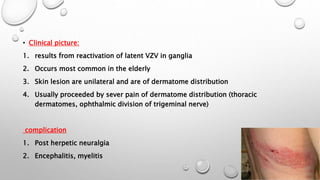
This document summarizes several herpesviruses that can cause infections in humans, including HSV, HZV, CMV, and EBV. HSV can cause oral and genital sores and remains latent in nerves. HZV, which causes shingles, results from reactivation of the varicella zoster virus. CMV is transmitted through bodily fluids and can cause severe disease in immunocompromised individuals. EBV commonly causes infectious mononucleosis and has been linked to some cancers.