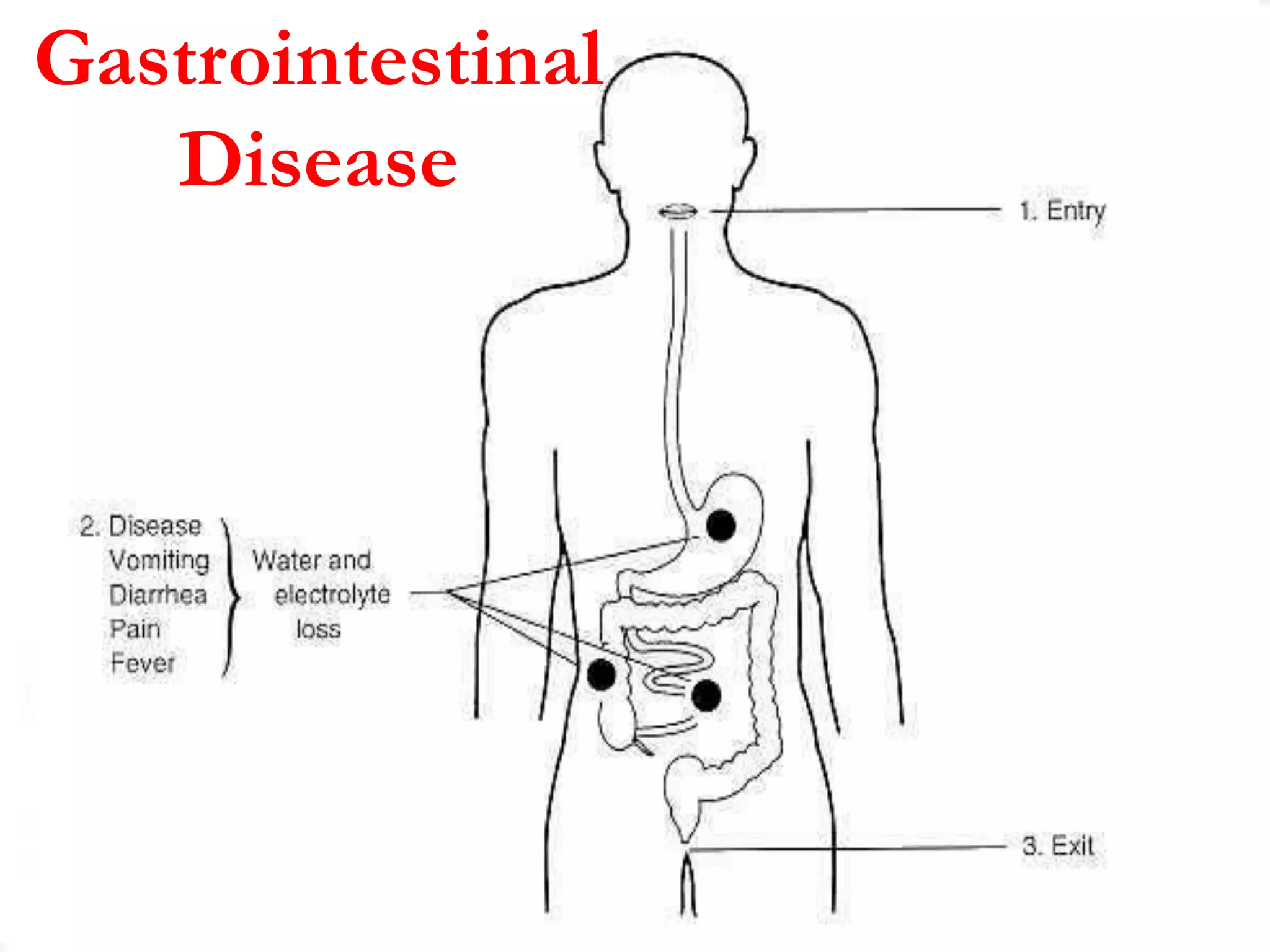
Enterobacteria are Gram-negative bacteria in the family Enterobacteriaceae, including pathogenic E. coli. E. coli can cause urinary tract infections, neonatal meningitis, and intestinal diseases. There are five classes of pathogenic E. coli that cause diarrhea - enterotoxigenic E. coli, enteroinvasive E. coli, enterohemorrhagic E. coli, enteropathogenic E. coli, and enteroaggregative E. coli - each with distinct pathogenic mechanisms. E. coli is diagnosed through culture, biochemical tests, and examining reactions on media like MacConkey agar and triple sugar iron agar. Treatment depends on the site and strain of infection.
































![• ETEC an imp. cause of diarrhea in infants and travelers in
underdeveloped countries.
• EIEC resemble Shigella in their pathogenic mechanisms and
illness they produce.
• EPEC induce watery diarrhea similar to ETEC.
• The distinguishing feature of EAggEC strains is their ability
to attach to tissue culture cells in an aggregative manner.
These strains are associated with persistent diarrhea in
young children.
• EHEC causes a diarrheal syndrome, there is copious
bloody discharge and no fever. Frequent life-threatening
situation is its toxic effects on the kidneys (hemolytic
uremia).
EHEC has recently been recognized as a cause of serious
disease (e.g. the Jack-in-the-Box outbreak in the
Northwest).Pediatric diarrhea caused by this strain can be
fatal due to acute kidney failure
(hemolytic uremic syndrome [HUS]).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enterobacteracae-140419230441-phpapp01/75/Enterobacteriaceae-48-2048.jpg)



