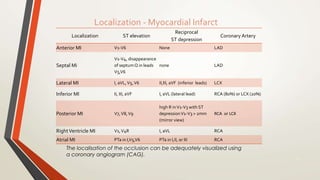
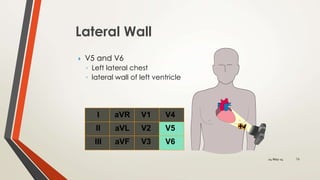
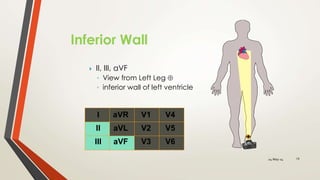
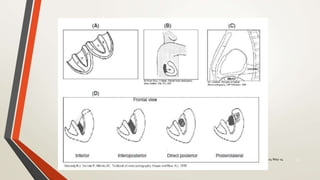
An 81-year-old Saudi male presented with worsening abdominal pain over the last 2-3 days and a history of hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, and chronic abdominal pain. His vital signs were evaluated and ECG, blood tests, and surgical evaluation were planned to assess for possible myocardial infarction, appendicitis, or peptic ulcer. The document discusses electrocardiography and the localization of myocardial infarction based on ECG findings.